Auger cast piles, often interchangeably called continuous flight auger (CFA) piles, are an essential modern foundation solution in geotechnical engineering. The piles are set using a drilling and grouting procedure that is able to guarantee the structural integrity of the installation in soil of varied conditions. This article will explain the salient features, installation procedure, and applications of auger cast piles, elaborating on the reasons behind their preference in projects that demand both reliability and efficiency. Whether you are a builder, an engineer, or simply an inquisitive party attracted to novel construction techniques, you will arm yourself with the knowledge of auger cast piles and their role in safe and sustainable building practices.
Introduction to Auger Cast Piles
Auger cast piles, often interchangeably called continuous flight auger (CFA) piles, are an essential modern foundation solution in geotechnical engineering. The piles are set using a drilling and grouting procedure that is able to guarantee the structural integrity of the installation in soil of varied conditions. This article will explain the salient features, installation procedure, and applications of auger cast piles, elaborating on the reasons behind their preference in projects that demand both reliability and efficiency. Whether you are a builder, an engineer, or simply an inquisitive party attracted to novel construction techniques, you will arm yourself with the knowledge of auger cast piles and their role in safe and sustainable building practices.
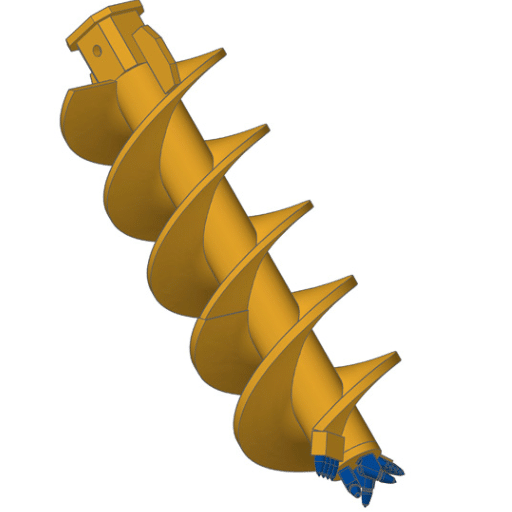
These are deep foundation elements, formed by drilling into the ground using a hollow stem auger. They are cast piles formed by lining the drilled hole with concrete or grout placed from the bottom as the auger is withdrawn. Reinforcement is then inserted within the fresh concrete. This method is highly efficient and induces very low levels of vibration and noise, making it ideal in environmentally sensitive or densely populated areas. Thus, auger cast piles find wide application in projects requiring strong and dependable foundations.
What are Auger Piles?
Such a deep foundation system with the right blend of efficiency and structural reliability is an auger pile-like system. In the construction of such piles, there is no casing or bentonite support, which even makes the system very beneficial in sites with troublesome ground conditions. With the recent engineering advances, most auger piles would be between 12 and 24 inches (300 and 600 mm) in diameter and could go up to 100 feet or perhaps more in depth, depending on the soil condition and project requirement.
One of the key advantages of auger piling is the stabilization gained for soils during construction. One continuous auger keeps the borehole open as it advances into the ground. Concrete or grout is simultaneously introduced, which reinforces the soil and reduces the risk of collapse. Such effectiveness causes auger piling to be faster than other methods, especially in soft clays and loose sands or silt.
Auger piles are widely employed in residential, commercial, and industrial projects. These piles lend themselves to foundation construction in urban areas where noise, vibration, and environmental concerns have to be at a minimum. Their load-bearing capacity varies widely, depending on the design, but they usually carry compressive loads of 200 to 1,000 kips (890 to 4,450 kN). With proper reinforcement, such as steel cages, auger piles can also resist lateral and seismic loads, providing a versatile engineering solution to present-day challenges.
Types of Auger Piles
Auger piles, also called CFA piles or drilled displacement piles, ought to be distinguished by their construction and method of installation. These different types ensure versatility with respect to different site-specific conditions and project requirements. The main types of auger piles are given below:
Continuous Flight Auger (CFA) Piles
CFA piles are the most commonly installed ones. They are constructed by drilling into the ground with a continuous auger while pumping concrete through the hollow stem of the auger into the hole left by the auger. Usually, they get used in sandy or loose soil whenever caving is a possibility. Load capacities of CFA piles vary, but under proper design and reinforcement, they may develop compressive strengths of up to 1,200 kips (5,340 kN). CFA piles require very little vibration to set into place, which makes them very suitable for urban noise-sensitive locations.
Hollow Stem Auger (HSA) Piles
The solid drill stem augers have hollow stems through which soil samples can also be withdrawn or grout can be injected into the hole as the auger bores. They find application in various projects that require exact soil investigations or smaller load-capacity piles. Their versatility makes them useful in both cohesive and non-cohesive soil types, with load capacity generally up to 800 kips (3,560 kN).
Drilled Displacement Piles (DDP)
Drilled Displacement Piles are designed to effect improvement in soils during their installation. The drilling procedure displaces the soil laterally rather than removing it, thereby greatly reducing spoil and also contributing to ground stability. These piles are more appropriate for use in granular soils or in cases where ground improvement is warranted. DDP systems can realize bearing capacities similar to those of CFA-type piles, generally surpassing 1,000 kips (4,450 kN), and simultaneously, they help in controlling settlement.
Helical Auger Piles
The helical piles are installed with the screw blade and are used when lighter load applications are required, such as residential and temporary structures. The load-bearing capacity of helical piles ranges from 30 to 300 kips (130 to 1,335 kN), depending upon soil type and depth of installation. Helical piles are easily uninstallable and relocatable, which makes them a great and sustainable option for certain projects.
From the insight into the technical capabilities of a particular variety, engineers shall determine the most appropriate solution in auger piling germane to the geotechnical, structural, and environmental aspects of a project; the latest equipment and construction methods can further ensure that this precision will also translate into the proper installation of the pile and real-time monitoring of the installation itself.
Benefits of Using Auger Piles
The advantages of auger piling are many and various, including aspects of speed, flexibility, and environmental concerns. The key benefits include:
- Quick Installation: These piles are installed quickly, without any vibrations or noise, in consideration of sensitive areas in urban or residential neighborhoods.
- Cost-Effective: In cohesive soils, casing is not necessary, thereby saving on material costs and installation time.
- Versatile Application: Auger piles can be installed in all soil conditions, such as soft clays, dense sands, and silty soils, thus broadening their use across various geotechnical environments.
- Minimal Environmental Impact: A very minimal amount of spoil is generated with these piles, causing the least generation of waste, and ultimately reducing environmental disturbance.
- Enhanced Accuracy: As drilling and monitoring technologies advance, installation accuracy can be enhanced to ensure the section adheres to design specifications, thereby enhancing structural reliability.
All these factors make auger piling a cost-effective and green solution that can meet contemporary construction demands.
Auger Cast Piles and Their Characteristics

Definition of Auger Cast Piles
Auger cast piles, otherwise called Continuous Flight Auger (CFA) piles, belong to deep foundation solutions where the land is drilled with a hollow-stem continuous flight auger. When the desired depth is reached, grout or high-strength concrete is pumped under pressure through the hollow stem as the auger is slowly withdrawn. This operation ensures the grout or concrete remains as one continuous column, preventing soil collapse and enhancing structural integrity. Reinforcement steel, commonly in the form of reinforcing cages or steel beams, is then inserted into the grout while it is still fresh so as to enhance its load-bearing capacity.
They’re very flexible and can be installed in a variety of soils, from loose sands and soft clays and even saturated soils. Auger cast piles are designed to efficiently carry both axial and lateral loads and thus can be used for several applications, such as foundations for buildings, bridges, and larger infrastructure works.
Technical Specifications: Geotechnical recent data indicate that auger cast piles have greater load capacities, bearing axial loads of anything from 30 tons to over 150 tons per pile, depending on diameter, depth, and soil conditions. Common diameters go from 12 to 48 inches, and depths can reach up to 100 feet, so great structural flexibility is provided.
The installation process was somewhat quiet and with little vibrations, which is important in cities or other sensitive environments where disturbances to surrounding structures must be minimized. With the advent of monitoring technologies like real-time instrumentation for torque, pressure, and flow rate, installers would ensure optimum pile integrity and performance. These monitoring systems further boost the reliability and efficiency of auger cast pile construction, making it a top choice in the modern era of engineering.
Auger Cast vs. Traditional Piles
Comparing auger cast pile construction against other traditional piling systems brings about certain very distinguishing features in its installation methods, capacity to carry loads, cost efficiency, useful life, and effect on the environment.
| Aspect | Auger Cast Piles | Traditional Driven Piles |
|---|---|---|
| Installation Method | Drilling and concrete grouting using continuous flight auger | Impact-driven methods using hammering |
| Noise & Vibration | Minimal noise and vibration | High noise and vibration levels |
| Load Capacity | 60-300 tons (depending on conditions) | Limited range, requires enhancements |
| Environmental Impact | Minimal soil contamination, no dust/debris | Dust, debris, noise pollution |
| Urban Suitability | Excellent for sensitive environments | Limited use near residential areas |
These piles are installed by drilling and pouring concrete grouting using a continuous flight auger, thus causing the least amount of vibration and disturbance to the ground during installation. This approach works well, especially in urban or sensitive environments, with traditional piles using impact-driven methods causing noise, vibrations, and disturbance to nearby structures.
Structurally, auger cast piles generally provide higher load-bearing capacities, as the grout mixture is specifically prepared, and the pile shaft adheres coherently with the soil, forming a stable, continuous shaft. Cost, in other words, becomes more favorable in favor of the augmentation cast pile. However, except for the first setting up of equipment, which may be more expensive for cast piles than the driving piles, the reduced time needed for project completion, subsequent absence of vibration suppression measures, and enhanced agility of augment cast pile extension over different soils and geological situations against project delays would make cast piles more favorable.
Applications of Auger Cast Piles
These piles display high versatility and are applied in various construction situations. They are used for heavy-load projects, especially for deep foundations in city areas, because they require minimal vibration, or in other words, noise must not be generated. Because these piles can carry immense loads, they are best suited for heavy structures such as high-rise buildings, bridges, and industrial buildings.
Key applications include:
- Urban Construction: High-rise buildings, commercial complexes
- Infrastructure Projects: Bridges, overpasses, highway structures
- Industrial Applications: Heavy machinery foundations, storage facilities
- Marine Structures: Seawalls, bulkheads, retaining walls
- Poor Soil Conditions: Areas where conventional shallow foundations would prove inadequate
- Environmentally Sensitive Projects: Near hospitals, schools, residential areas
Their adaptability lends itself to different geotechnical conditions, while the minimized environmental impact makes them prime candidates for large developments as well as for environmentally sensitive construction projects.
Installation Techniques for Auger Piles
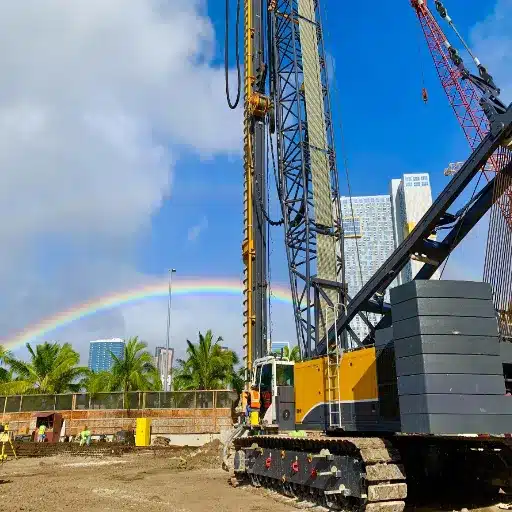

Equipment Used for Auger Piling
The installation process requires specialized equipment to ensure precision and quality:
- Drilling Rig: This is the most powerful kind of auger drilling rig, designed to drill deep into the soil using a continuous flight auger. The rig is fitted with a high-torque rotary head to function well under varied soil conditions.
- Continuous Flight Auger: A CFA comprises basically a hollow steel stem with continuous flights so that drilling and concrete pumping can be carried out simultaneously during the extraction of the auger. The soil extraction and concrete placement are accomplished most effectively with this design.
- Concrete Pumping System: A concrete pumping system of very high capacity is required for delivering concrete into the ground through the auger’s hollow stem during the withdrawal of the auger, thereby providing an uninterrupted flow that ensures the maintenance of pile integrity.
- Reinforcement Cage Installation Equipment: The installation of steel cages into the fresh concrete needs machinery or special tools that ensure the installation complies with structural load requirements.
- Monitoring Systems: Modern monitoring systems are frequently used to ensure checking drilling parameters such as auger depth, torque, soil resistance, and concrete volume per design to meet quality standards.
Thus, these components combine to provide an accurate, efficient, and environmentally cautious auger piling process, much needed even in a complicated or urban setup.
Step-by-Step Installation Process
- Preparation and Evaluation of the Site:
A thorough geotechnical site investigation should be carried out to analyze the soil condition for the site and pinpoint possible obstructions. Debris from the site should be cleared, ensuring that equipment can adequately access the area. All safety measures should be established, and pile locations should be set out according to the design layout. - Borehole Drilling:
Using the auger rig, the borehole is drilled to the final specified depth. The auger flights displace soil and carry it to the surface. The entire process should be under continuous supervision to ensure its alignment, depth, and diameter, as specified in the project specifications. - Avoiding the Collapse of the Borehole:
Maintaining borehole stability can be of great concern, especially when one encounters challenging soil conditions. Temporary casing or drilling fluid may be used where necessary to circumvent collapse from taking place, thereby preserving the borehole until it may be further processed. - Placing Concrete:
Concrete placement in the borehole may begin either through the tremie pipe or directly down the auger stem, whichever method is selected, once the drilling has reached the desired depth. Slow withdrawal of the auger then occurs while concrete is being placed so that the borehole is filled without voids. - Installing Reinforcement:
Once the borehole is filled with concrete, a reinforcement cage will be lowered into the fresh concrete. This should be ensured to be in the proper position regarding alignment and load-bearing capacity as specified in the structural design. - Curing and Quality Verification:
Allow curing of the concrete piles according to engineering specifications. Carry out quality checks during and after installation, which may include non-destructive testing and instrumentation monitoring, so as to satisfy the design specification and structural integrity.
This detailed procedure ensures the installation of auger piles with precision, in accordance with the engineering and environmental requirements.
Advantages of CFA Piles
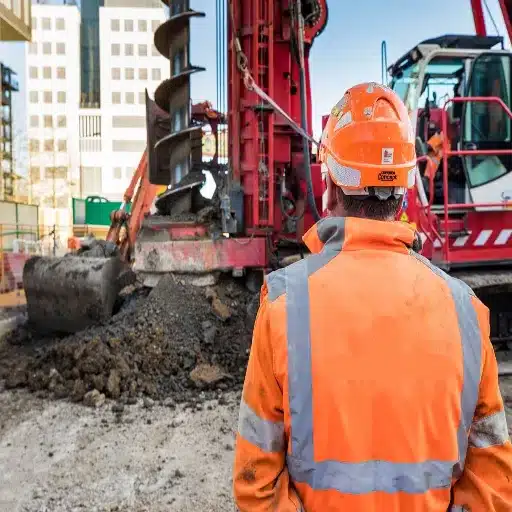

Continuous flight auger (CFA) piles consist of provisions that give them the choice of being used under different construction scenarios. Key advantages include:
- High Load-Bearing Capacity: Piles capable of supporting large compressive loads, often of the order exceeding 1,000 kN, all depending on the nature of the soil and pile dimensions
- Minimal Ground Disturbance: Non-displacement piles that do not cause ground heave or surface damage, particularly advantageous near sensitive infrastructures or historic buildings
- Low Environmental Impact: Less noise and vibration during installation, satisfying stringent environmental and urban construction criteria
- Logistical Efficiency: Combining drilling and concrete placement into one single operation reduces installation time substantially
- Real-time Monitoring: Integrated monitoring systems record torque, concrete pressure, and depth data, enhancing accuracy by up to 20%
- Soil Versatility: Can be employed in almost any soil condition, including granular soil, silts, or clays
- Design Flexibility: Pile diameters ranging from 300 mm to 1,200 mm and depths varying beyond 30 meters
Pile Load Testing for Auger Piles
Pile load testing has become an important quality assurance measure used to determine the load-carrying capacity and settlement behavior of auger piles with the respective applied load. The prevalent techniques include:
Static Load Tests
They subject the pile to incremental loading with measurements of settlement over time. This testing is, in theory, the most accurate conglomerate or considered a gold standard in any evaluation of piles, as it tests the pile capacity directly under specified conditions.
Dynamic Load Tests
By hammer impact and other similar techniques, it estimates pile capacity from wave equation analyses. These are less time-consuming than static tests, but need greater care to calibrate and interpret.
Both methods may follow ASTM standards for testing procedures to maintain consistency and reliability (e.g., ASTM D1143/D1143M for static tests). The data acquired from these tests proves valuable in justifying design assumptions and in the acceptance of works to engineering specifications.
Comparing Auger Piles with Other Pile Types

Auger Piles vs. Driven Piles
The distinction between auger piles and driven piles lies in their construction methods, bearing capacity, and their suitability in varying subsurface conditions.
| Feature | Auger Piles | Driven Piles |
|---|---|---|
| Construction Method | Continuous flight auger with grout/concrete injection | Prefabricated, installed by hammering or vibration |
| Noise & Vibration | Low levels, suitable for urban areas | High levels, limited urban use |
| Load Capacity | High, precise installation | Very high, reliable performance |
| Soil Interaction | Coherent shaft-soil adhesion | Compacts surrounding soil |
| Quality Control | Requires careful monitoring | More predictable installation |
Auger Piles vs. Helical Piles
| Aspect | Auger Piles | Helical Piles |
|---|---|---|
| Construction | Drilling a borehole, filling with concrete | Steel shafts with helical plates screwed into the ground |
| Load Capacity | High compressive loads, dense soil is effective | Generally lower capacity, suitable for light loads |
| Installation Time | Longer installation, specialized equipment | Faster installation, smaller equipment |
| Site Disturbance | Moderate disturbance | Minimal site disturbance |
| Soil Suitability | Dense soil situations | Weak or loose soils, restricted areas |
| Performance Limitations | Higher cost, longer installation | Hindered by rocky or very dense soils |
When to Choose Auger Piles
Based on the decisions relative to choosing auger piles, several key scenarios warrant their selection:
- High Load Requirements: When projects demand significant load-bearing capacity and structural stability
- Cohesive Soil Conditions: In soils that are mostly cohesive in nature or comprise loose to medium-dense materials
- Vibration-Sensitive Locations: Sites with slight or almost no vibration tolerance, as the mounting procedure produces little noise and disturbance
- Deep Foundation Needs: When specifications call for deep penetration to bypass unsuitable surface layers and reach stable bearing strata
- Urban Environments: Projects in densely populated areas where environmental considerations are paramount
- Time-Sensitive Projects: When installation efficiency and reduced construction time are critical factors
Decision Framework: The selection is based on a detailed evaluation of site-specific geotechnical conditions and project requirements. Engineers must consider load requirements, soil profile, installation restrictions, cost considerations, and environmental constraints to determine the most appropriate foundation system.
Ultimately, its selection is based on a detailed evaluation of site-specific geotechnical conditions and project requirements, ensuring that the chosen foundation system will stand up to the peculiar demands of each project.
Reference Sources
Using Continuous Flight Auger Pile Execution Energy to Assess Subsurface Variability
Experience and Prospects in the Use of Auger Cast Piles
Modeling Auger Cast Pile Installation Effects on Group Behavior
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
In piling terms, what are auger cast piles and the installation procedures?
The auger cast piles or continuous flight auger piles serve as a deep foundation system. Their installation consists of drilling an auger in the soil, filling the hollow shaft with concrete, while simultaneously withdrawing the auger. This type of pile-soil bonding, if done properly, assures one of the best foundation solutions.
What is the installation process for auger cast piles?
The installation procedure includes drilling-type equipment for augering in the soil. Throughout the process, concrete is pumped through the hollow center of the auger shaft while the auger is being drilled continuously into the soil so that the pile is formed in one uninterrupted operation. Fluid concrete fills the hole in place of the withdrawn auger, thus furnishing a solid pile that supports the superstructure.
What does grout do in the auger cast pile?
It is the grout that fulfills the function of filling the void created by the withdrawal of the auger. The volume of grout matters much in achieving the bonding and bearing capacity so desired from the pile. Properly handled, grout assures that the pile can gruesomely bear the load of the building or structure in terms of strength.
How do they compare with auger piles with driven piles?
Auger piles are installed by augering and filling with concrete, thus reducing disturbances to the soil. This might have significance in an environmentally sensitive area. Driven piles get hammered into the soil, thus resulting in vibrations and displacements. Auger cast piles are usually preferred because they provide a stable foundation with less noise and disruption.
What are the advantages of auger cast piles in construction services?
Many virtues can be attributed to auger cast piles used in construction services. They have, among others, large bearing capacities adaptable to many types of soil and can be installed well in sites with limited access. Besides making a favorable choice for any construction project, these piles can be installed in a short time.
How deep can auger cast piles be drilled?
Auger cast piles can typically be drilled in diameters ranging from 12 inches to 24 inches, depending on the site conditions and bearing requirements. The pile depth is governed by the engineering specification for a specific project and by the load it has to support.
What is meant by ‘load test’ for auger cast piles?
The meaning of load testing for auger cast piles is putting a predetermined applied load on the pile installed and observing the response to check whether the given pile satisfies the design requirements. This test further assures that the pile satisfies the structural requirements for safe load transfer and binding with the surrounding soil, which is crucial for safety and reliability in the foundation.
What is the kind of rebar used in auger cast piles?
Reinforcement in auger cast piles is sometimes applied as a means to increase the structural strength of the pile. In auger cast pile installation, the reinforcement is placed in the fluid concrete, thereby increasing the load-carrying capacity and ensuring that the pile adequately supports the structure.