Fuel management is perhaps the most central element of fleet operations in guaranteeing efficiency, cost savings, and other accounting-linked facets of productivity. In traditional monitoring techniques, industrial yard fuel managers are frequently denied the real-time data and utmost accuracy essential to render proper decisions. RFID fuel management systems, as it were, disrupt fuel management tracking and provide higher levels of accountability to avoid pilferage or loss through errors. This article examines how RFID is revolutionizing fuel management for fleets and provides an analysis of what RFID can do, its benefits, and possible solutions to problems faced by fleet operators. So, let’s dig a little into how the adoption of RFID fuel management systems can help positively.
Understanding RFID Technology in Fuel Management

Fuel management through RFID technology in-demand application is the process of using radio waves to automatically identify and track tags attached to objects, such as vehicles or fuel dispensers. Using this technology, fuel dispensing becomes automated, wherein vehicle or driver information is verified through RFID tags. It prevents the unauthorized use of fuel, maintains dispensation records manually, and tracks fuel consumption accurately in real time. By integrating RFID systems, fleet operators will be able to reduce fuel pilferage, raise operational efficiency, and keep detailed knowledge of consumption trends.
What is RFID and How Does it Work?
Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) is a wireless technology that employs electromagnetic fields for automatic identification and tracking of tags attached to objects. The system normally has three main components that comprise an RFID tag, an RFID reader, and an antenna. The RFID tag may be active (battery-powered) or passive (it gathers energy from the signal emitted by the reader) and stores electronically stored information. The reader sends radio waves to activate the tag, and in response, the tag sends its stored information back to the reader for further action.
RFID depends on two main bandwidths: the Low Frequency (LF) and High Frequency (HF), plus the Ultra-High Frequency (UHF), with each having different advantages. For example, one of the advantages of UHF is that it can read tags from a longer distance, sometimes reaching 30 feet, which is why it is used extensively in supply chain and logistics applications. The best advantage of RFID technology is its high level of accuracy. In inventory management, recent systems have an almost 99% accuracy rate, which drastically reduces errors when compared to manual stocking and cataloging.
RFID applications span a variety of industries. Retailers use RFID to track inventory more efficiently, decrease stock-outs, and improve the shopping experience for customers. Equipment tracking and patient monitoring in healthcare are also handled with RFID, together with patient safety, and improve operational efficiency. In the transportation and logistics sector, RFID is also used for fleet management and automating toll collection. Given that the tags can store data such as manufacturing data and expiry dates, RFID is invaluable to any application that requires high-accuracy, data-heavy tracking.
Being efficient and seamless, this technology is ever-evolving, with recent developments of RFID integration into IoT ecosystems further paving the way for its use in the next-generation smart operations and connected devices.
The Role of RFID in Fuel Tracking
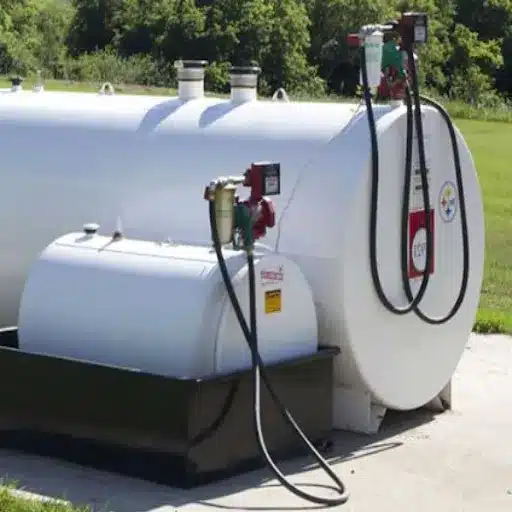
RFID has stepped up as an excellent method to optimize fuel tracking and other management issues faced by industries such as transport and logistics. Combining RFID tags with fuel tanks and fuel dispensers enables organizations to carry out real-time monitoring and accurate fuel consumption tracking. This brings accountability to the fore while outlawing the theft of fuel, which is, in itself, a matter of serious concern, widely prevalent in many fleet operations.
Some studies show that fuel management using RFID can reduce operational costs by 20% due to better supervision and minimizing wastage. Data on refueling time, volume dispensed, and vehicle identification can be recorded automatically by RFID readers stationed at fuel stations or even docked in fleet vehicles, thereby escaping errors of manual data entry. Similarly, RFID-enabled fuel management systems used to maintain fuel inventory provide insights into usage patterns and trends at a much finer granularity.
An example of an industry concern is in smart fuel distribution networks, where RFID ensures delivery to the intended vehicle or equipment. This, in turn, saves the environment from spillage and fraud and ensures auditing is transparent. With the continued development of RFID, including a larger range and good data-encryption methods, the technology will only find more offensive roles in fuel tracking, ensuring greater operational efficiency, and hence further cost-cutting, for industries worldwide.
Benefits of Using RFID for Fuel Management
Enhanced Accuracy and Monitoring
Using RFID technology to monitor fuel consumption gives real-time data and more accurate usage data, eliminating human error in its manual recordings. Industry-based studies show that management-based companies using RFID for fuel-waste management report up to a 30% decline in fuel wastage because of greater oversight, along with precise monitoring of consumption patterns.
Better Security and Fraud Mitigation
Using RFID, with its advanced encryption techniques, helps to curb unauthorized access and theft of fuel. For instance, industries can ensure that only authorized vehicles or equipment are refueled by linking fuel dispensation to a specific vehicle or piece of equipment, thus saving immense amounts of money that would otherwise be lost through fraudulent activities.
Operational Efficiency
Automatic refueling cycles for large fleets and less downtime caused by processing lead to operational cost savings with RFID refueling systems from entering and reconcile data manually. From the inception of fuel distribution and usage down to refueling of a fleet, all identification and data recording can be automated. This advantage translates to great cost savings, especially for logistics and transport companies running massive operations.
Better Inventory Management
An RFID application allows fuel inventory to be updated in close-to-real-time, therefore providing fuel-level information that helps with the management of fuel stocks. Monitoring inventory allows proactive measures to avert a stock-out or overstock, thus leading to efficient procurement planning and cost savings. Some people in the business have reported up to 20% reductions in inventory management costs after adopting RFID.
Environmental Sustainability
The demand for optimized fuel consumption and elimination of wastage assists the RFID in reducing carbon footprints. Better and cleaner fuel handling also uplifts the environmental sustainability agenda.
Data-Driven Insights
Linking RFID with data analytics platforms empowers better insights into fuel consumption trends and maintenance requirements. Such knowledge supports predictive scheduling of maintenance activities, based upon which decisions are made to improve performance financially and operationally in the long term. A recent survey indicates that organizations using RFID have witnessed an improvement of 15-20 percent in fleet performance metrics.
Industries can realize measurable enhancements in areas concerning accuracy, efficiency, security, and sustainability through integrating RFID technology into the fuel management systems. Such benefits make RFID an indispensable tool in modern fuel logistics and resource optimization.
Components of an RFID Fuel Management System
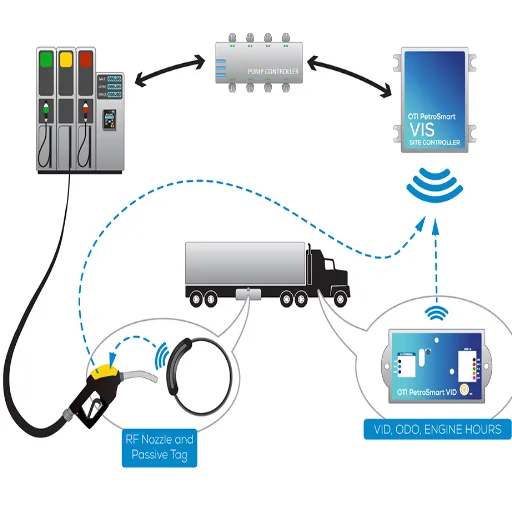
The RFID fuel management system consists of several major components:
- RFID Tags: These are attached to vehicles or equipment so that they may be identified during fuel operations.
- RFID Readers: These capture data by scanning tags for authorization and tracking purposes.
- Fuel Dispensers: These ensure, through RFID readers, that fuel is dispensed only to authorized vehicles.
- Centralized Software: Platform-level software that collects, stores, and analyzes data for monitoring fuel use and creating reports.
- Control Panels: Interfaces allow the control of access, configuration of settings, and general supervision of the system.
These work synergistically to boost efficiency, map the fuel theft potential, and provide accurate data on fuel management.
Key Elements of RFID Systems
RFID systems require actual core components for their proper functioning, and different industries optimize the design and performance of these components accordingly: for example, logistics, the retail industry, and even fuel management. Below is the breakdown of a few of these elements:
- Tags: The RFID tags are small devices that store information and get attached to an object or a vehicle. There are several types of tags; the two most common being active and passive tags, with active tags having batteries to power themselves, and passive ones being powered by the RFID reader. Unique identifiers, such as electronic product codes (EPC), are used to ascertain identity.
- Readers: These devices emit radio waves to energize passive tags and retrieve data stored on them. Readers are configured to operate within a defined range and frequency to be compatible with the specific applications of RFID. They can be fixed or handheld, letting them cater to varying working environments.
- Antennae: These are conduits for the communication between RFID tags and readers. Antennae are critical for creating and receiving radio signals; the kind of antenna selected can affect the overall reading range and level of accuracy.
- Middleware and Software: These data-processing platforms or middleware that interface with data collected by the reader enable analysis, real-time monitoring, or reporting for insight upon operation; all software integrates seamlessly with any existing systems.
- Data Storage and Integration: These systems refer to storing and managing data collected by either cloud-based or on-premises databases, allowing integration with other enterprise tools such as inventory management systems or fuel monitoring systems.
By bringing all of the above together, the RFID systems provide higher productivity, smoother operations, enhanced security, and decision-making based on data for almost any application.
Integrating RFID with Fuel Dispensing Systems
Implementing RFID in fuel dispensing has benefits in operation and accuracy. RFID technology provides the refueling process an automatic recognition of vehicles and their credentials. As the vehicle comes near the dispenser, the system reads the vehicle’s RFID tag to ensure that refueling is done only for the authorized vehicle. Therefore, unauthorized dispensing may lead to data-entry errors and theft of fuel.
Furthermore, employing an RFID-based fuel management system produces more accurate fuel consumption data, vehicle mileage, and operational characteristics to allow real-time surveillance and analytics, allowing for business optimization of fuel consumption and finding areas to cut costs. It requires attaching RFID tags on vehicles with the dispensers having RFID readers, coupled with backend system integration for data handling.
Public transportation, logistics, and mining frequently use RFID for stress management and operational efficiency. The use of RFID becomes successful when the system is well configured and has proper staff training and ongoing maintenance to ensure the system stays reliable for maximum return on investment.
Automated Fuel Management Solutions
Automated fuel-management solutions play a crucial role in changing how industries monitor and control fuel usage, offering smarter tools to adjust operations and control costs. These systems use advanced technologies such as telemetry and IoT-based devices to remotely monitor fuel levels, consumption patterns, and refueling activities in real time. For example, GPS tracking may be integrated with automated fuel dispensers to create an accurate record of all vehicle fuel usage while preventing fuel theft or unauthorized consumption.
Research states that companies that install fuel management systems can save as much as 30% on fuel costs by reducing fuel wastage and spotting inefficiencies. The systems have advanced analytics that can be used for predictive maintenance to ensure smooth working of equipment and a reduction in unexpected downtime. Besides, monitoring fuel while keeping it over a cloud-based system ensures data is accessible across multiple locations from afar, thus improving systems for fleet management and operational decision-making.
These solutions stand to immensely benefit fuel-intensive industries such as transportation, agriculture, and construction. Among the forecasts, there exists an indication that the global fuel management system market is projected to grow at a CAGR of more than 7% through 2030, thereby showing increased adoption of these technologies globally. This also means that efficiency is being enhanced towards sustainability by advocating efficient fuel usage with lower environmental impacts.
Implementing RFID Fuel Management Solutions

RFID fuel management solutions have many advantages, including improving the accuracy and efficiency of the tracking of fuel tracking. The systems automate fuel dispensing and recording processes to remove errors resulting from manual intervention. RFID technology also enhances security by guaranteeing that only authorized vehicles and operators have access; this decreases the chances of misuse or theft. The other attractiveness of RFID systems lies in the fact that they collect data in real-time, by which each business can study fuel consumption patterns and operational optimization as well as make informed decisions toward cost savings and sustainability.
Steps for Successful Implementation
- Assess Business Needs and Set Objectives: Start by determining the precise challenges and requirements your organization faces. Ensure you clearly set the objectives your organization aims to achieve, be it minimizing fuel theft, increasing operational efficiency, or controlling costs.
- Choose the Right RFID Solution: Select and purchase an RFID fuel management system that suits your business needs. Check its compatibility with your current infrastructure, scalability, and feature set, like real-time data collection and reporting.
- Do a Site Survey: Review your facility to ascertain optimal positions for RFID hardware such as readers and antennas, to achieve adequate coverage and functionality. Take care of any environmental circumstances that may affect performance.
- Develop a Comprehensive Implementation Plan: Draft detailed implementation plans that include timelines, resource allocation requirements, and training guides. Collaborate with capable vendors or system integrators for a smooth rollout.
- Install and Test the System: Install RFID hardware and link it up with your existing systems. Carry out exhaustive testing for functionality, data accuracy, and security features before the deployment stage.
- Train Staff and Develop Protocols: Train employees rigorously in the use and application of the system. Establish fuel-dispensing protocols, access control, and data-monitoring protocols that will yield maximum benefit from the RFID solution.
- Monitor and Optimize the System: Keep aggregating performance metrics and analyzing usage data to locate any inefficiencies. Maintain and update the system as needed for ever-changing business requirements, securing its long-term relevance.
Adhering to these steps closely will guarantee a smooth transition into an RFID-based fuel management solution to secure optimal gains and efficiency for your organization.
Common Challenges and Solutions
Implementing an RFID-based fuel management system can bring along innumerable challenges. Some common difficulties with possible solutions are listed below.
High Initial Costs
Challenge: Costs to procure or otherwise gain access to RFID technology, installation, necessary hardware, and software may be high.
Solution: Conduct thorough cost-benefit analyses to justify potential future savings. Scour the market for modular products that can be implemented in phases, thus minimizing the financial burden initially.
Integration with Existing Systems
Challenge: This can pose problems in ensuring compatibility with legacy systems and third parties.
Solution: RFID solutions should be chosen with commercial-level APIs and flexible commercial and technical integration capabilities. Work hand in hand with suppliers to customize or configure the solution to your current infrastructure.
Data Accuracy and Interference
Challenge: Factors like metal surfaces and weather conditions may cause interference.
Solution: Go for good-quality RFID tags and readers that suit the given environment. Test the system frequently under real-world conditions to be able to identify and resolve problems.
User Training and Adoption
Challenge: User resistance to change or lack of knowledge about new processes.
Solution: Set up comprehensive training programs accompanied by clear documentation. Involve your employees early on to solicit their feedback and gain traction.
Maintenance and Scalability
Challenge: Maintenance activities and system scaling to accommodate growth can be difficult.
Solution: Set a proactive maintenance plan and choose a vendor that supports scalable solutions that allow your system to grow with your business.
Once these challenges are addressed with suitable strategies, the RFID-based fuel management system implementation will run smoothly and sustain performance into the future.
Measuring the Impact of RFID on Fuel Efficiency

In measuring fuel efficiency and how RFID technology affects fuel efficiency, recording the actual statistics of performance and doing the analysis for improvements is undertaken. Begin by considering changes in fuel consumption rates, vehicle idle times, miles per gallon, and frequencies of refills before and after using RFID. By automating processes with data collection, RFID systems eliminate clerical errors and allow for precise tracking of fuel utilization, inventory management, and route optimization. Besides that, RFID tags ensure that fuel is given only to authorized vehicles so that misuse or theft is avoided. Using the reports based on system generation, businesses can look for patterns or weaknesses and make changes based on data that would ultimately benefit fuel-use efficiency. Such regular analysis ensures that the system meets operational goals and can provide real-term benefits for the future.
Enhancing Fleet Fuel Management with RFID
RFID technology enhances fleet-fuel management in terms of security, accuracy, and efficiency. Fuel is dispensed only to authorized vehicles by RFID tags, reducing the chances of misuse. The system keeps track of fuel usage in real time so operators can look at patterns of usage and pinpoint when it is being used inefficiently. The automated collection of data reduces human errors and saves time so that the company can focus more on optimizing fleet operations. All of the above features position RFID as a reliable solution to bringing down costs and better management of fuel.
Reducing Human Error in Fuel Tracking
Human error in fuel tracking systems should be reduced to optimize the operational efficiency of organizations and minimize financial losses. Such is the problem that automated systems like RFID and fuel management software aim to tackle. In doing so, the data collection is mainly automated, eliminating or minimizing errors caused by manual entry, such as different amounts of fuel recorded or wrong vehicle details being input. These systems would yield accurate consumption data in real time to help operators make decisions.
Integration with GPS and telematics systems is also implemented, enabling cross-checking of fuel consumption against vehicle routes to detect inconsistencies, such as unauthorized fuel use or inefficient driving practices. Regular maintenance and appropriate training on system usage will ensure accuracy and reliability. With the implementation of these strategies, inconsistencies would be minimized; manual processes would be fewer, thus increasing the efficiency of fuel management.
Improving Fuel Quality Monitoring
Discussing fuel quality issues further means discussing contemporary technology and best practices to ensure that a fuel performs to its specs. One of the best ways to realize this is by deploying real-time monitoring systems for fuel that can, at the point of use, monitor density, temperature, and contaminants. The benefit here lies in the immediacy of adverse alerts once fuel deviates from the levels of acceptability. When inconveniently not in operation, tracking of fuel samples via laboratory tests usually reveals common impurities like water, sediments, or microbial contaminants, any of which can cause engine performance issues or outright long-term damage to machinery.
An additional key to quality assurance is to provide filtration systems during fuel storage or fuel transfer; such filtration reduces contamination risks. Proper storage practices involve keeping tanks sealed, cleaning storage facilities regularly, and monitoring for condensation to maintain fuel quality. Personnel can also be trained to identify degraded fuel and adhere to proper handling instructions, therefore diminishing the probability of quality problems in this way. Finally, an assurance of fuel quality can be further obtained by sourcing fuel from reputed fuel suppliers who themselves apply strict quality control measures to maintain fuel quality and ensure its consistency over the shelf life at their end.
Case Studies: Successful RFID Fuel Management in Fleets
The implementation of RFID technologies by many fleet operations has served to date for fuel management, cost reduction, and increasing operational efficiency. One logistics company found a way to reduce fuel theft and unauthorized fueling by 20% through the integration of RFID tags with automated fuel dispensers. Another company in the public transit field, employing the RFID system for the purpose of fuel usage tracking in real time, could identify below-par performing vehicles and work on their optimal performance, raising fuel efficiency by 15%. The construction fleet uses RFID in automated record-keeping to reduce manual errors and ensure compliance with fuel usage regulations. These cases make clear the importance of RFID in enhancing accountability and simplifying fleet operations.
The Future of Automated Fuel Management

The future of automated fuel management centers around increasing efficiency, cost reduction, and sustainability. With RFID and IoT technologies, fuel consumption will be monitored more precisely to minimize waste and maximize accuracy. These will integrate with data analytics platforms to produce actionable insights for better decision-making while furthering automation to reduce human errors and save time. Also, with the increasing diffusion of renewable energy and alternative fuels, the development of automated fuel systems will probably evolve to accommodate such sustainable options. This will enable industries to compete and comply with environmental regulations and objectives simultaneously.
Trends in RFID Technology for Fuel Management
RFID (Radio-Frequency Identification) technology, which allows for precise tracking and data collection, is revolutionizing fuel management. One particular trend is the coupling of RFID and Internet of Things devices so that fuel consumption and inventory levels can be monitored in real-time, thereby keeping accurate records and preventing theft or unauthorized use. Other significant advances involve providing RFID-enabled fuel cards and vehicle tags to expedite an automated fueling process with a link from the specific transaction to a vehicle or driver. Also, higher-end systems are becoming more and more compatible with cloud platforms for centralized data management of several fueling stations. This constellation of trends is providing fuel management systems with greater operational efficiency, cost optimization, and transparency.
Preparing for the Next Generation of Fleet Fuel Management
A proper positioning for the next generation of fleet fuel management includes pushing for the pursuit of sustainable and tech-based practices. By investing in telematics and IoT solutions, fleet managers can monitor, analyze, and take appropriate action on fuel use, vehicle performance, and route optimization. Furthermore, AI-enabled predictive analytics would allow a company to predict maintenance and, therefore, help with fuel efficiency. Another important area in moving in this direction would be the use of alternative fuels, especially electric/hybrid, to reduce carbon emissions and meet environmental regulations. Lastly, a cloud-based platform would enable one to keep data accessible and facilitate collaboration, thus supporting their ability to track resources with all stakeholders.
Reference Sources
1. RFID-Based Vehicle Toll Collection System for Toll Roads (2021)
2. Automatic Vehicle Fueling System Using PLC-Controlled Robotic Arm (2024)
3. Fleet Management IoT (2023)
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Describe the RFID bleeding-fuel management system.
An RFID fuel management system is a sort of hardware and software application meant to automate the processing related to the tracking and management of fuel transactions in different areas of the world. Radio-frequency identification technology provides real-time tracking of fuel usage for an entire fleet of vehicles or machines. By working with RFID tags integrated with fuel dispensers, the system registers fuel transactions and monitors fuel levels so as to manage fuel security.
How can RFID improve fuel management?
The RFID provides each fuel nozzle and vehicle with a unique identification number. It allows the system to accurately capture data relating to fuel transactions and, thereby, greatly reduce any possible human intervention. Using RF channel(s), the RFID system transmits data back to the central database concerning fuel consumption with significant levels of detail, enabling efficient tracking of fuel consumption across multiple locations, such as ports or fuel depots.
What are the benefits of using RFID for fuel tracking?
When using RFID for fuel tracking, users benefit from higher accuracy for recording fuel transactions, tracking fuel level status in real time, and withstanding adverse environmental conditions. Other benefits include automated data collection to minimize manual data entry, increasing operational efficiency and hence better fuel management, reduction of wastage, and operator safety.
Can the RFID fuel management system track a number of different fuel types?
Yes, the RFID fuel management systems are capable of tracking various types of fuel such as diesel, gasoline, or alternative fuels. Having each fuel filler equipped with an RFID tag lets the system know exactly which fuel type is being dispensed, making sure that the right type of fuel is used for each machine or vehicle. This is important to maintain fuel quality and, thus, optimize fleet performance.
How does RFID provide real-time fuel tracking?
Real-time tracking is rendered in RFID systems through the use of an arrangement of RFID tags installed on or near fuel dispensers and other attributes in the vehicle and roadside. When fuel is dispensed, the RFID system records the transaction details that include the amount dispensed, the time of transaction, and the vehicle’s side RFID identification of the transaction. This information is then transmitted wirelessly to the dashboard or to a central database for immediate access by management for purposes of analysis and reporting.
How important is the fuel nozzle for RFID fuel management?
Since RFID fuel management is a process of fueling a vehicle or machinery, the fuel nozzle is an important point in this system. If it is properly equipped with RFID technology, it would be possible for the system to register fuel transactions accurately and transmit them to the fleet management system. This would mean that every single transaction is recorded, and reports about the consumption and efficiencies of fuel will be compiled from this data.
In what manner are RFID fuel management systems expected to enhance fleet efficiency?
By automating fuel tracking and providing real-time fuel consumption data, RFID fuel management systems greatly increase fleet potential. Capturing extensive details from an onboard diagnostic (OBD) system embedded in the fleet’s vehicles enables the system to analyze fuel consumption and suggest measures for route optimization and idle time reduction, which directly contribute to improved fuel management, cost savings, and overall service enhancement for the fleet.
Why is data capture important in RFID fuel management?
Buffer data is important to fuel management in RFID because it allows for the precise tracking of fuel transactions and consumption. By maintaining track of the information included with each fuel dispense, the system could generate reports to help in recognizing trends, identifying irregularities, and addressing concerns related to fuel theft or waste. This information promotes improved decision-making fuels benefits, and, above all, encourages better fuel management practices among the fleet.







