Sometimes people think it is just about pumping gas-there is maintenance and a proactive approach to it. Let’s mention here that an efficiently maintained fueling station means safety first, customer satisfaction, and maximized profits. The article will delve into pressing tips and solutions for the maintenance of your gas station, ranging from equipment checks and cleanliness to compliance. Whether you’re a seasoned service station operator or fresh on the scene, this information will help you run operations smoothly while limiting costly downtime headaches and providing a warm welcome to every visiting customer. Read on for ideas to keep your station running at its best.
Understanding Gas Station Maintenance

Safety, efficiency, and profitability are tightly bound with the proper maintenance of any gas station. Key areas for consideration are inspecting fuel pumps to ensure correct dispensing of fuel and leakage, monitoring underground tanks for compliance and containment, and keeping the fueling area clean to enhance customer experience. Proper signage and lighting facilitate safety and usability; emergency procedures should also be clear and well-established. Compliance with local regulations and adherence to a routine inspection schedule can prevent major, costly repairs and fines, ensuring the gas station runs smoothly and reliably.
Importance of Regular Maintenance
Routine maintenance ensures equipment and facilities last longer, operate efficiently, and are safe, especially in industries dependent on critical operations, such as fueling stations. Studies reveal that preventive maintenance can reduce repair costs overall by 40%, considering that a minor problem caught early never results in a costly breakdown. For instance, failing to inspect underground storage tanks may ultimately lead to leakage; such leakage could have become an environmental hazard, with fines exacted on the offender-EPA estimates that cleanup costs for leaking tanks run from thousands to hundreds of thousands of dollars.
Data also reveal that machines or systems that receive regular maintenance operate up to 20% more efficiently than their counterparts, thus saving energy and operational costs. Scheduled maintenance, therefore, reduces downtime, which maintains productivity while ensuring customer satisfaction, as well as avoiding financial losses that arise due to equipment breakdowns. When a company embraces a standardized maintenance schedule, aided by modern tools such as automated monitoring systems, it embraces proactive management and facilitates regulatory compliance. These observations make clear the critical need to ensure maintenance becomes non-negotiable in the working life of any functional and sustainable business model.
Components of a Fueling Station
A fueling station, hence, is a system consisting of several components working in unison to ensure the safe, efficient, and reliable delivery of fuel to vehicles and equipment.
Fuel Storage Tanks
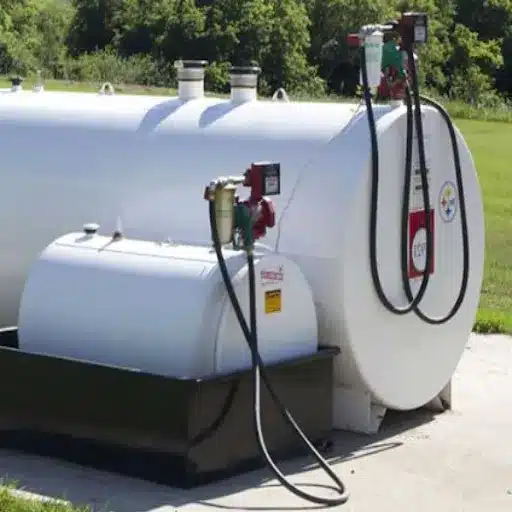
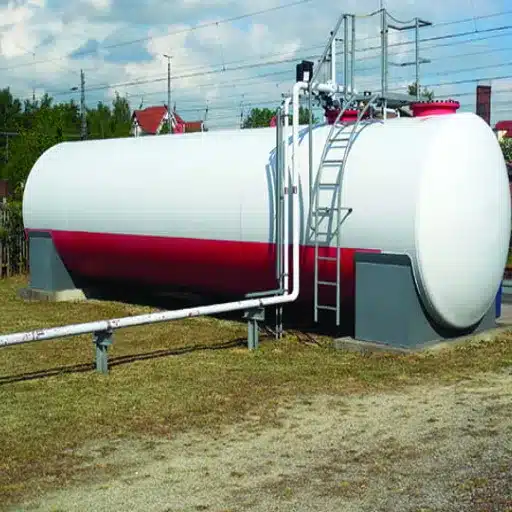
Fuel storage tanks serve as reservoirs for gasoline, diesel, or alternative fuels. These tanks are usually made of steel or fiberglass and are built in such a way that they do not cause leaks or damage from climatic conditions. These days, tanks even go as far as having double walls and leak detection systems to adhere to safety regulations and lower the risk of contamination. To ensure environmental safety and operational efficiency, the industry dictates that such tanks, especially USTs, be regularly inspected.
Fuel Dispenser and Pumps
The fuel dispensers function as the consumer interface instead. They come equipped with other components like nozzles, hoses, flow meters to gauge the quantity, and electronic or mechanical systems to discharge the fuel properly into the vehicle. Modern heavy fuel oil dispensers can also double as payment kiosks; they may also have digital readouts and dispense several types of fuel, such as ethanol blends and CNG, ensuring they cater to a varied customer base.
Piping System
The piping system connects the storage tanks to the dispensers. The highest-quality materials may be used in the installation: corrosion-proof steel or polyethylene to eliminate the possibility of leakage and ensure durability. Secondary containment systems may even be fitted to provide for minimizing fuel spills in case the lines fail.
Vapor Recovery Systems
Vapor recovery systems clean atmospheric vapors emitted during fuel loading due to pollution and are an environmental hazard; thus, the emphasis should be on emission control. Stage I manages vapors during the fuel delivery process, while Stage II is generated during vehicle refueling.
Fuel Management System
An encompassing fuel management system monitors and keeps in check the fuel inventory, fuel sales, and fuel usage. Such systems are often IoT-enabled and may include features such as real-time monitoring, predictive analytics, and maintenance alerts. Operators use this data to optimize costs and improve supply chain efficiency.
Safety Features and Monitoring Systems
Safety management is a crucial part of any fueling station. Automatic shut-off valves, a fire suppression system, and an emergency stop switch are all traditional safety implementations. Now, stations also rely on automated monitoring systems for 24/7 leak detection and tank gauging, so that any issue could be spotted immediately and an accident could be prevented.
Canopy and Lighting
The canopy and lighting offer shelter and visibility for a safer and more pleasant environment for visitors. LEDs have grown in popularity in recent years, mainly due to their low energy consumption and long life, which makes operating costs lower.
While combining the above elements into an operational system, the fuel station charts its course for efficient operation, keeping safety, care for the environment, and quality of service in mind. With ever-changing advances in technology and evolving modern practices for compliance, the design and operation of fueling stations will continue to become more forward-thinking.
Overview of Preventive Maintenance
Preventive maintenance is a condition-based maintenance that assures equipment runs reliably and efficiently along its intended lifespan. It reduces unplanned downtime and also lengthens asset life. Industry-wide statistics indicate that a good preventive maintenance program can cut maintenance costs by up to 25% and increase equipment uptime by 10-20%.
Key elements of preventive maintenance include periodic inspections, repairs, and replacement of components before they are worn out. Studies have shown that servicing mechanical systems like pumps and compressors regularly can save energy by 15%-20% because these systems are maintained for the best running conditions and avoid energy wastage.
Technology like predictive maintenance and condition-monitoring sensors complements traditional methods by supplying real-time data and analytics. Facility managers can predict a potential problem before it becomes a major problem. An organization, therefore, with a combination of both technology and scheduled maintenance activities, can work more efficiently in terms of cost for repairs in the long run.
Maintenance Checklist for Gas Stations

| Component | Maintenance Tasks |
|---|---|
| Fuel Dispensers |
|
| Storage Tanks |
|
| Fuel Pumps and Lines |
|
| Safety Systems |
|
| Canopy and Lighting |
|
| Environment |
|
| General Facility Inspection |
|
By using this checklist, gas stations can assure operational efficiency, service safety, and regulatory compliance.
Daily Inspection Tasks
Fuel Dispenser Inspection
- Notice for any leaks, damages, or wear and tear in fuel dispenser hoses and nozzles
- Make sure that the payment systems, like the card readers, work well
- The display screens must offer clear price and transaction information
Tank and Fuel Monitoring
- Keep daily checks of fuel inventory levels to avoid shortages or overstocking, etc. An automated system with modern sensors can give highly reliable data
- Look out for contamination in storage tanks; for instance, water intrusion can lower the fuel quality
Spill Prevention
- Look over the spill containment equipment, such as spill buckets, checking whether it is clean and functional
- Keep checking the nearby storm drains to make sure they hold no traces of fuel or hazardous materials
Safety Equipment Check
- Make sure that all fire extinguishers are in readiness, charged, and easily accessible
- Test the emergency stops fitted on the fuel dispensers to respond immediately should there be a need
- Alarm and Security Camera Verification: These systems should be checked thoroughly to prevent any incident and/or to respond to any incident
Cleaning of Restrooms and General Facilities
- Clean and disinfect the restrooms several times a day so that they remain hygienic
- Keep the bottles filled with supplies for use, such as toilet paper, soap, and hand towels
- Do any repairs need to be made, especially where they are visible, once again, for customer satisfaction
Lighting and Signage
- Check for illumination outside and inside due to a time frame at night. Safety standards require such areas as dispenser areas to be lit at 10-foot candles of illumination
- Make inspections for signage visibility and accuracy, i.e., safety warnings, promotional materials, and price boards
Waste Disposal
- Empty trash containers and dispose of waste according to local regulations
- Check the recycling containers to be sure customers have an adequate option to recycle materials such as cardboard or aluminum
Pavement and Site Conditions
- Ensuring all pavements are visually inspected for the formation of new cracks, potholes, or oil stains that could jeopardize safety is advocated. According to studies, timely maintenance of smaller cracks has proven to decrease 80% of repair costs
- Ensure that accessibility parking spots and walkways are marked with clear indications
Customer Interaction (Optional)
- Train staff to observe and follow up on customer inquiries or complaints promptly. Competent service awards a greater than 70% retention for customers
Upon prioritizing this agenda for daily work, gas stations can successfully fortify safety, ensure legal compliance, and offer a better customer experience.
Weekly and Monthly Maintenance Activities
Weekly Maintenance
- Fuel Pumps and Dispensers Inspections: Check for any visible damage, malfunctions, or leakages. Clean dispenser filters if clogged to enable maximum efficiency
- Inventory Check: Conduct proper level checks of the fuel tanks and store inventory for sufficient supply and proper restocking
- Safety Equipment Checks: Test-fire extinguishers; spill kits and emergency shut-off systems need to be verified
- Cleaning and Sanitization: Deep clean store floors, restrooms, and exterior areas, including fuelling areas and walkways. This will keep hygiene standards up and customer satisfaction high
Monthly Maintenance
- Tank Inspections: Ullage checks and water contamination tests are done on fuel tanks by accepted industry standards to ensure environmental compliance
- Compliance Audits: Permits, certifications, and safety checklists are to be reviewed and updated as per local and federal law. Document findings to avoid penalties
- Equipment Servicing: Arrange professional services for fuel pumps, HVAC, and the ventilation system for operational efficiency and longevity
- Security System Check: Inspect CCTV camera systems and alarm systems to ensure proper operation, with actions taken to correct any faults that might arise
Following these weekly and monthly maintenance schedules ensures the smooth running of the operations with minimum risks to safety, hence building customer confidence.
Annual Compliance Checks
Annual compliance checks ensure that your business obeys regulatory standards and works effectively. Usually, these checks entail verifying permits and licenses to ascertain their validity and ensure they will be renewed on time. Fire safety equipment, such as extinguishers and sprinkler systems, must be inspected and serviced every year so that they’re legally compliant and safe for the workplace. Likewise, health and safety audits must be carried out to identify hazards and take corrective measures. Environmental compliance checks need to be done to ensure that measures actually follow the standards of waste management and pollution control. Involving certified professionals regularly during these checks ensures that everything is done thoroughly and prevents costly interruptions or penalties.
Fuel Dispenser and Pump Maintenance

Fuel dispensers and pumps require fixing to work correctly, be accurate, and be safe. There is contemporary maintenance, such as inspections for leaks or wear and markings on the caliper to verify the correctness of the dispensing, and it is also used for every cleaning to remove blockages. Filter inspection and replacement guarantee fuel quality. This is to say, it is recommended to follow the manufacturer’s maintenance protocols and have professional servicing at certain periodic intervals. Adherence to these practices reduces downtime, enhances reliability, and complies with industry regulations.
Calibrating Fuel Dispensers
Ensuring proper amplitude measurement in refilling fuel dispensers economizes fuel losses and maintains regulatory compliance. The calibration process usually requires comparing the recorded volume from the dispenser to that of the certified standard: a calibrated prover can or meter, and accordingly, the equipment might be adjusted to comply wherever it deviates beyond acceptable tolerance. Regular calibration indeed ensures customer satisfaction and protects the business from financial penalties and lawsuits. The calibration interval depends on the rate of usage, environmental conditions, and regulations. This procedure can be carried out either by professional technicians or by an in-house maintenance team. Auditable documentation must be preserved at all times. For precise calibration, following the manufacturer’s instructions and employing certified tools is crucial.
Inspecting Nozzles and Hoses
The inspection of nozzles and hoses must be performed to ensure that equipment functionality remains in working order and for safety purposes. Start with a visual check of the hoses for cracks, bulges, or leaks, while inspecting whether all connections are tight. Clogging of nozzles or corrosion must not be allowed, as this will affect performance and efficiency. Periodic flushing of nozzles with suitable cleaning solutions is an excellent measure to prevent blockages. Furthermore, check to make sure hoses are not kinked or overly worn, as such conditions precipitate premature failures on their own. Inspection intervals should follow those prescribed by the manufacturer, and any damaged part must be replaced immediately to prevent any operational downtime or hazards. The thorough inspection procedure is one of the ways to prolong the service life of the equipment and improve its performance.
Repairing Common Fuel Pump Issues
Typical fuel pump repairs require diagnosing the problem for proper functioning. When the engine has difficulty starting and runs sporadically, it can reveal a clogged fuel filter, low fuel pressure, or a faulty pump motor. Check for fuel pump fuse and relay issues first, as they are often simple and easy fixes. Next, if the pump does not maintain the proper pressure, check the fuel lines and filter for blockages or leaks. Cleaning or replacing any of these elements will often return normal functioning. Also, ensure that electrical connections to the pump are tight and corrosion-free; poor wiring can hamper performance. Replacement would be required if problems are beyond repair, such as with a defective pump motor. Regular maintenance and keeping up with the vehicle’s service schedule will go a long way toward preventing any fuel pump problems.
Tank Management and Maintenance
The proper treatment and maintenance of a tank ensure its installation in working order and longevity. Inspect the shell regularly for signs of wear or corrosion; dents and cracks are two cases in point. Cleaning of tanks must be allowed by evacuation of sediment or any kind of debris, since it may impede their operation. Ensure that the levels within the tank are on the higher side, for if it ever dips too low, repeated damage will be done due to such opening action or through the action of overfilling. Refer to the instruction manual for the inspection and replacement of components such as valves, seals, and fittings. Perform scheduled maintenance inspections and ensure that all safety and environmental regulations are being observed.
Regularly Inspecting Storage Tanks
An appropriate inspection and maintenance process is essentially needed to keep storage tanks in good repair and allow their use during the period of the intended life. Per standard practices, tanks must be periodically assessed for common hazards such as corrosion, leakage, and structural degradation.
A study, however, revealed some interesting facts regarding tank failures: corrosion accounts for 25% of failures. Hence, it has implications for regular checks for rust or metal thinning, especially in older tanks.
Visual inspection must be performed monthly for any visible damage. Comprehensive internal and external inspections, including ultrasonic thickness testing, should be performed every 5 to 10 years, depending on the tank’s material and the manner of its use. The data indicated that tanks exposed to very severe environmental conditions or the storage of hazardous materials may require more frequent inspections.
In addition to improving safety and efficiency while reducing downtime, technological advances have seen the use of drones equipped with high-resolution cameras and remote sensors for tank inspections. By adhering to these practices, the structural integrity of storage tanks is maintained while potential costly repair charges are avoided, as it could pose an environmental threat via discharge from leaks.
Tank Cleaning Procedures
Tank cleaning is an important procedure to maintain storage tank performance and avoid contamination. The procedure usually begins with isolating the tank and rendering it safe by ensuring that there is neither product nor residue left inside. Nowadays, automated tank cleaning systems (ATC) are widely applied. Rotating high-pressure jet sprays are employed in such systems to decrease manual entry and hence increase safety and efficiency.
Certain industries depend heavily on CIP technology for periodic cleaning cycles, maximizing efficiency concerning time and resources. Sources state that CIP systems can save about 40 percent less water and cleaning agents than traditional methods, hence supporting sustainability practices. The use of biodegradable detergents further decreases environmental impacts.
Safety will be a considerable factor in cleaning tanks. If the tank does not undergo gas freeing and adequate ventilation, workers may be exposed to harmful fumes. Also, PPE, including respirators and chemical-resistant suits, must be donned by workers during manual cleaning operations. To keep the cleaning processes compliant and effective, regular inspections and adherence to regulatory guidelines will have to be undertaken.
Still, robotic tank cleaning systems garner more interest because they can access confined spaces and clean thoroughly without risking human safety. Whenever these systems are coupled with cameras and sensors, operators can observe the whole process from afar, thus imparting even greater safety and accuracy to this cleaning operation.
Addressing Downtime and Efficiency
To reduce downtime in tank cleaning matters greatly in sustaining operational efficiency. Unplanned downtime statistics hold that unplanned downtime might even take time from an industrial facility’s management for approximately tens of thousands of dollars per hour, encouraging and forcing cleaning processes to be as fast as possible. In such situations, automated cleaning processes offer better possibilities; in fact, autonomous cleaning procedures have been known to take 70% less time than manual cleaning techniques.
High-pressure jet systems and robotic cleaners enhance speed and reduce manual intervention while allowing tanks to return to operation promptly. Another way could include advanced scheduling and predictive maintenance to ascertain optimal cleaning times that minimize interruption of production schedules and streamline workflow. An integrated approach with these technologies and systems would improve productivity while conforming to safety and hygiene standard regulations.
Regulatory Compliance in Gas Station Maintenance

Compliance with applicable regulations about gas station maintenance involves meeting specifications or requirements prescribed by local, state, or federal governments, intended for the protection of the environment, public safety, and operational standards. These generally mandate USTs to be inspected at given intervals so that any possibilities of leaks and leakage are checked; hazardous wastes are disposed of in an approved manner; and provisions relating to air quality are observed. Records of maintenance and inspection must be kept to prove during audits that the station complied with regulations. Adhering to such provisions helps to prevent environmental contamination, which would be grounds for possible litigation, fines, or closure of the facility in extreme events.
Understanding Regulatory Requirements
The fuel industry operates in an environment that is seething with regulations spotlighting the protection of the environment and human safety. The EPA, in particular, mandates that gas stations install state-of-the-art leak detection systems on USTs, the working of which should be tested every year, so the proper authorities are alerted early of any leaks that may cause groundwater contamination.
By many standards, air pollutant control laws also call for vapor recovery systems to be used at fuel dispensers in the course of restricting emissions of volatile organic compounds (VOC) and other pollutants. The EPA also maintains the same principles concerning stations on hazardous waste disposal laws-they must dispose of chemicals, oil, and fuel by certified means of disposal. Failure to meet such laws tends to cost big, with fines mostly set at $10,000 to $50,000 per day of an ongoing violation.
On the larger scale, the newer data now point to the importance of environmentally sustainable practices. For example, a few states have adopted incentives for conversion to EV charging stations—a plus to the generational trend toward cleaner energy. Taking on such measures mitigates compliance risk and positions the business on the environmentally friendly track that customers seek. In keeping with these transforming laws lies the very basis of operational conduct and the ultimate fulfillment of sustainability of the industry.
Documentation and Record Keeping
Proper documentation and record-keeping must be ensured to remain in tune with changes in regulations. Accurate and up-to-date records must be kept, monitoring changes in policies, implementation of sustainable practices, or compliance efforts. Apart from meeting all regulatory requirements, these inclusions also lend themselves to transparency and long-term operational sustainability.
Staying Updated with Safety Standards
Research and keep abreast of the changes in regulations. In order to achieve compliance, follow updates from recognized sources such as OSHA, ANSI, or regulatory bodies deemed relevant for your industry. Through industry newsletters, workshops, and seminar attendance, and by leveraging tools and platforms that track regulatory updates, one can simplify matters. By reviewing workplace policies and employee training regularly, safety measures can be built up to meet current standards, therefore reducing hazards and fostering a safe working environment. Professional organizations and forums may also aid in learning best practices and emerging trends.
Key Takeaways
- Regular maintenance can reduce repair costs by up to 40% and increase efficiency by 20%
- Daily inspections are crucial for safety and operational continuity
- Proper documentation and compliance prevent costly fines and legal issues
- Investment in modern monitoring systems provides long-term operational benefits
- Well-maintained facilities improve customer satisfaction and retention rates
Reference Sources
Analysis of a Gas Station Hybridization with a Solar Thermal Plant Using ETAP
Assessment of Health, Safety, and Environmental Risks of Zahedan City Gasoline Stations
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Why Is Gas Station Maintenance Essential for Owners?
Gas stations must undergo maintenance in order to prevent accidents and promote smooth operations. Basic maintenance prevents the occurrence of issues with, for example, fuel leakage or equipment malfunction, which result in environmental damage and monetary loss. Gas station owners may therefore have tailored maintenance systems so that their fueling equipment is operating best.
What Should Be in a Maintenance Checklist for Gas Stations?
A full maintenance checklist for gas stations must have regular inspections of the fuel dispensers, tanks, and fueling equipment. It is important to check for leaks or test the fuel flow, which ensures that the fuel delivery is accurate. In addition, one must also keep the nozzles, pumps, and connections in good shape, lest they become contaminated through sludge and microbial growth.
How Does Preventive Maintenance Help Avoid Downtime?
Properly cleaning a tank removes water, dirt, rust, and dust accumulation within the tank. Improper cleaning could lead to corrosion within the tank. Clean tanks provide for better fuel quality, hence maintenance of the fuel dispensing equipment and tanks is extremely required.
What Gas Station Owners Should Know About the Regulatory Requirements
Gas station owners must be aware of the regulatory requirements to maintain and inspect their fueling equipment. Operating within these regulations ensures safer operations and reduces the chances of environmental damage. Regular inspections and keeping accurate records enable gas stations to meet these obligations and continually perform at their best.
How Will Fuel Delivery Be Accurately Assured by Gas Stations?
To produce an accurate fuel delivery, gas stations should frequently calibrate their fuel dispensers and make inspections, checking for any sort of leaks in the complete fuel system, proper fuel flow, and good condition of every component. By considering any issue beforehand, ample services will be made available to the customers regularly.
What Are Some Maintenance Tips for Fuel Dispensers?
Maintenance tips for fuel dispensers may include regularly checking for leaks and whenever all connections are properly tightened. Also important to look for any wear or damage in the dispensers and clean them to prevent any sort of buildup. Establishing a preventive maintenance program will help gas station owners keep their dispensers in good shape so they keep functioning properly.
How Many Times Are Gas Stations Supposed to Inspect Their Equipment?
Depending upon usage, equipment may need to be inspected regularly, perhaps even on a weekly or monthly basis. Very frequent inspections ensure the discovery of any signs of wear and tear, leakage, or microbial growth. By keeping routine inspection intervals, gas stations can either immediately effect solutions to prospective problems, thus avoiding the user from great inconvenience.