Moving fluids at the right proficiency and speed involves a transfer pump, which has become an integral element in several industries and applications. Whether it’s water, fuel, chemicals, or any other fluid, understanding how a transfer pump works and its distinct advantages will help you make an informed choice for your specific needs. This article examines how transfer pumps function, their purpose, and the advantages that make them essential in numerous applications. Whether you are a practitioner in this field or simply interested in learning about transfer pumps, get ready to explore everything about this remarkable equipment.
Introduction to Transfer Pumps
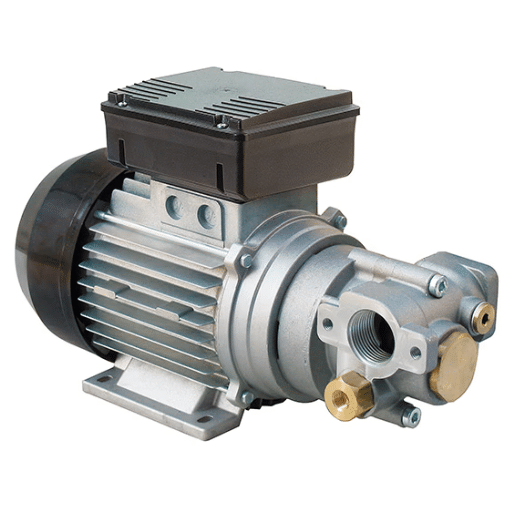
A transfer pump encompasses devices built for the forceful movement of liquids from one point to another. They find use in a variety of industries where liquids, such as water, fuel, or chemicals, need to be transferred. They work by creating pressure to either push or pull liquids along with their connected hoses or pipes, ensuring their speedy and fruitful transfer. Their importance can be viewed from the point of view of saving time; reducing.
What is a Transfer Pump?
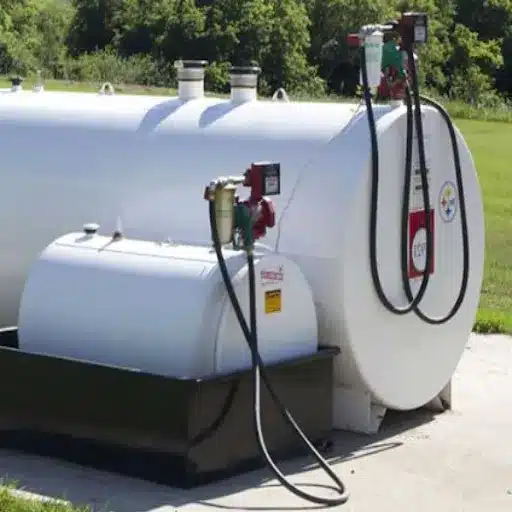
A transfer pump is a general category of mechanical equipment that efficiently and reliably moves liquid from one point to another. These pumps find application in areas where water, fuel, oil, chemicals, and other fluids need to be transferred from homes, through commercial establishments, and up to industrial uses. They work by creating pressure inside the liquid, forcing it to flow through connected pipes or hoses in a harmonious and controlled manner. Transfer pumps are highly versatile, available in manual, electric, or gas-powered models, with selection criteria varying according to application and corresponding requirements. The chief benefits of transfer pumps are saving time, reducing physical effort, and accurately and safely handling fluids.
How Do Transfer Pumps Work?
Transfer pumps essentially work by applying mechanical action to displace liquid from one place to another. Usually, this involves creating a pressure difference that sucks the liquid into the inlet and pushes it out of the outlet. Transfer pumps employ various mechanisms, including centrifugal, diaphragm, or positive displacement, depending on their specific design and application.
Key Operating Mechanisms:
- Diaphragm Pumps: Work on a reciprocating motion to draw and discharge liquid, suitable for high viscosity or chemically aggressive fluids
- Centrifugal Pumps: Use rotational impellers to create a vortex that pulls fluid outward, ideal for high flow rate and low viscosity fluids like water or light oils
- Positive Displacement Pumps: Such as gear or rotary vane pumps, displace a fixed volume of liquid with each cycle, suitable for dosing or high-viscosity liquids
Transfer pumps have evolved and further improved their capabilities through advancements in material and design. Such advancements include the application of corrosion-resistant materials, such as stainless steel and high-grade plastics, to provide durability, enabling the pumps to handle harsher chemicals. From an efficiency and accuracy perspective, more sophisticated developments, such as electronic flow control and pressure monitoring systems, are now available to enhance accuracy beyond manual control, even in complex industrial processes.
Regarding the efficiency of transfer pump types, centrifugal pumps are capable of achieving flow rates of several thousand gallons per minute, depending on their size and configuration, making them highly useful in applications such as irrigation and water treatment. Diaphragm pumps, on the other hand, are typically used in applications where chemical compatibility and leak-proof operation are of utmost importance, such as in pharmaceutical or agricultural settings. Selecting an appropriate type of transfer pump is crucial for achieving proper performance and maintaining the highest quality of the transferred liquid.
Importance of Transfer Pumps in Fuel Management
As such, transfer pumps play an instrumental role in the efficient and safe management of fuels in industries such as transportation, agriculture, and construction. They must ensure an exact and legitimate transfer of fuel from storage tanks to equipment or vehicles, preventing spillage and contamination. Recent industry data indicate that improper handling or inefficient fuel transfer mechanisms can lead to significant losses, with some studies suggesting that approximately 5% of fuel is lost annually due to leakages, evaporation, or mishandling during transfer.
Industry Impact:
Equipped with features such as automatic shut-off, flow rate control, and the ability to handle various types of fuel, including diesel, petrol, and biodiesel, transfer pumps are substantially advanced today. High-performance pumps with flow rates of 30-50 gallons per minute considerably reduce downtime, thereby increasing production efficiency.
Moreover, the use of explosive-proof design and corrosion-resistant materials in pump construction, along with other modern pump innovations, provides additional safety benefits when handling volatile or hazardous fuels.
Such fuel management systems, with the best possible transfer pumps installed, offer a significant opportunity for cost savings and environmental conservation. Accurately metering fuel usage and preventing waste, these systems lower operational costs and carbon footprints, which is a larger endeavor worldwide to promote energy efficiency. Besides the obvious use of such systems, sectors that require precise fuel transfer processes, such as the aviation and marine industries, would primarily rely on these reliable pump systems due to regulatory compliance requirements. Hence, the transfer pumps have gained significance in the modern and contemporary approach to fuel management.
Types of Transfer Pumps

Transfer pumps are classified according to their construction and the method of application. The common types are:
| Pump Type | Operating Principle | Best Applications | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| Centrifugal Pumps | Using rotational energy to move fluids | Transferring bulk fluids under relatively low pressure | High flow rates, simple operation |
| Diaphragm Pumps | Reciprocating motion for precise transfers | Various liquids, including higher viscosities | Accurate, handles corrosive fluids |
| Gear Pumps | Mechanical gear displacement | Pumping oils and viscous substances | Industrial applications, consistent flow |
| Peristaltic Pumps | Compressing flexible tubing | Sensitive or delicate liquids | No contamination, gentle handling |
All types of pumps have characteristics tailored to the specific needs of a particular application, enabling them to carry out reliable and efficient fuel and fluid transfer.
Different Types of Transfer Pumps
Transfer pumps are versatile tools with a broad spectrum of applications, and understanding their advantages helps to make informed decisions about which type is suitable for a particular purpose. Let’s look at how each works and the best application for it:
Centrifugal Pumps
They have been used for water-fuel transfer for many years due to their simplicity and efficiency. It deals with large volumes of low-viscosity liquids and most commonly acts in homes, commercial places, and industries.
Diaphragm Pumps
Able to handle liquids with low and high viscosities, diaphragm pumps are commonly used in chemical process plants, oil transfer, and wastewater treatment. These pumps are of prime importance when corrosive or abrasive fluids are involved.
Gear Pumps
Convert oil, fuel, or any other viscous material with the utmost efficiency. Robust construction and steady operation bring in high demand in industries for hydraulic systems and lubrication applications.
Peristaltic Pumps
Suitable for shear-sensitive or delicate fluids. They find applications in medical devices, food and beverage processing, and chemical dosing that require ensuring the fluid remains uncontaminated.
Each transfer pump type targets various characteristics required for optimal performance in industries under different conditions. Choosing the pump that will best satisfy the fluid viscosity, application environment, and transfer rate requirements is vital.
Manual Pumps vs. Electric Pumps
Manual Pumps – Advantages
- Low initial costs
- Minimal operation/maintenance costs
- Highly portable
- Perfect for off-grid or remote areas
- Simple operation
- No power supply required
Manual Pumps – Limitations
- Cannot handle continuous operations
- Limited to small volumes
- Requires physical effort
- Lower flow rates
- Not suitable for high-pressure applications
When selecting between manual and electric pumps, their performance, efficiency, and suitability for specific applications must be considered. Manual pumps are well-suited for applications where portability is desired and/or simplicity is a priority. They are operated by hand or foot, acting as a suction force, and are thus suitable for small amounts of flow and/or pressure in small water transfers, agricultural applications, or backup systems.
Electric Pumps – Advantages
- Handle high-volume tasks efficiently
- Standard flow rate consistency
- Can achieve thousands of gallons per minute
- Greater accuracy and automation possibilities
- Suitable for industrial processes
- Continuous operation capability
Electric Pumps – Limitations
- Higher initial costs
- Increased maintenance costs
- Requires a stable power supply
- Less portable than manual options
- More complex operation
However, electric pumps can handle high-volume and high-pressure tasks more efficiently. Working either by electricity or battery, they ensure a standard flow rate; hence, these pumps find applications in industrial processes, irrigation systems, and large-scale water transfers, among others. These are somewhat complementary pump types, with at times fully competing fields of application. For manual pumps, the overriding factors are cost and simplicity in smaller applications; for electric pumps, it is efficiency and scalability for high-demand operations. Deciding factors will be based on specific needs from the applications, cost, and availability of power resources.
Specialized Fuel Transfer Pumps
The fuel transfer pumps are typically specialized and designed to meet the unique requirements of industrial and commercial applications, ensuring that fuel is transported efficiently and safely in challenging environments. These pumps typically feature explosion-proof motors, corrosion-resistant materials, and advanced controls that can handle a variety of fuel types, including diesel, gasoline, and biofuels.
High-Volume Pumps
Among the more common high-volume pumps are those pumping fuel at rates above 100 gallons per minute (GPM), which are hence necessary for large-scale operations such as refueling aircraft, ships, or construction equipment. Centrifugal pumps, for example, are commonly used in the industry to handle large volumes of fuel with very little energy input.
Portable Fuel Transfer Pumps
Working portable fuel transfer pumps offer increased portability, often powered by battery or hand crank for use in remote locations. Their features may include an automatic shut-off, contamination filtration, and spill prevention from transfer.
Environmental Compliance
In the investigation of environmental APIs, many specialized pumps are now designed by regulations, which results in fewer emissions and leakages during fuel transfer. This not only ensures safety during operation but also helps companies realize their sustainability goals within fuel-based industries.
Using a Transfer Pump

For any transfer pump to work, first ensure that it is suited for the particular liquids being transferred. Connect the proper hoses to the pump and tighten them securely to avoid any leakage. Place the intake hose into the source container, and the output hose into the receiving container. Follow all instructions provided by the manufacturer regarding the safe operation of the pump, including the manual, electrical components, and any other relevant information. Stay closely involved in the entire transfer process to prevent overflows, and always double-check for proper shutdown after use. Clean the pump and hoses as needed to maintain efficiency and avoid contamination.
How to Choose the Right Fuel Transfer Pump
Choosing the right fuel transfer pump is crucial for meeting your specific needs, ensuring efficiency, safety, and compatibility. Here are some significant considerations and aspects to consider:
Key Selection Criteria
1. Type of Fuel
Various pumps are compatible with different kinds of fuel, including gasoline, diesel, kerosene, and biofuels. For instance, diesel transfer pumps are typically constructed with heavier materials better to withstand the viscosity and requirements of diesel fuel.
2. Flow Rate
Measured primarily in gallons per minute (GPM), the flow rate indicates how quickly a pump can deliver fuel. For small-scale use, pumps with a flow rate of anywhere from 5 to 15 GPM are preferred. At the industrial or commercial level, a larger flow rate, ranging from 15 to 50 GPM, is necessary to handle large-scale volumes.
3. Power Source
The pump may be specified differently, depending on the power source available to you. Common types include manual pumps, battery-powered pumps, electric pumps (operating on AC or DC power), and engine-driven pumps. Any power source, whether battery or manual, is more suitable for use in remote areas where electricity may not be available.
4. Pump Material and Durability
Verify that the pump material is resistant to corrosion and compatible with the type of fuel being transferred. Aluminum or stainless steel is used to make a durable product. Seals and gaskets should be resistant to the properties of the fuel.
5. Portability and Installation
The pump options offer lightweight and portable mounting abilities for mobile performance. On the contrary, stationary systems are better suited for permanent installations, such as those found at fuel stations or industrial setups.
6. Additional Features
Some of the modern pumps feature an automatic shut-off nozzle, an anti-drip design, a filtration system, or a flow meter for accurate fuel dispensing. These features enhance the ease of use and minimize the risk of spills or contamination.
By assessing these details and the operation’s requirements, one can select a fuel transfer pump that meets their needs, ensuring smooth and secure fuel handling.
Steps to Use a Transfer Pump Safely
- 1Read the Manufacturer’s Manual: Before using the pump, read the user manual thoroughly. This preparation makes one aware of the safety instructions, limitations, and usual operating procedures associated with that particular equipment.
- Inspect the Pump and Components: Verify that the pump and its accessories exhibit no signs of damage, wear, or leaks. Ensuring everything is securely fastened and properly set up before use can prevent issues from arising or spills during operations.
- 3Location Selection: Place the pump on firm, stable ground, away from any flammable substances or sources of ignition, such as open flames. The work area should have sufficient ventilation to provide egress from harmful fumes.
- 4Safety Gear: Use protective gear, such as gloves, goggles, and non-slip shoes, to safeguard against potential hazards and exposure to harmful substances.
- 5Proper Filling Procedure: From the side of the transfer pump, secure the hoses to the inlet/outlet ports tightly, ensuring no leakage is possible. The transfer operation should always follow capacity, which is particularly important during tank filling. This involves transferring liquid with the correct capacity and directing it correctly. Otherwise, any spills might occur.
- 6At the Transfer Process: Nearby supervision of the entire fuel transfer process is almost a must. Do not overfill tanks. Once the transfer is complete, immediately turn off the pump from the controls.
- 7Clean and Store: Cleaning the pump, along with its related components, after use is essential to prevent contamination or corrosion. Store it in a dry, safe place, away from areas with extreme temperatures or direct sunlight exposure.
By following these steps, you can ensure the safe, efficient, and reliable operation of your fuel transfer pump.
Transferring Fuel: Best Practices
Essential Best Practices:
- Ensure equipment compatibility with fuel type
- Use grounding and bonding connections to prevent static electricity
- Secure all hoses, connections, and fittings before starting
- Monitor transfers closely to prevent overfilling
- Maintain proper ventilation during operations
- Clean equipment thoroughly after use
- Inspect for damage or wear regularly
Safety and efficiency come first during fuel transfers. Ensure the equipment being used is suitable for the type of fuel being transferred to prevent any accident or damage to the equipment. Grounding and bonding connections should be used to prevent the generation of static electricity. Before starting the transfer, ensure that all hoses, connections, and fittings are securely in place.
The fuel transfer should be monitored closely to prevent overfilling or spills; therefore, the pump should be stopped immediately if necessary. During the transfer process, especially when handling flammable fuel, ventilation should be maintained to prevent the danger of vapor accumulation. Once the transfer is complete, clean the equipment thoroughly before inspecting it for any damage or wear. Proper servicing and storage of equipment will ensure long-term reliability and safety.
Consistently following these best practices will enable one to minimize risks, work within established standards, and conduct safe fuel transfer operations.
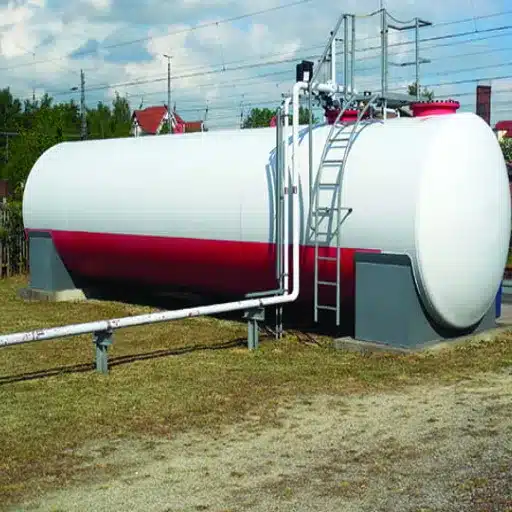
Diesel Transfer Pumps

Diesel transfer pumps serve the purpose of transferring diesel fuel safely and efficiently from one container to another. These pumps have multiple applications in various industries, including agriculture, construction, and transportation. Some key factors to consider when selecting a diesel transfer pump include the flow rate, power source (manual, electric, or engine-driven), and, of course, the type of diesel fuel used. The pump must meet safety and quality standards to ensure a dependable and secure operation.
What is a Diesel Transfer Pump?
A diesel transfer pump refers to a specialized piece of equipment primarily used for the efficient transfer of diesel fuel from one source to another, typically from a storage tank to another piece of machinery or a vehicle. It is an essential piece of equipment for industries that utilize diesel-powered instrumentation in their processes, ensuring fuel flows smoothly into operations.
Nowadays, these diesel transfer pumps come in various designs, ranging from manual hand pumps to electric and engine-driven models. The pumps vary with their flow capacities, which are typically expressed in gallons per minute (GPM) or liters per minute (LPM). To cater to various applications, the generally used pumps can transfer at rates ranging from nearly 10 to 100 GPM. It is said that electric-powered diesel transfer pumps are favored, as they move quickly and are easy to operate, while manual ones seem to be better suited for smaller volumes and storage settings.
Other things which can be considered are compatibility between the pump and diesel fuel materials, like corrosion-resistant metals and seals, whether some materials can deteriorate by reacting to diesel over time, and some advanced features may even incorporate automatic shut-off, in-line filtration to keep out contaminants, and explosion-proof certifications for safe operations in hazardous environments.
Diesel transfer pumps have a wide range of applications in agriculture for refueling tractors and other heavy-duty machinery, in construction for providing a consistent diesel supply to power machinery, and in the transport sector for refueling fleet vehicles. When opting for a design best-suited for the specific application, operators are assured of safe, rapid, and efficient fuel transfers with minimal downtime and reduced potential for fuel wastage.
Applications of Diesel Transfer Pumps
Diesel transfer pumps are necessary in various industries because they allow the safe and efficient transfer of fuel. Here are some of the key applications and descriptions of the advantages and working principles:
| Industry | Applications | Key Benefits | Typical Flow Rate |
|---|---|---|---|
| Agriculture | Fueling tractors, harvesters, and irrigation pumps | Faster refueling, enhanced operational efficiency | Up to 150 L/min |
| Construction | Excavators, loaders, generators | Compact, portable, accurate metering | Variable based on equipment |
| Transportation | Fleet management, commercial freight | Automatic shut-off, fuel meters, cost control | 30-50 GPM typical |
| Mining | Heavy-duty vehicles, large equipment | Durable materials, harsh environment operation | High volume requirements |
| Marine | Fishing boats, barges, small craft | Saltwater corrosion resistance | Marine-specific rates |
The worldwide diesel transfer pump market has experienced steady growth, with the development of automatic nozzles, flow-rate control, and leak-proof designs advancing to state-of-the-art standards. These improvements not only enhanced the safety of operations but also expanded its range of applications. Matching the correct type of pump to the application can help the industry achieve high levels of efficiency, significantly decrease environmental impact, and substantially reduce operational costs.
Benefits of Using Diesel Fuel Transfer Pumps
Diesel fuel transfer pumps offer numerous benefits, and these pumps have proven essential in various industries, including agriculture, construction, and transportation. The primary advantage of a diesel transfer pump is its efficiency, as fuel is transferred quickly and safely, resulting in minimal downtime and maximized productivity. As an example of efficiency, diesel transfer pumps usually deliver high flow rates, with some capable of a whopping 15 GPM. With this rate of flow, large heavy equipment is refuelled just in time to start their operations.
Key Benefits Summary:
- Efficiency: High flow rates up to 15 GPM for quick refueling
- Safety: Automatic shut-off nozzles and leak prevention mechanisms
- Environmental: Reduced fuel wastage by approximately 20%
- Portability: Lightweight and compact designs
- Cost Savings: Optimal fuel use and waste prevention
- Precision: Real-time fuel measurement and dispensing accuracy
More importantly, the modern diesel transfer pumps are equipped with safety features such as automatic shut-off nozzles and leak prevention mechanisms. These features and innovations help prevent spills that could cause environmental contamination, aligning with conservation goals. The advancement of pump design has led to improved fuel management, allowing some pumps to reduce fuel wastage during transfers by approximately 20%.
Portability remains yet another advantage. Most of these pumps are light and compact and can be installed as either fixed or mobile units. For industries operating in remote locations, the portability feature gives diesel transfer pumps the advantage of providing a continuous means of fuel delivery.
Another reason for cost savings is the optimal use of fuel and the prevention of waste. Operators can check the measurement of fuel transfer in detail and in real-time, ensuring accurate fuel dispensing and avoiding unnecessary losses. Hence, diesel fuel transfer pumps are not only convenient options but also genuine economic solutions for demanding industrial needs.
Factors to Consider When Buying a Transfer Pump
Critical Selection Factors:
- Flow Rate: Match pump capacity to transfer requirements
- Compatibility: Ensure the pump can handle specific fluids
- Power Source: Consider electrical, battery, or mechanical power
- Durability: Choose rust-resistant, quality materials
- Portability: Evaluate weight and dimensions for mobility
- Safety Features: Look for automatic shut-off and pressure relief
Detailed Buying Considerations
Flow Rate
This consideration requires you to select a pump that meets your fuel transfer requirements. Pumps with a high flow rate are better suited for large volume transfers, whereas those with a low flow rate are more suitable for small, minute transfers.
Compatibility
It has to be a pump capable of handling the fuel or another liquid you want to transfer, and, quite logically, not every pump can handle every fluid type.
Power Source
Depending on the working situation, select the pump that operates on electrical, battery power, or another type of mechanical power.
Durability
Make sure the pump you choose is made from good-quality, rust-resistant material, so that it lasts long and is resistant to exposure to rough conditions.
Portability
If it is to be used in the field, then portability becomes an important criterion, meaning it must be lightweight. Any design with fewer dimensions would be highly beneficial for transportation and on-site use.
Safety
Look for pumps that possess safety features, such as automatic shut-off, pressure relief, or other mechanisms, which protect against leaks and ensure safe use.
Focusing on these critical factors should help in selecting a transfer pump that best fulfills their current needs and does so reliably.
Price of a Transfer Pump
Transfer pump prices can vary greatly depending on the type, capacity, and features they offer. Prices start at around $50 and can go up to $150 for small, portable pumps used primarily for household tasks. Mid-range transfer pumps, which cost between $150 and $500, are suitable for various medium-duty applications, such as elevating water or other liquids in agricultural or industrial settings. High-capacity, heavy-duty pumps cost more than $1,000 when used in heavy industrial or commercial applications, with some models exceeding $5,000 if advanced features such as electronic automatic controls or special materials with chemical resistance are specified.
| Price Range | Pump Type | Applications | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| $50 – $150 | Small, Portable Pumps | Household tasks, light-duty | Basic functionality, manual operation |
| $150 – $500 | Mid-Range Pumps | Agricultural, medium industrial | Electric operation, moderate flow rates |
| $1,000 – $5,000+ | Heavy-Duty Pumps | Industrial, commercial applications | Electronic controls, chemical resistance |
Price points are also influenced by the type of power the pump runs on—electric, gasoline, or manual—and, of course, the brand’s reputation, along with safety or efficiency features. Accessories, such as hoses or adapters, can make a considerable difference in cost, so it is prudent to consider all related costs when purchasing a transfer pump. Knowing the various prices and selecting the best based on your needs will give you an informed decision that weighs functionality against cost.
Quality and Reliability of Fuel Transfer Pumps
The following considerations merit attention when deciding on pump quality and reliability: durability, performance consistency, and ease of maintenance. Typically, high-quality pumps are made of strong materials, such as aluminum or stainless steel, to resist wear and corrosion. Reliable pumps typically feature motor efficiencies, leak-proof designs, and overheating protections, enabling them to operate optimally under varying conditions. Opinion polls and third-party certifications might offer insight into how well a pump stands the test of time. Additionally, performing regular maintenance routines, such as cleaning and inspections, significantly helps extend the pump’s lifespan and maintain its optimal working condition. Equipped with all these parameters, one can select that very fuel transfer pump that is reliable and of superior quality, thereby fulfilling their application needs.
Quality Indicators:
- Materials: Aluminum or stainless steel construction
- Motor Efficiency: Consistent performance under varying conditions
- Design Features: Leak-proof designs and overheating protection
- Certifications: Third-party testing and approval
- Maintenance: Easy cleaning and inspection capabilities
- Warranty: Comprehensive coverage and support
Choosing the Right Transfer Pump for Large Volumes
When selecting transfer pumps for large volumes of fluid, I tend to focus on a few vital factors. Primarily, the flow rate should be ensured to be adequate and can indeed get the job done smoothly within the set period. Then comes the quality of construction and compatibility with the fluids I intend to transfer, because these pumps should be durable and resistant to chemicals. There is also an emphasis on energy efficiency and ease of maintenance, as I strive to minimize operational costs. Considering all these aspects, I end up with a reliable and high-performing pump suited for my needs.
Large Volume Considerations:
- Flow Rate Adequacy: Ensure the pump can handle the required volume within the timeframe
- Construction Quality: Durable materials for long-term reliability
- Chemical Compatibility: Resistance to corrosive or aggressive fluids
- Energy Efficiency: Lower operational costs through efficient design
- Maintenance Ease: Simple servicing to minimize downtime
- Scalability: Ability to handle varying volume requirements
Conclusion
Transfer pumps are a critical component in modern industrial and commercial operations, providing efficient, safe, and reliable fluid handling solutions across various applications. From simple household tasks to complex industrial processes, understanding the different types, features, and selection criteria ensures optimal performance and value.
Key Takeaways:
Whether you’re managing fuel transfers in agriculture, handling chemicals in manufacturing, or simply moving water for irrigation, the proper transfer pump can significantly impact efficiency, safety, and cost-effectiveness. By carefully considering factors such as flow rate, compatibility, power source, and safety features, you can select a pump that meets your specific needs while ensuring reliable, long-term operation.
Investing in quality transfer pump equipment pays dividends through reduced downtime, improved safety, enhanced environmental compliance, and increased operational efficiency. As technology continues to advance, transfer pumps will only become more sophisticated, offering even greater precision, automation, and environmental benefits for users across all industries.
Reference Sources
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What does a transfer pump do?
The operational action done by a transfer pump includes fluid movement. Transfer pumps, therefore, transfer liquids such as water and diesel fuel from one place to another. A suction action is developed, whereby the liquid is drawn from a source, such as a storage tank, and pushed through the hose to the other side; this is a necessary action for refueling cars, moving liquid from one tank to another, or emptying a vessel.
How does a fuel transfer pump work?
The fuel transfer pump, which utilizes mechanical energy to generate suction and transport fuel, acts in reverse when dispensing. Those impulses drive a pump: the electric motor or manual operation impeller or gearing arrangement presses the fuel toward the nozzle or hose, whereby it is dispensed or transferred quickly and efficiently to its destination.
What are the different types of transfer pumps?
There are various types of transfer pumps available on the market, including electric, manual, and submersible. The electric pumps are powered by electricity and can transfer large quantities of liquids in a short time. Manual pumps are operated by hand and are suitable for small jobs. Submersible pumps work best when submerged inside a liquid while pumping it out from a well or tanks.
What is a diesel transfer pump?
Diesel transfer pumps are specifically designed for transferring diesel fuel. These pumps can be either electric or manual, depending on the specific application. They are designed to handle the viscosity and other characteristics of diesel fuel, allowing for efficient transfer without damaging the pump or contaminating the fuel.
How do pumps move fuel from one place to another?
Pumps create a pressure difference, allowing fuel to flow from one location to another. Various means achieve this, such as centrifugal force from an impeller and positive displacement from gears. A pump’s design largely determines its efficiency, flow rates, and appropriateness for different types of fuel, including gasoline and diesel.
How much does a transfer pump cost?
The cost of a transfer pump varies significantly based on its type, brand, and power rating. Manual pumps are generally less expensive, whereas electric or fuel transfer pumps can cost several thousand dollars, depending on their size and features. Price must be weighed against the boost in performance and quality.
Can transfer pumps transfer water?
Yes, several transfer pumps can transfer water and other types of liquids. It is crucial to ensure that the pump is designed for the specific liquid to be used. Some pumps are optimized for diesel fuel, while others are optimized for gasoline, but are not very effective for water. Always refer to the manufacturer’s specifications for accurate compatibility information.
What are manual pumps, and how are they operated?
Manual pumps are operated by hand, requiring physical effort to create suction and move the liquid. They are commonly used for smaller tasks, such as transferring fuel or water in limited quantities. Manual pumps are advantageous due to their portability and simplicity, making them ideal for situations where electricity or large equipment is unavailable.







