Fuel nozzles must be adequately maintained to ensure that critical machinery, vehicles, and industrial systems operate efficiently and reliably for an extended period. When a fuel nozzle is well-maintained, it helps optimize fuel delivery with minimal interruptions in operations, avoiding expensive repairs and avoidable downtime. This article will take you through the importance of scheduled maintenance, standard checks to keep in mind, and best maintenance practices to help you ensure they remain in tip-top shape. A seasoned technician or a curious professional will find everything they need in this comprehensive guide to maintain their fuel nozzles in peak condition. Begin your maintenance schedule today to ensure smooth functioning tomorrow!
Understanding Fuel Nozzles
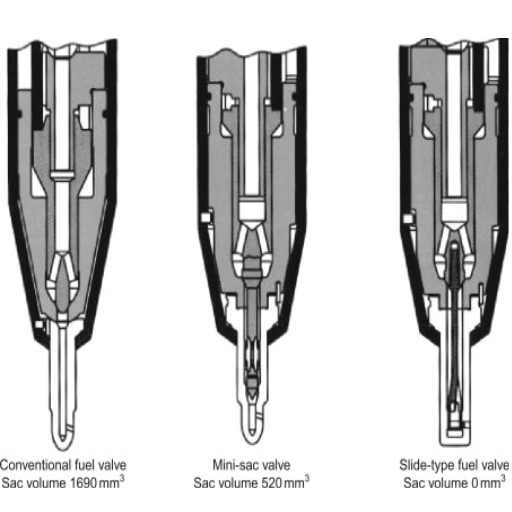
Fuel nozzles are considered one of the most critical components of an engine’s fuel delivery system, controlling the flow of fuel and ensuring its efficient atomization for combustion. The atomizing process maintains engine performance, reduces emissions, and optimizes fuel consumption. Designed for precision, fuel nozzles operate by dispensing fuel at high pressure, ensuring accuracy and durability. Lack of inspection and maintenance can hinder the functioning of fuel nozzles, leading to blockages, wear, or leakage, which in turn impact the engine’s performance and efficiency. Proper care of the fuel nozzle ensures the overall system is in good condition, working perfectly, and lasts for many years.
What are Fuel Nozzles?
A fuel nozzle has always been an essential part of fuel-injection systems, which, in effect, spray a fine atomized mist of fuel into an engine’s combustion chamber. In turn, this ensures that the best possible air-fuel mixture is optimally created for effective combustion, which directly governs performance, fuel efficiency, and emissions of that engine.
In the present day, fuel nozzles must operate under extremely high-pressure conditions, reaching up to 30,000 psi in highly sophisticated diesel engines, aiming for accurate delivery and atomization. There are many different varieties and sizes, depending on the manufacturer, system, and whether it is for gasoline-powered automobiles or heavy industrial equipment. Fuel nozzles would typically be manufactured from stainless steel alloys that provide good durability and resistance to wear from extreme temperature and pressure conditions.
Performance Impact
In some cases, when nozzles are worn out or clogged, they can induce poor engine performance, higher fuel consumption, and increased pollution. Studies have shown that with proper maintenance and timely replacement of fuel nozzles, fuel conservation of approximately 10% and a significantly reduced pollutant emissions are achieved. Innovative designs, such as multi-hole and electro-control nozzles, have also contributed to the development of cleaner and more responsive engines.
Regular checks should be conducted to enhance the lifespan and functionality of fuel nozzles, in conjunction with the use of high-quality fuel and filtration systems.
The Role of Fuel Nozzles in Fuel Delivery
Fuel nozzles represent a crucial infrastructural aspect responsible for supplying fuel to the engine, thereby affecting efficiency and performance. They are capable of atomizing the fuel into fine droplets, thus promoting good mixing with air to optimize combustion. According to some studies, efficient fuel atomization can lead to an overall improvement in engine efficiency of up to 15%, while also reducing fuel consumption and carbon emissions.
The latest direct injection technologies, too, have allowed the peculiarities of fuel nozzles to shine through. In Toyota’s gasoline direct injection (GDI) system, fuel is injected directly into the combustion chamber through the fuel nozzles, allowing for optimized control of the air-fuel mixture. It has been demonstrated that this system improves fuel efficiency by 20% and reduces particulate emissions compared to conventional port fuel injection systems.
Furthermore, high-performance modern fuel nozzles, often customized according to engine requirements with multi-hole patterns and variable spray angles, provide better fuel distribution and ignition efficiency, which are essential for meeting the more stringent emission criteria of Euro 6 and EPA Tier 3. Integrating electronic controls into the operation of fuel nozzles has led to further refinements in their functionality, enabling real-time adjustments based on parameters such as engine load and road driving conditions.
Combining advanced materials, cutting-edge design, and state-of-the-art control systems, modern fuel nozzles lead the way to greener and more powerful engines. Maintaining and upgrading them is still one of the most reliable ways to reap the rewards they offer in modernity.
Types of Fuel Nozzles
Fuel nozzles come in different types, each designed to meet the performance requirements unique to its respective engine. Common types are as follows, along with their features and applications:
| Nozzle Type | Description | Applications | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| Direct Injection Nozzles | Designed for modern engines that require high efficiency and precision. These spray fuel directly into the combustion chamber at high pressures, often beyond 2,000 bar in state-of-the-art systems. | Gasoline direct injection (GDI) and diesel engines | Optimal atomization, improved combustion, reduced emissions, enhanced fuel economy |
| Port Injection Nozzles | Deliver fuel to an intake manifold, just before the intake valve. Allows fuel to mix with air before reaching the combustion chamber. | Gasoline engines prioritize price and reliability | Cheaper and simpler design, though less efficient than direct injection |
| Single-Hole Nozzles | Feature a single spraying hole and are commonly found in older designs or specific low-pressure applications. | Engines with simple combustion requirements | Simple design, suitable for basic applications |
| Multi-Hole Nozzles | Multiple holes provide excellent atomization and fuel distribution. The number and orientation can be tailored to the combustion chamber geometry. | High-performance and high-efficiency engines | Uniform fuel-air mixture, excellent atomization |
| Piezoelectric Nozzles | Utilize piezoelectric actuators to achieve ultra-fast response times and high precision. | High-end diesel and advanced gasoline engines | Multiple injections per cycle, optimized performance, reduced emissions |
| Variable Flow Nozzles | Adjust the flow rate, altering the fuel spray rate according to operating conditions. | Hybrid vehicles and adaptable situations | Adaptable to engine load variations, flexible operation |
Every type of fuel nozzle plays a pivotal role in defining engine performance, and its specification shall be altered according to the ever-growing demands of modern powertrains. Advances in materials and manufacturing technology only now promise further improvements in fuel nozzle durability, efficiency, and accuracy.
Importance of Regular Fuel Nozzle Maintenance

Regular maintenance of the fuel nozzle is crucial to keep the engine running optimally and efficiently. With time, particles and impurities in the fuel could clog or damage a nozzle. This may lead to poor atomization, reduced power output, and increased emissions and fuel consumption. Regular cleaning and inspection help prevent these issues from occurring, increase the engine’s lifespan, and maintain its performance. Additionally, following the manufacturer’s maintenance instructions helps avoid expensive repairs and ensures the reliable operation of the fuel delivery system.
Benefits of Routine Inspection
Improved Fuel Efficiency
Preventive checks of the fuel system can yield up to a 15% improvement in fuel efficiency, according to industry studies. Regular maintenance ensures optimal fuel delivery and combustion.
Cost Savings
Detecting wear and tear prevents minor problems from escalating into major breakdowns. Preventive maintenance costs up to 30% less compared to reactive repairs.
Enhanced Safety
Consistent inspection prioritizes safety by recognizing potential hazards before they lead to accidents. Proper maintenance prevents leaks and mitigates risks.
Environmental Benefits
Well-maintained components promote a smaller environmental footprint since less engine effort results in fewer emissions and regulatory compliance.
Operational Efficiency
Machinery running at high efficiency creates smoother workflows, less reliance on breakdowns, and extended equipment lifespan for long-term cost savings.
Consequences of Neglecting Maintenance
Critical Risks of Poor Maintenance
Failing to maintain a company’s assets can put its livelihood at risk, affecting both operational and financial aspects. Research reveals that industrial-level downtime results in annual losses of $50 billion, with equipment failures accounting for nearly 42% of these losses.
- Unexpected Equipment Failures: Direct interference with production schedules, leading to delayed deliverables and poor customer satisfaction
- Reduced Energy Efficiency: Malfunctioning equipment consumes excess energy, increasing utility costs significantly
- Safety Hazards: OSHA statistics show injuries from equipment accidents are more likely in places lacking proper maintenance procedures
- Environmental Compliance Issues: Malfunctioning systems emit pollutants beyond permitted levels, resulting in fines and reputation damage
- Shortened Equipment Life: Continued neglect forces businesses to pay for frequent replacements or costly repairs
How Regular Maintenance Saves on Fuel Consumption
Regular maintenance reduces fuel consumption, which in turn saves money and enables greater efficiency. Clean and functioning engine components remain top priorities:
- Air Filter Maintenance: Dirty air filters can reduce fuel efficiency by 10% because clogged filters force the engine to work harder
- Tire Pressure: Maintaining proper tire pressure reduces rolling resistance and improves fuel economy by 3%
- Motor Oil Quality: Using the recommended grade of motor oil yields a 1-2% mileage advantage by reducing friction among engine components
- Oxygen Sensor Replacement: Timely repair of faulty oxygen sensors can increase fuel efficiency by up to 40%
- Fuel Injector Cleaning: Regular tune-ups and clean fuel injectors help ensure the engine burns fuel efficiently.
Periodic care helps reduce fuel expenses and carbon emissions simultaneously, contributing to a more sustainable operation. By keeping systems in top shape and handling wear and tear promptly, both businesses and individual users can maximize fuel efficiency and extend the longevity of vehicles or machinery.
Best Practices for Fuel Nozzle Maintenance

General Cleaning
Fuel nozzles must be cleaned regularly to minimize clogging and ensure smooth fuel flow. It is good practice to use cleaning substances specifically meant for fuel systems.
Inspect for Damage
Regularly checking the nozzles for cracks, leaks, or any form of wear and replacing the damaged parts immediately will enable extraordinarily efficient and trouble-free operation.
Filter Inspection
Ensure the filters inside the fuel nozzle are not clogged and are working efficiently to avoid fuel contamination.
Lubricate Moving Parts
Lubricate all moving parts of the nozzle with the recommended lubricant to ensure proper functioning and prolong the product’s lifespan.
Test Functionality
Check the flow rate and shut-off capability of the nozzle periodically to ensure it operates safely and efficiently.
Following these good practices will ensure the optimal working condition of the fuel nozzle and reduce the likelihood of expensive repairs.
Step-by-Step Maintenance Guide
Inspecting the Nozzle Regularly
Inspect the nozzle for signs of wear and tear, such as cracks, rust, or leaks. Any compromise in the safe operation of the nozzle must be checked upon. Studies show that regular inspections can reduce mechanical failures by 30%, enhancing reliability over time.
Thorough Cleaning of the Nozzle
Clean the nozzle with a suitable non-corrosive solution from both the outside and inside to ensure the removal of all dirt, grime, and fuel residues. Blockage refers to the reduction of flow and the inability of the nozzle to function correctly. Cleaning every two to four weeks, depending on usage, helps in maintaining efficiency.
Check Seal Integrity
Seals in fuel nozzles prevent leaks; therefore, they should be checked to ensure their integrity. It is recommended to replace faulty seals immediately, as they are the primary source of inefficiencies in operations, and leakage can result in an average fuel loss of almost 15%.
Change Filter Screens
Regularly replace the filter screens inside the nozzle to prevent clogging from debris or contaminants. The typical recommended replacement cycle for the filter screens is between three and six months, depending on the working environment. Having clean filter screens ensures the unobstructed flow of fuel and helps prevent damage to the nozzle.
Adjust the Calibration of Flow Rate
Check the flow rate using a standard method of measurement or testing equipment. This is to determine if worn parts cause any unusual flow. The calibration must meet accepted industry standards regarding fuel efficiency and optimum performance.
Lubricate the Moving Parts
Lubricants recommended by the manufacturer are applied to the moving parts, such as swivel joints or lever mechanisms. This promotes less friction and longer component life, while also ensuring smooth operation, especially under high usage conditions.
Test the Automatic Shut-Off Feature
Testing the automatic shut-off should ensure that it works correctly when activated by an overflow of the fuel flow. Non-working shut-off systems pose serious safety hazards and can lead to fuel loss, making testing an essential part of the maintenance program, which should be conducted at least yearly.
Conduct Pressure Tests Regularly
Perform pressure testing to verify that the nozzle can withstand operational pressure without failure or leakage. Such high-pressure testing shall ensure compliance with safety codes to prevent the nozzle from any inconvenience while subjected to heavy use.
If you follow these step-by-step guidelines, you will be provided with a safer, more efficient, and durable fuel nozzle at lower operational costs, while also minimizing the chances of unexpected failure.
Tools Required for Proper Maintenance
Adjustable Wrenches and Pliers
Essentials for loosening or tightening nozzle components securely without damaging the fittings.
Cleaning Brushes and Solvent
For removing residue, debris, and fuel buildup from nozzle surfaces, internal and external.
Pressure Testing Equipment
Required to perform high-pressure acceptance tests to ensure the nozzle is functioning safely under normal and extreme conditions.
Replacement Seals and O-Rings
Essential for addressing aging and wear, ensuring proper sealing to prevent leakage during operation.
Calibration Tools
Used for adjusting and verifying nozzle flow rates for maximum performance and fuel savings.
Protective Gear
Including gloves, safety goggles, and aprons, one should wear protective gear to protect oneself during maintenance activities.
By blending these tools, maintenance work can be expedited to ensure smooth and safe operation of fuel nozzles.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Critical Maintenance Errors
It is essential to avoid these common errors if one wants to maintain the lifetime and efficiency of fuel nozzles while ensuring safe operation.
- Ignoring Regular Maintenance: If maintenance is neglected, clogged or malfunctioning fuel nozzles might generally reduce efficiency and increase the chance of accidents.
- Using Improper Tools: Maintenance works carried out with wrong or inappropriate tools can damage the nozzle parts, affecting their performance and longevity.
- Neglecting Safety Protocols: By forgoing the use of appropriate protective gear and disregarding safety procedures, maintenance personnel put themselves at risk of injury or contamination.
- Over-Tightening or Under-Tightening Components: Any kind of over-tightening or under-tightening of the nozzles can result in leakage, cracking, and operational problems.
- Overlooking Calibration Needs: The lack of calibration of the nozzles results in an incorrect flow rate, which adversely affects fuel efficiency and can lead to severe system malfunction.
Impact of Fuel Quality on Nozzle Maintenance

Fuel quality is central to nozzle maintenance and performance. Inferior or contaminated fuel can cause clogging, corrosion, wear, and early degradation of nozzle parts. Dirt, water, and microbial growth cause impurities that resist the proper flow of fuel, thereby reducing efficiency or causing damage to the system. Therefore, use good-quality, clean fuel to avoid these hazards, keep the nozzle longer, and operate it under the best conditions. An excellent way to safeguard your nozzles is to filter the fuel and conduct continuous inspections for fuel quality.
Understanding Diesel Fuel vs. Gasoline
| Characteristic | Diesel Fuel | Gasoline |
|---|---|---|
| Density & Energy Content | Denser with more energy per gallon, achieving greater fuel efficiency | Lighter and more volatile fuel with lower energy density |
| Ignition Method | Auto-ignites through high cylinder pressure (compression ignition) | Requires spark plugs for ignition (spark ignition) |
| Engine Characteristics | More rugged, longer lifespan, greater torque capacity for heavy-duty applications | Smoother acceleration, quieter operation, common in passenger vehicles |
| Emissions Profile | Higher nitrogen oxides and particulate matter, but improved with ULSD and exhaust treatment | Burns cleaner with less soot, but produces more carbon monoxide and volatile organic compounds |
| Environmental Impact | More efficient but higher air pollution potential | Less particulate matter but greater greenhouse gas emissions per gallon |
Understanding these differences is crucial when selecting the appropriate fuel type for a specific application or environmental consideration.
How Fuel Quality Affects Nozzle Performance
The quality of fuel is a very important factor affecting the operation and longevity of fuel nozzles in engines. Contaminants and inconsistencies could clog the nozzle, create uneven spray patterns, or degrade its efficiency. Consider an example of high-sulfur content fuel; although it is becoming less prevalent due to the stringent enforcement of regulations, sulfur buildup would corrode the components of the nozzle over time. It is safe to say that fuel contaminated with water or particles will surely affect the precision of nozzles through abrasion or blockage, thereby compromising engine performance.
Impact on Nozzle Lifespan
The data indicate that nozzles using poorly filtered fuel will lose approximately 30 percent more of their lifespan compared to nozzles using cleaner fuel sources.
Fuel types of the present-day generation, such as ultra-low sulfur diesel (ULSD) and biodiesel blends, are developed to prevent such issues. Even so, any minor trace of impurity or inconsistency arising from blending could still be present, despite the use of clean fuels.
Besides the very matter of lubricity affecting the operation of a nozzle, diesel would naturally lubricate the moving parts of the engine. Whereas those of lesser lubricity exert wear upon the nozzle, these rarely have an additive that improves such performance. Now, it is advisable to test fuel quality regularly and install effective filtration to ensure it operates at its best. Such a setup should prevent the nozzle from wearing out, allowing the engine to run with improved efficiency while saving on long-term maintenance costs.
Preventing Contaminants from Entering the Fuel Tank
Contaminants in the fuel tank can cause serious issues, including decreased engine performance, clogged fuel systems, and long-term damage to vital engine components. One way to prevent contamination is to ensure the fuel tank is sealed when not in use. Dust, dirt, and water are common contaminants, although even in minute quantities, they can ruin the fuel. Research has shown that even as little as 0.1% water in the fuel can decrease its lubrication ability, thereby causing rust or corrosion inside the tank.
- High-Quality Fuel Filters: Current filtration systems employing multi-stage filters are designed to remove ultra-fine contaminants, including those as small as 2 microns. Regular filter checks and timely replacements provide the best opportunity to prevent pollutants from entering the fuel supply.
- Proper Fuel Storage: Good fuel storage practices involve using clean, airtight containers and storing fuels in dry, shaded locations, thereby minimizing the opportunities for debris or moisture intrusion.
- Reputable Fuel Suppliers: It is also essential to source fuel from reputable suppliers to prevent the receipt of contaminated fuel. Typically, reputable fuel suppliers obtain certificates issued under strict quality control to verify purity.
- Fuel Testing: The use of fuel testing kits is recommended to detect contaminants early, allowing for immediate corrective action.
By combining these practices, operators of vehicles and other industries that rely on diesel-powered machinery can protect their fuel systems. In this way, they will be able to extend engine life and avoid costly downtime due to contamination-related failures.
Cost Implications of Poor Fuel Nozzle Maintenance

Poor fuel nozzle maintenance can result in significant financial implications for individuals and businesses. Clogged or damaged nozzles can reduce fuel efficiency and contribute to increased fuel consumption, ultimately resulting in higher operational costs. Additionally, when a nozzle does not function properly, it can result in uneven fuel distribution throughout the engine, leading to wear and potentially expensive repairs. Further neglect may cause the system to fail, thus requiring costly replacements. To mitigate the risks as mentioned above, fuel nozzles must be inspected and cleaned regularly; in this way, they will perform optimally, resulting in long-term cost savings.
Understanding Potential Expensive Repairs
Neglecting routine maintenance can lead to expensive repairs as minor issues develop into major problems. Research reveals that neglecting routine oil changes allows sludge to accumulate, thereby damaging the engine, for which repair costs can exceed $4,000. Thus, timely replacement of brake pads prevents a rise in repair costs from $150 to $500 or more due to damaged rotors.
Electronic System Costs
More sophisticated modern systems, such as fuel injection systems or electronic control modules, mean that neglecting maintenance will lead to higher repair costs. For example, replacing electronic control modules can be in the price range of $500 to $1,500, depending on the vehicle, a cost that is often avoidable through periodic diagnostic checks.
Experts believe that scheduled maintenance will identify many issues early, allowing vehicle owners to save thousands of dollars over the vehicle’s lifetime. External effects, such as poor roads and severe weather, can limit the adverse effects. These conditions can damage the proper suspension system and tires, resulting in repair charges that average around $1,000 and above for the localities involved. Maintaining adequate tire pressure and avoiding potholes are just a few of the proactive measures that can help reduce these costs, underscoring the importance of vehicle care and awareness.
Calculating Cost Savings from Proper Maintenance
Good vehicle care has helped significantly reduce maintenance costs. Regular tire pressure checks and timely oil changes can prevent expensive repairs and increase fuel efficiency, resulting in annual savings of hundreds of dollars. Furthermore, minor problems can be addressed ahead of time, much like the adage “prevention is better than cure,” such as replacing worn brake pads; otherwise, they can escalate into more significant and costly repairs if left unattended. Cutting corners on maintenance is not in one’s interest in the long run.
Long-Term Benefits of Keeping Fuel Nozzles Running Smoothly
Maximizing Equipment Performance and Longevity
Maintenance of fuel nozzles is crucial for achieving optimal equipment performance, minimizing unnecessary fuel wastage, and ensuring the longevity of the fueling equipment. Keeping the nozzles clean prevents them from becoming clogged with dirt or dust, which can affect fuel flow and operational efficiency. It is said that functioning nozzles save on downtime and repair costs while ensuring uninterrupted and reliable fuel delivery. Early repairs and scheduled checks on wear and tear will ensure, far ahead of time, that unforeseen breakdowns do not occur, thus maintaining safety and long-term customer satisfaction.
Enhanced Equipment Performance
Regular maintenance ensures fuel nozzles operate at peak efficiency, delivering optimal fuel atomization and combustion for maximum engine performance.
Reduced Fuel Wastage
Well-maintained nozzles prevent fuel loss through leaks and ensure proper fuel delivery, minimizing waste and reducing operational costs.
Extended Equipment Lifespan
Proactive maintenance prevents premature wear and damage, significantly extending the service life of fuel delivery systems.
Operational Reliability
Regular inspections and maintenance ensure uninterrupted fuel delivery, minimizing downtime and maintaining consistent operations.
Safety Compliance
Proper maintenance helps prevent accidents and ensures compliance with safety regulations, protecting personnel and facilities.
Customer Satisfaction
Reliable fuel delivery systems maintain service quality and customer confidence, contributing to long-term business success.
Reference Sources
“Cavitation treatment of high-viscosity marine fuels for medium-speed diesel engines”
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Fuel nozzle maintenance and its importance.
Fuel nozzle maintenance involves the periodic inspection and servicing of fuel nozzles in the engine, ensuring optimal fuel delivery and engine performance. It is considered essential maintenance because it prevents clogging of the fuel nozzles, ensures proper fuel consumption, and also prevents expensive repairs due to fuel nozzle failure. Regular maintenance also helps protect the turbine, compressor, and other engine components.
When should one perform routine fuel nozzle maintenance?
According to one’s aircraft engine maintenance manual, routine fuel nozzle maintenance should be performed after every 200 to 600 hours of flying time. This maintenance should consist of fuel nozzle inspections, cleaning, and testing to ensure the correct operation and efficiency of the fuel nozzles.
What are good practices for fuel nozzle inspection?
Before each inspection, use the borescope to check for carbon buildup at the tip. This ensures that there are no blockages in the fuel nozzle. Additionally, inspections of the adapter assembly at the sealing areas help prevent leakage and other functional problems with the fuel nozzle. Moreover, ultrasonic cleaning is applied to fuel nozzles every 200 to 600 hours to maintain good performance.
What causes blockage in fuel nozzles and how to prevent it?
While blockages may result from low-quality fuel, carbon deposits, or contaminants entering the fuel system, prevention involves using the highest quality fuel, paying attention to regular inspections and cleanings of fuel nozzles, and ensuring the fuel tank is free from debris. Preventative maintenance activities can also help avoid these fuel nozzle-related performance problems.
How does the low rejection rate of a fuel nozzle make engine performance go bad?
Unequal distribution of fuel in the combustor occurs when a nozzle delivers a poor fuel flow, resulting in inefficient combustion and increased fuel consumption. Moreover, as fuel leaks from the fuel nozzle, it can cause extremely high temperatures within the engine, damaging the compressor turbine vanes and thereby degrading the life of the hot section. Good maintenance of fuel nozzles ensures maximum engine efficiency by delivering a misted spray pattern from the nozzle.
What should I do if I notice a fuel nozzle leak?
When a fuel nozzle leak is noticed, it would be essential to carry out a nozzle leak and function test immediately to determine how severe the problem is. Raw fuel could reach the nozzle in the event of leaks, which would exacerbate damage and lead to an operational shutdown. Refer to your maintenance manual for instructions on correcting the leak and carrying out the necessary repairs immediately.
How can fuel nozzle maintenance influence fuel consumption?
Fuel consumption is directly affected by the maintenance of fuel nozzles, as they ensure the fuel is optimally delivered to the engine. A well-maintained nozzle program enables the optimal atomization of fuel into air, resulting in improved combustion and, consequently, enhanced fuel economy. The absence of fuel nozzle maintenance, on the other hand, increases fuel consumption and results in higher operating costs.
Can fuel nozzle maintenance prevent engine shutdown?
Yes, maintaining fuel nozzles ensures that the entire fuel delivery system performs optimally, thereby preventing engine shutdown. Regular inspections and cleaning prevent the nozzles from clogging and leaking, which results in engine failure. By maintaining fuel nozzles, the engine can be stabilized, ensuring smooth operation throughout its life.







