Fuel management optimization and operations present significant challenges for fleet operators worldwide. Firms have begun seeking more innovative and more reliable fuel operation management and cost-reduction solutions, driven by increasing fuel prices and growing environmental awareness. The RFID Fuel Management System is a new-age technology that aims to revolutionize the method by which fuel consumption for fleets is monitored and controlled. This blog lays a parallel foundation for the significant benefits of fuel management using RFID technology, including enhanced transparency, reduced fuel theft, and increased efficiency. Are you a fleet manager seeking to reduce costs or a business looking for innovative solutions? If yes, this guide will educate you on why RFID is the future and the transformation of fuel management systems. Join us as we take you through technology, functioning, and impact on fleet operations.
Overview of RFID Fuel Management Systems
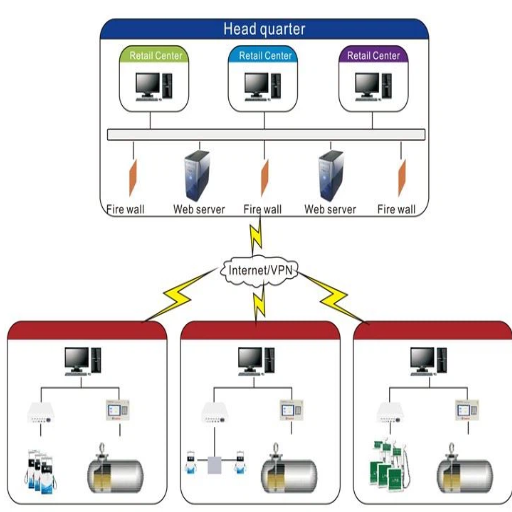
The RFID Fuel Management System utilized Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technology to track and control fuel usage efficiently. These systems use RFID tags on vehicles or fuel dispensers, which transmit data such as the vehicle’s ID, the type of fuel, and transaction information to the central system. This ensures accurate monitoring, prevents unauthorized fueling, and reduces errors or discrepancies. Along with a bit of automation in fuel tracking facilitated by so-called RFID technology, the other benefits include enhanced accountability, reduced fuel theft, and improved operational efficiency for fleet managers and companies.
What is an RFID Fuel Management System?
Fuel management systems utilize integrated radio frequency identification (RFID) technology to ensure smooth and secure fueling operations. Each system comprises three components: RFID tags, readers, and a central computer system. RFID tags, either on the vehicle or at the fuel dispenser, store pertinent information such as vehicle identification numbers, types of fuel permitted for use, and driver information. As soon as fueling initiates, the RFID reader reads this information and immediately transmits it to the central system for verification.
Recent technologies in the RFID world, in turn, help increase efficiency for fuel management. For example, these newer systems cut fueling time by as much as 30% since identification and authorization are almost instantaneous. Furthermore, according to some studies, fuel theft is reduced by more than 60% when RFID systems are used, as access is limited to pre-approved vehicles and accounts. Fleet managers are provided with consumption pattern details, enabling them to pinpoint inefficiencies and save approximately 20% in costs each year.
Faster cost savings are only one of the advantages. With accuracy, RFID fuel management systems automate data collection, eliminating human errors and discrepancies. Additionally, integration with IoT devices and cloud-based platforms enables scalability and remote monitoring, making these systems an absolute necessity for industries such as logistics, transportation, and construction. By providing transparency, security, and convenience, RFID Fuel Management Systems continue to revolutionize the way fuel resources are managed worldwide.
Key Components of RFID Fuel Management
RFID Fuel Management Systems utilize the interplay of hardware and software configuration to render the separate and parallel monitoring of fuel usage. The following are the general elements building the foundation of these systems:
Tags and Readers of RFID: These are RFID tags affixed to the vehicle or container to store basic data, including the vehicle ID, fuel type, and capacity. There is a wireless communication system in which the tags communicate with RFID readers installed at the dispensing stations for authentication and recording fuel transactions. Readers can be built for close-range, mid-range, and long-range operations, ensuring that data capture occurs without delays in a busy environment.
Automated Fuel Dispenser: Fuel dispensers with RFID connectivity will dispense fuel only to authorized vehicles or equipment. This facility prevents unauthorized access or fuel dispensing, eliminating the need for manual intervention that is familiar with conventional fueling methods, thereby reducing the possibility of manual errors. Frequently, pre-set fuel limits and flow controls are implemented for enhanced precision.
Centralized Fuel Management Software: At the center of the RFID system is the software platform that ties together the entire fuel management system. Software provides a real-time dashboard for tracking fuel consumption, tank levels, and transaction history, as well as creating reports and analytics for an instant view of inefficiencies. Strategies can be identified with cost savings in mind.
IoT and Cloud Integration: Smart devices and cloud computing add another compelling dimension to RFID Fuel Management. IoT sensors continuously monitor fuel levels, temperature, and pressure in real-time, while cloud platforms securely store the data and provide access to stakeholders from anywhere. This fusion enables high scalability, ensuring that businesses can expand their operations further without compromising operational efficiencies.
Data Encryption for Security: From a security perspective, the question is how to prevent fraud from occurring in the fuel supply. In this vein, RFID systems utilize encrypted protocols and secure login mechanisms. Authentication protocols are also used to ensure data cannot be misused or accessed by unauthorized persons, thereby safeguarding fuel resources and operational data.
GPS and Fleet Tracking: Many RFID fuel management systems incorporate GPS capabilities that track vehicle location and routes. This information, when combined with fuel usage data, provides insights for route optimization and reduces unnecessary fuel wastage.
Working together, these components manage resources efficiently, ensure operational transparency, and deliver significant cost savings. The RFID Fuel Management Systems have brought great indignation to industry players. This results in increased accountability for businesses, diminished fuel loss or theft, and hence streamlined operations. It is said that fuel management systems reduce fuel discrepancies by 20% to 30%, which speaks to their worth in every industry worldwide.
Benefits of Using RFID in Fuel Management
RFID technology offers numerous advantages for fuel management, enabling operational efficiencies and cost savings. The key point is the automation of dispensing and tracking fuel, thereby avoiding human errors and ensuring accurate record-keeping. RFID-enabled systems monitor vehicles using a unique tag number and allocate fuel in real-time according to actual usage.
Organizations using RFID fuel management have seen reductions in fuel theft and unauthorized usage. For instance, case studies suggest that such automated RFID systems may reduce fuel misapplication by 25%, hence matching fuel costs with legitimate operational requirements. From their end, these systems facilitate data transparency for fleet managers, enabling them to analyze fuel performance, identify inefficiencies, and make informed decisions.
Another significant benefit: cost savings. Leakage control and enhanced efficiency in refueling processes can save companies approximately 15-20% per year in their fuel budgets. This proves especially useful for industries with massive fleets, such as logistics and transportation, where even small inefficiencies can quickly accumulate into substantial losses. Then, such real-time reporting and analytics-based RFID systems reduce fuel waste and enable environmental sustainability, lowering the overall carbon footprint of businesses.
The implementation of RFID yields a high-tech fuel management solution that provides comprehensive operational oversight, enhanced fuel accountability, and a return on investment, making it essential to any next-generation fuel management strategy.
Implementing RFID Technology in Fuel Management

Fuel management through RFID technology involves integrating RFID tags and readers into the fueling process. RFID tags are placed on the vehicles or fuel tanks, and the readers are installed at fueling stations. Approaching the fueling station, the RFID reader reads and grants dispensing of fuel only to authorized vehicles, thereby denying dispensing fuel to unregistered vehicles. This therefore protects the virtual records of fuel consumption, forbids illegal fueling, and prevents error. Through this system, real-time monitoring is possible via centralized software, which enables the analysis of fuel consumption trends, facilitating rational decision-making. The installation of such straightforward systems will help companies increase efficiency, enhance security, and reduce costs.
Steps to Implement RFID in Fuel Stations
Assessment and Planning: Begin by assessing the specific needs of the fuel station. Study present methods of fueling, identify areas of inefficiency, and note security loopholes. Depending on the number of vehicles processed daily and the variety of vehicle types serviced, conduct the necessary estimates regarding the scale of RFID implementation. Arrange for future infrastructure changes to accommodate RFID-enabled dispensers, software integration, and an interface that is easy to use for both workers and customers.
Selection of RFID Technology: Select RFID Tags and readers that are compatible with the operations considered. Typical applications for passive RFID tags are those that require low cost and maintenance-free operation. Higher-end applications, on the other hand, require a longer read range and greater data storage capability, which can be achieved with active RFID systems. The reader, therefore, should be capable of integrating with existing systems at the station and providing real-time communication and monitoring facilities.
Installation of Hardware and Software: Install RFID readers at fuel dispensers compatible with RFID tags carried by vehicles. Deploy the central software with ease to manage and monitor transactions. The software should also be capable of tracking fuel consumption, producing reports, and issuing alerts for any unauthorized fueling. Conduct an upgrade of the IT infrastructure to include secure servers and encryption protocols for enhanced data protection.
Interface with Payment Systems: Ensure the RFID system is compatible with automated payment systems for seamless cashless transactions. Regardless of whether it is through prepaid or postpaid accounts linked to the RFID tags, customers can complete their refueling without interacting with anyone, which enhances convenience while reducing wait time. The payment system must offer a variety of payment options, including loyalty programs for frequent users.
Testing and Calibration: Test the RFID system extensively to validate and confirm that it accurately reads and transmits data seamlessly and remains stable. Resolve issues that arise from the assays or pilot tests performed on the RFID system. Recalibrate the system continuously to maintain efficient working time.
Staff Training and Public Awareness: Train fuel station staff to conduct the entire system procedure competently and efficiently; meanwhile, train staff to resolve common problems and assist customers as needed. Inaugurate awareness camps aimed at spreading information about how the new RFID system would improve people’s lives, including faster services, enhanced accuracy, and better security. Demonstrations or tutorials can be designed for them to promote increased use.
Data Management and Analysis: Utilize detailed data gathered by the RFID system to monitor usage patterns and identify inefficient paths. Such real-time information could be used to manage fuel inventory, cut operational expenses, and forecast trends in demand. A reliable management strategy for data guarantees regulatory compliance, irrespective of the circumstances, in enhancing decision-making.
Scaling and Maintenance: Consider scaling once the initial implementation proves successful to accommodate a broader customer base or multiple fuel stations. Regular maintenance of hardware and timely software updates keep the system robust and efficient, and cooperative efforts with technology providers for ongoing support and improvements.
With the therapeutic procedure, fuel stations can now breathe new life into their processes and deliver better services to their customers, while maintaining high efficiency and achieving long-term cost savings through advanced RFID implementation.
Challenges in Implementation and How to Overcome Them
Many aspects surround the installation of RFID technology in fuel stations, presenting complex challenges between initial costs and technical hurdles. The most significant of these is the high upfront investment required for hardware, installation, and the recent integration of systems. Consequently, these costs often become prohibitive for smaller or independently owned fuel stations. To remedy this, a phased implementation can be considered, where only a few key-level stations initially implement RFID. Then, high scaling can follow, or financing options might be sought, along with some grants available for technological advancements.
Next comes the realm of security and system breaches. From the base perspective of an RFID system carrying highly sensitive data, such as payment information, cybersecurity should be prioritized as a top concern. This can be done simply if the fuel stations employ advanced encryption protocols and keep their systems regularly updated with the latest patches that fix vulnerabilities. Additionally, working alongside professional technology providers who dedicate themselves to supporting the RFID system and ensuring its compliance with the latest industry standards can significantly enhance security.
Factors such as interruptions during implementation or employees’ inadmissibility could contribute to operational shipwrecks, thereby impeding the smooth operation of fuel stations. Comprehensive training of employees on the usage and maintenance of the RFID system will ensure the smooth transition with minimal downtime. Additionally, launching the technology during off-peak times would reassure fuel stations that their customer service will not be interrupted.
Finally, environmental factors affect the reliability of RFID signals, including interference from metal surroundings and undesirable weather conditions. To address this, companies can invest in high-frequency RFID systems, which are well-equipped to handle these testing conditions and provide a greater signal strength. Regular maintenance and performance analysis are equally essential for maintaining the system’s long-term peak efficiency.
If these challenges are addressed with suitable solutions, then fuel stations can undergo a smooth transition to advanced RFID systems, resulting in improved operational efficiency and an enhanced customer experience.
Case Studies of Successful RFID Fuel Management Implementations
Case Study 1: Shell’s RFID Technology Acquisition
As a global Tier One player in fuel distribution, Shell has been implementing RFID technology at several of its fuel stations to streamline operations and enhance customer convenience. In an RFID method of fuel payment, customers could drive away from the pump without having to alight from their cars, thus reducing transaction time to some extent. Reports showed that wait times at the pumps dropped up to 30%, depending on the location and traffic, whilst operational efficiency significantly improved by 20% for specific busy locations. Besides increasing customer satisfaction, it helped Shell grow as a technology-oriented organization.
Case Study 2: Petro-Canada’s Fleet Fuel Management System
Petro-Canada introduced an RFID-based fuel management system for fleet operators. Each vehicle in the fleet was equipped with an RFID tag linked to a centralized database, where fuel authorization was automated and consumption patterns were tracked and recorded. Over the two years, fuel fraud decreased by 25%, resulting in significant savings for companies. On the other hand, rigorous investigations have shown that fleet managers can now track fuel usage in real-time, which enhances their decision-making and operational accountability.
Case Study 3: IndianOil’s RFID Implementation Along Highway
IndianOil, being the largest fuel retailer in India, implemented RFID technology on highways to modernize toll and fuel management. After synchronizing RFID tags on vehicles for both payment and refueling, IndianOil stations experienced a reduction in manual intervention at both tolls and pumps. This innovation achieved a dual purpose: reducing average refueling and toll clearance times by 40% and increasing highway throughput by 18%. It also aligns with the broader government vision for smart infrastructure in transportation.
Case Study 4: RFIDs At BP Retail Locations To Counter Fraud:
RFID solutions were deployed by British Petroleum (BP) at select retail locations, aiming to prevent fuel theft and unauthorized transactions. BP was able to enforce control over the fuel dispensing process using RFID tags linked to registered user accounts and fuel dispensers. It resulted in a tangible decrease in pilferage and unauthorized consignments by 15%, which had a positive effect on profit margins and helped form stronger security measures.
From real-life cases, it becomes apparent how RFID technology brings value to the fuel management systems of the various sectors. With these case studies, which demonstrate improvements in customer convenience, operational efficiency, and fraud detection, all of these are examples of how advanced RFID systems have reshaped the operational landscape of the fuel industry.
RFID Fuel Management for Fleet Operations

Such RFID fuel management systems are indeed highly effective in fleet operations, making it essential to monitor and control fuel consumption in real-time. With RFID tags on vehicles and pumps, the system ensures that no fuel shall be dispensed to unauthorized vehicles. Thus, it stops misuse and wastage. Furthermore, these systems can automate all processes related to fuel usage reports; hence, fleet operations can be streamlined, costs reduced, and efficiency improved. RFID systems provide excellent data, such as fuel transactions, that enable informed decisions and maintain accountability across the entire fleet.
Optimizing Fleet Performance with RFID
RFID technology plays a crucial role in optimizing fleet performance through automation and real-time data analysis. Integration of RFID and fleet management systems reduces manual errors and enhances operational transparency. The system tracks vehicle usage, driver behavior, and fuel consumption all automatically, empowering fleet managers to improve efficiency through informed decision-making. It has also prevented downtime by establishing maintenance schedules and ensuring timely vehicle upkeep. Other than that, fuel theft is avoided since dispensing can only be done against an authorized vehicle, coupled with auditable logs of every transaction, which reinforces accountability. Employing RFID technology leads to cost savings and sustainable development by conserving resources.
Tracking Fuel Usage and Reducing Waste
The modern art of RFID has evolved into an excellent means of reducing fuel usage and waste in fleet management. This type of software setting tracks fuel consumption in all vehicles with accuracy and in real-time, allowing for the identification and prompt rectification of anomalies such as inefficient usage patterns. It is estimated that up to 20% of fuel waste can be reduced through the use of RFID systems, which help detect overconsumption and unauthorized usage. Determining fuel levels and exact amounts of usage enables fleet managers to optimize routes, eliminating unnecessary mileage and reducing fuel costs.
Moreover, the systems enable better compliance with environmental standards, based on the prevention of excessive emissions resulting from fuel wastage. These technologies ensure high accuracy in reporting methods through automatic data collection, eliminating errors associated with manual entries. This level of efficiency streamlines operations and greatly intensifies sustainability efforts. With the help of RFID tracking, businesses can achieve higher accountability levels, conserve resources, and push greener initiatives for their fleet activities.
Integrating RFID with Other Fleet Management Systems
RFID technology can be easily integrated with other fleet management systems to enhance functionalities, promote data flow, and enforce greater operational efficiency. The combination of RFID and GPS tracking offers real-time visibility into vehicle locations and asset usage with a high degree of accuracy. For instance, RFID tags could provide very detailed information on the times when a vehicle enters and exits a depot. At the same time, the GPS tracks the actual route taken and distance covered, aiming to give a 360-degree view of the fleet’s activities.
Furthermore, RFID telematics-based systems facilitate proactive maintenance. Vehicle mileage, engine hours, and other critical metrics of vehicle status can be automatically recorded by RFID-enabled sensors, enabling operators to schedule preventive maintenance and avoid costly failures and breakdowns. According to some industry reports, fleets comprising vehicles maintained through a combination of RFID and telematic systems are said to have witnessed maintenance cost reductions of about 25% and an upsurge in vehicle availability by 15%.
The integration of RFID with warehouse management systems also enhances inventory and asset management. Fleet operators not only track vehicles but also the goods inside them to ensure that loads are accurate and to minimize discrepancies during transit. This type of integration has helped some logistics providers increase their inventory accuracy rates to above 95%, resulting in faster deliveries and fewer operational errors.
When combined with data analytics platforms, RFID helps gather valuable usage trends that empower companies to strategize around route optimization, fuel efficiency, and driver performance. Studies show that fleets using integrated RFID systems can reduce fuel costs by up to 20%, underscoring the system’s potential to create cost-competitive and sustainable operations. In essence, merging the possibilities of RFID with other contemporary tools helps companies create ecosystems that maximize productivity while meeting the imperatives of 21st-century businesses.
Future Trends in RFID Fuel Management

Innovative fuel management in RFID systems is expected to further integrate with IoT and data analytics platforms. Such advances will allow real-time tracking of fuel consumption, predictive maintenance, and intelligent decision-making. With the adoption of blockchain technology, fuel transactions will become even more transparent and secure. Additionally, renewable energy programs may steer the development of RFID systems toward managing alternative fuel sources, enabling them to remain adaptable to the ever-changing industry needs while also embracing sustainability goals.
Advancements in RFID Technology
Recent developments in AI have significantly expanded the capabilities of RFID technology, enabling the creation of intelligent systems that are faster and more efficient. Today, AI algorithms are being combined with RFID systems to enhance data analysis, allowing for the derivation of actionable insights from the massive streams of data generated by RFID. In inventory management, for example, these integrations predict stock depletion, improve supply chain logistics through real-time tracking, and forecast demand trends.
Industry reports have forecasted that the global RFID technology market is expected to grow to nearly $31.4 billion by 2030, with applications expanding across various industries, including retail, healthcare, and manufacturing. The integration of AI and RFID enhances operational efficiency by reducing human intervention, minimizing errors, and improving accuracy. Additionally, machine learning models trained on RFID data are capable of uncovering patterns in consumer behavior, enabling more effective marketing and product placement techniques.
In terms of asset tracking, AI-powered RFID systems certainly perform well. Hospitals maintain records of equipment and medications to ensure availability whenever needed, utilizing AI-enabled RFID tags. These innovations demonstrate how the AI-RFID synergy can be applied to data grooming and operational strategies in various other fields.
Predicted Changes in the Fuel Management Landscape
The fuel management ecosystem is undergoing considerable changes, driven by new technologies and evolving environmental mandates. One notable trend is the growing reliance on AI and IoT-enabled systems to optimize fuel efficiency and reduce waste. Innovative fuel management solutions analyze real-time data to provide companies and fleet operators with thorough insights into fuel usage patterns, preventive maintenance requirements, and cost-saving measures.
Consequently, such sustainability trends are shaping the rapid conversion to alternative fuels. Worldwide, governments and industries are setting highly ambitious targets for carbon reduction, thereby creating markets for cleaner energy sources: biodiesel, hydrogen, and electric power. The most recent forecast indicates that the alternative-fuel industry worldwide is expected to grow at a CAGR of over 8% from 2023 to 2030, clearly marking the urgent need for technology that assists in this conversion.
Telematics and post-tracking systems are also of paramount importance for future fuel management. They enable fleet managers to monitor vehicle performance and fuel consumption, ensuring compliance with environmental laws and enhancing operational efficiency. Moreover, the integration of vehicle-to-everything (V2X) communication technology simplifies fuel allocation by allowing seamless communication between vehicles and infrastructure.
However, with the dawn of these changes, accompanied by the aggressive incorporation of renewable energy sources, an era of innovation in fuel management dawns, promising both cost efficiency and environmental sustainability. Establishing strong frameworks to support this shift will be highly critical from both the business and governmental perspectives in response to these swiftly evolving demands.
The Future of Fleet Fuel Management
Changes in legislation, environmental considerations, and technological advancements will shape the future of fleet fuel management. Advanced technologies, such as AI-based analytics and telematics, ensure better fuel consumption tracking, optimize routes, and lower operating costs. Electric and hybrid vehicles are also gaining traction in fleet operations due to pressures towards sustainability and tighter emissions regulations. Furthermore, alternative fuels such as hydrogen and biofuels already provide long-term solutions for reducing carbon footprints.
Supporting these changes, organizations should focus on implementing intelligent fuel management systems that utilize real-time data for efficiency. Infrastructure tools such as EV charging stations, in combination with renewable energy integration, will be at the heart of this change. Therefore, it will be incumbent upon governments to provide grants for green fleet programs and ensure that these policies promote sustainability objectives. These, in unison, will craft a more affordable and greener future for fleet fuel management.
Benefits of Using RFID for Fuel Management

Fuel management systems stand to benefit from the implementation of RFID in several possible ways:
Accuracy: Automating fuel dispensing and tracking helps reduce errors, ensuring the correctness of data.
Security: Due to the vehicle-specific RFID tag that links to the fuel pumps, unauthorized fuel use is prohibited.
Operational Efficiency: This automated process saves a significant amount of time on data entry, thereby enhancing the workflow.
Cost Efficiency: Proper tracking of fuel use helps minimize waste and identify inefficiencies, leading to cost reduction.
Real-Time Monitoring: Up-to-the-minute data on fuel consumption enables managers to make informed decisions about fuel allocation.
With its benefits, RFID proves to be a modern technique for fuel management.
Improved Efficiency and Accuracy
The occasional use of RFID in fuel management systems signifies far greater efficiency and accuracy. Research has shown that organizations using RFID for fuel tracking have noted up to a 15% reduction in fuel wastage. The improvement primarily stems from RFID’s precise monitoring capabilities, enabling fuel to be dispensed only to authorized vehicles or equipment.
Additionally, RFID automation prevents human errors, which are often evident in manual tracking systems. The data are collected in real-time, so discrepancies are eradicated, and actionable insights become instantly available. Studies show that automation in tracking can improve data accuracy by more than 90%, allowing decision-makers to rely on this data to optimize operations. Additionally, streamlining the processes related to fuel, from checking usage to maintaining inventory, reduces administrative burden and thus helps increase operational productivity. In this regard, the improvements highlight the importance of RFID technology in boosting efficiency and accuracy in fuel management.
Cost Savings for Fleet Operators
RFID technology for fuel management is one of the ways that I’d suggest for saving significant costs in fleet operations. Another way: higher accuracy of fuel tracking eliminates wastage and unauthorized use. Considering lower administrative overheads, as well as type considerations for efficiency, actually translates directly into lower operational expenses and a better allocation of resources, making it a good investment for fleet budget optimization.
Enhanced Security and Monitoring
RFID technology enhances security in fuel management by allowing only authorized vehicles and personnel to access the pumps. This system prevents theft and unauthorized use of fuel by associating each car with a unique identifier and a corresponding fuel card. Furthermore, real-time monitoring of fuel consumption and vehicle positions enables fleet managers to pinpoint any unusual activities quickly. To heighten the degree of accountability, a more comprehensive log is to afford investigation into any irregularity and strengthen corollary safeguard actions. This implies a more robust arrangement to safeguard fuel resources and a better operational monitoring mechanism.
Reference Sources
Radio-frequency identification
RFID-Based Vehicle Toll Collection System for Toll Roads
Automatic Vehicle Fueling System Using PLC-Controlled Robotic Arm
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is an RFID Fuel Management System?
An RFID fuel management system is a technology that uses radio frequency identification (RFID) to automate and streamline the process of tracking fuel usage and inventory. It typically consists of RFID tags attached to fuel nozzles or vehicles, which wirelessly communicate with a central software system to record fuel transactions and maintain accurate inventory levels.
How does RFID technology enhance fuel management systems?
RFID technology enhances fuel management systems by providing real-time data on fuel consumption and inventory. With RFID tags equipped on fuel nozzles and vehicles, operators can wirelessly track the amount of fuel dispensed, monitor odometer readings, and ensure that fuel is being used efficiently. This leads to better control over fuel storage and reduces the risk of theft or misuse.
What are the key components of a fuel management system?
The key components of a fuel management system include RFID tags, an island control unit, fuel nozzles, and a software system that tracks and records fuel transactions. The island control unit manages the fuel island operations, while the software system compiles data from the onboard diagnostics (OBD) of vehicles to generate reports and monitor performance metrics.
How do RFID tag-only systems differ from traditional fuel management systems?
RFID tag-only systems primarily focus on identifying and tracking fuel usage by utilizing RFID tags. Unlike traditional systems that may rely heavily on manual input and physical cables to connect to the fuel nozzle, RFID tag-only systems streamline the process by wirelessly transmitting data, reducing human error, and increasing efficiency.
What information can be gathered from the vehicle data in a fuel management system?
The vehicle data collected in a fuel management system can include information such as odometer readings, hour meters, and fault codes from the machine or vehicle’s electronic module. This data is crucial for analyzing fuel efficiency and diagnosing any issues that may affect fuel consumption.
Can RFID-based fuel management systems be applied across various industries?
Yes, RFID fuel management systems are versatile and can be implemented in various industries, including transportation, construction, and agriculture. These systems enable businesses to monitor fuel usage, control costs, and optimize efficiency, making them a proven and reliable solution across various sectors.
What are the benefits of using a fuel management system with GPS location tracking?
Integrating GPS location tracking with a fuel management system enhances operational visibility by providing real-time data on the location of fuel trucks and equipment. This capability enables companies to track fuel usage on the road and ensure that fuel is dispensed accurately at designated fuel islands, thereby improving accountability and reducing losses.
How do fuel transactions get recorded in an RFID fuel management system?
Fuel transactions are recorded in an RFID fuel management system when a fuel nozzle equipped with an RFID tag is used to dispense fuel. The system wirelessly captures transaction data, including the amount of fuel dispensed, the vehicle’s unique identification, and the transaction time, which is then compiled into comprehensive reports for analysis and review.