The very act of dispensing fuel has been an essential part of the transportation and logistics sectors for generations. There have been risks of inefficiencies, delays, or lack of precision in the fuel-giving methods used today. To restore effective fuel management and delivery, an automated fuel dispensing system enters the scene. The systems, in a nutshell, automate processes to make them easier for both businesses and consumers. Fewer errors, greater efficiency. This article will guide the reader through the key characteristics of automated systems, their advantages, and why they are emerging as the current gold standard in fuel distribution systems. Whether you are interested in the productivity advantages, environmental benefits, or cost-saving opportunities, this blog will shed light on the future of fuel management.
Introduction to Automated Fuel Dispensing Systems

Automated fuel dispensing systems are high-end technology developed for a more streamlined fuel distribution procedure. These systems operate with the assistance of computerized controls and real-time monitoring, ensuring that fuel is dispensed with precision and with minimal human intervention. They provide the efficient operation of the systems by preventing errors, for instance, by tracking fuel usage and ensuring that overdispensing does not occur. These systems enjoy popularity among businesses and fueling stations for their cost control and environmental benefits, featuring features such as leak detection and precise fuel tracking. They stand as one of the most reliable and user-friendly solutions available today.
What is an Automated Fuel Dispensing System?
From the perspective of fuel management, automation of dispensing involves systems that integrate technology. The system utilizes electronic control components and astute card readers, operating in conjunction with a common database to automate the fueling process. Some of their attributes include real-time data tracking to monitor fuel consumption or inventory levels, and access control using PIN or RFID cards to restrict fuel dispensing to authorized users only. Currently, some systems are also integrated with a telematics solution to give further insight into vehicular fuel efficiency and performance.
Industry Impact: Recent statistics indicate an increasing industrial adoption of automated fuel dispensing systems. For instance, in markets where these computerized systems are used, fuel wastage has been reported to be controlled by up to 30 percent. Additionally, studies also highlight their role in environmental sustainability as some facilities are equipped with vapor recovery systems to curb emissions during refueling.
Automated Fuel Dispensing Systems increase efficiency and support sustainability goals, and hence become an essential component of modern motor transport, logistics, and retail fuel outlets.
History of Fuel Dispensing Automation
Early 20th Century
The advancement of fuel dispensing automation dates back to the early 20th century, when the first hand-operated fuel pumps replaced manual fuel transfer techniques to promote efficiency and safety.
1930s
By the 1930s, metered fuel pumps were introduced, providing accuracy by measuring the amount of fuel being dispensed. These advances were the beasts leaping from the nursery into an industry that was further developed.
1970s
The 1970s witnessed significant advancements in the integration of electronic components within fuel-dispensing systems. The automation processes were beginning to develop for more accurate control of the fuel by the operators.
1980s
Over time, in the 1980s, self-service stations gained momentum with the aid of card payment and computer-controlled pump systems. These factors, in themselves, went a long way to cutting down on labor costs and also provided convenience to customers.
21st Century
With the arrival of the 21st century, considerable emphasis has been placed on integrating digital technologies, including IoT-enabled systems and cloud-based platforms. Being a combination of such technologies, these systems allow remote monitoring and carry advanced analytics to optimize inventories and operations in fuel handling. For example, by 2022, studies on the advancement of automated systems indicated that real-time tracking could achieve dispensing accuracy of nearly 99%, thereby significantly reducing fuel loss and cost.
Another rationale for innovation is its contribution to sustainability. Environmental concerns are taken into account when designing automated fuel dispensing systems, including the use of AI to control vapor recovery and emission reduction processes. Some of these systems are further equipped with components powered by renewable energy, ensuring co-existence with nature.
Over the years, fuel dispensing automation has supposedly evolved from a mechanical tool to a system that secures efficiency, accuracy, and sustainability as a vital component of modern energy infrastructure.
Importance of Automation in Fuel Dispensing
Automation in fuel dispensing has been a game-changer in the energy industry, as it has increased operational effectiveness while reducing waste and prioritizing fuel management aspects with precision. Today’s highly automated systems provide an ingenious set of technologies for fuel-level distribution, tracking, and payments, thereby reducing downtime in the production system and human error.
Market Growth: For instance, based on global market report data, the fuel management system market is expected to optimize demand for automated solutions from 2023 to 2028, with sales anticipated to compound annually at an average rate of 6% or higher.
With fuel being dispensed automatically, administering a fleet becomes simpler through the monitoring and tracking of fuel utilization in real-time, thereby providing control over consumption patterns. Moreover, integration with Internet of Things devices and cloud platforms has enabled the storage and analysis of massive datasets, resulting in a reduction in fuel and emission costs. In instances of seemingly irregular fuel dispensation or leakage, advanced systems can actually identify such events and rectify them, thereby preventing violations of safety and environmental compliance standards.
This level of automation guarantees a better customer experience, with swift and convenient functions being facilitated at the fuel stations. Self-service kiosks with digital payment solutions, contactless technologies, and loyalty program integrations enable customers to go cashless and save time, aligning with the changing lifestyles and evolving consumer expectations. Generally, automation in fuel dispensing is necessary to achieve sustainability, improve operational workflow, and serve as a high-tech solution to offer maximum customer satisfaction.
Components of an Automated Fuel Dispenser
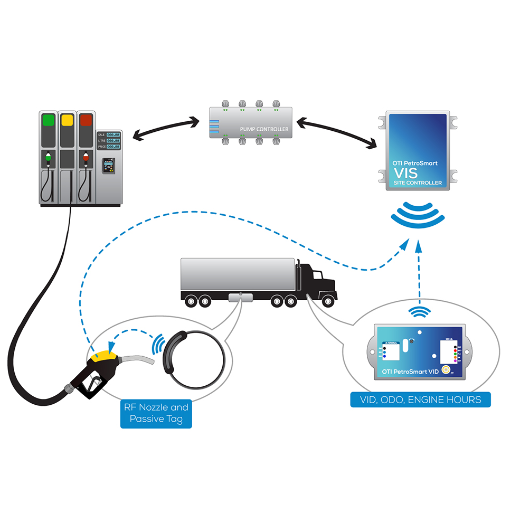
An automated fuel dispenser covers several key elements. Generally, it includes the dispenser itself, namely the pump and the nozzle, as well as an integrated digital payment system to facilitate transactions. There is also a central control system that controls the flow of fuel and stores data, as well as an interface screen that walks the customer through the steps. Lastly, many dispensers contain sensors that link to remote monitoring and maintenance options for efficiency and reliability.
Key Components of Automated Fuel Dispensers
Automated fuel dispensers comprise several integral parts designed for efficiency, accuracy, and user convenience. The main components would be:
| Component | Function | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| Pumping Unit | Draw fuel from underground storage tanks and pump it into the vehicle | Maintains steady flow rate and keeps exact measurements |
| Nozzle and Hose | Safely transfer fuel into the vehicle | Automatic shut-off mechanism prevents fuel spilling and overflowing |
| Metering System | Measure precise amount of fuel dispensed | Ensures accuracy in transactions |
| Payment Integration | Process digital payments | Card readers and contactless payments for secure transactions |
| User Interface | Guide customer through fueling process | Touchscreen or keypad displaying instructions, fuel prices, and transaction details |
| Control and Monitoring Systems | Regulate fuel flow and store transaction data | Support remote diagnostic procedures for real-time monitoring and maintenance |
| Safety Features | Safeguard installations and address emergencies | Sensors, actuated valves, and emergency shutdown systems |
Working together, these systems ensure that the entire process remains smooth and reliable, both from the customer’s perspective and that of the operator.
Technology Behind Fuel Dispensing Automation
Fuel dispensing automation is an advanced set of technologies that ensures precision, safety, and efficiency in the handling of fuel. Modern systems utilize embedded microprocessors and IoT technology to create an intelligent setup that enables real-time communication and data transfer. Digital sensors, for instance, monitor fuel flow rates with nearly perfect accuracy (approximately 0.5% of the volume dispensed), thereby ensuring that no fuel is lost and that all regulations are adhered to.
The other end of the automation system features a cloud-based connectivity option for centralized inventory control by the fuel stations. It can track fuel levels, analyze replenishment needs using AI-based algorithms, and provide dynamic monitoring insights to help prevent disruptions. Advanced payment systems are further integrated for contactless payment options via NFC technology, RFID tags, or mobile apps, thereby enhancing the customer experience while speeding up transactions.
Safety Performance: Additional information on safety: the area is being further secured with automatic shut-offs that take into consideration any leaks or irregularities. According to a study by the National Fire Protection Association, these modern sensors are so efficient in limiting the potential for fire that they can initiate a response within milliseconds.
These also help enhance safety measures, allowing them to be incorporated into maintenance schedules through predictive diagnostics, thereby decreasing downtime and associated costs.
Thus, with the establishment of all these technologies, the fuel dispensing infrastructures have become resilient for today and tomorrow.
Safety Features in Automated Fuel Dispensing Systems
With these advanced safety features, automated fuel dispensing systems were given to ensure security and reliability while fueling. One of the important ones is the flame and leak detectors, which can detect hazards within milliseconds, thus averting disaster.
Detection Capability: Industry sources indicate that modern leak detection systems can detect leaks that allow 0.05 gallons per hour before they are contained in time.
Another significant safety feature enhancement can be seen in emergency shut-off valves and pressure-sensing technologies, whereby unusual pressure differentials or emergencies capable of stopping fuel flow immediately provide protection for the environment and users. Additionally, enhanced data encryption in payment systems safeguards customer information from security breaches, aligning with the ever-increasing cybersecurity standards.
Additionally, from a real-time monitoring and IoT perspective, automated fuel systems make it possible to supervise potential safety issues remotely. An alarm or alert can be generated when an incident, such as overfilling, equipment failure, or unauthorized access, might have occurred, allowing for a timely response. This type of observation has been instrumental in reducing environmental incidents related to fuel handling.
Along with these features, by incorporating advanced predictive maintenance, an automated fuel dispensing system provides a secure and smooth experience while adhering to stringent safety guidelines. These improvements are a testament to the industry’s resolve to tackle new-age challenges and maintain a good reputation with customers.
Benefits of Using Automated Fuel Dispensing Systems

Enhanced Efficiency
The installation and implementation of an automated system expedite the fueling process and ensure a shorter waiting period for customers.
Improved Accuracy
The system holds errors to a minimum in the measurement of fuel and the processing of transactions.
Safety and Security
These are further enhanced with an emphasis on safety requirements so that accidents are impossible to happen, and the payment system is secure, through which the customer’s credit information is protected.
Cost Savings
Operating costs being lower and less petroleum being wasted are the two most significant savings for businesses.
Environmental Protection
Advanced monitoring reduced fuel spills and ecological impact, which is performed in the interest of sustainability efforts.
Improved Efficiency and Speed of Fuel Dispense
Modern fuel dispensing systems have become efficient and fast enough so that businesses that are handling large volumes can afford minimum delays and operational hassles. The latest technological developments utilize advanced pump automation, better-calibrated flow meters, and precision calibration to dispense fuel into vehicles quickly and accurately. Consider the high-speed dispensers that allow commercial vehicles to be fueled at a rate of 40-50 gallons per minute; this has certainly reduced refueling times for fleet operators.
Other technological developments include remote monitoring and centralized control systems, which enable real-time monitoring of fuel levels and pump performance, thereby preventing extended downtime due to maintenance or equipment faults. Then, again, the latest flow control technologies save time on application by ensuring a steady and uninterrupted fuel flow even amidst peak demand.
Operational Impact: Industry research suggests that upgrades to the fuel dispensing infrastructure may have resulted in operational efficiencies of up to 30%, directly affecting customer satisfaction and throughput rates.
Therefore, these enhancements provide a better refueling experience for customers while offering more efficient utilization for station operators, thereby sustaining long-term business growth.
Cost Savings and Reduced Labor Needs
The installation of the most modern fuel dispensation technologies offers numerous cost advantages and savings by simplifying operations and reducing overhead. Automated systems employing advanced analytics can continually monitor fuel levels, predict maintenance needs, or control inventory to the last unit, all without any human intervention.
Labor Cost Reduction: In other words, a market report cited that through automation, labor costs have diminished by 20% in fuel stations and agencies, as routine activities such as inventory tracking and pump management now require less human presence.
Furthermore, these dispensing units conserve electricity, thereby reducing operational costs over time. For instance, by implementing innovative energy management systems, a station operator could save up to 15% on annual utility expenses. Beyond improving efficiencies, these new technologies enable businesses to deploy resources more effectively, thereby making them more profitable while maintaining high service standards.
Enhanced Accuracy and Reduced Human Error
Advanced technology, including automated systems and artificial intelligence, has been integrated across various industries to enhance operational accuracy and reduce human error. Studies suggest that with AI-powered solutions handling monotonous tasks, an organization can reduce errors by up to 25% compared to manual processes. For example, automated fuel dispensing systems coupled with real-time monitoring systems and digital analytics accurately measure and compute to prevent discrepancies, thereby building customer trust.
Another layer of accuracy is provided by modern inventory management software, which keeps track of stock levels and demand trends through the use of machine learning algorithms. Such systems are said to increase inventory accuracy by as much as 30%, thus limiting overstocking and stockouts. Through predictive analytics, potential operational issues can also be foreseen and addressed before they hinder work-flow learning and decision-making processes. Hence, more successful with advanced technology transformation and increasing reliability-building, even by establishing more error-free structures.
Challenges and Considerations in Implementation

Implementing advanced technologies, such as machine learning and predictive analytics, introduces several challenges. One common hurdle is the required high initial investment for procuring and integrating these systems with existing processes. Organizations struggle to procure the necessary expertise, as these professionals are highly sought after. Additionally, inconsistencies in the data cannot be tolerated; poor or incomplete data can result in inaccurate predictions and inefficiency. Aside from these, businesses need to address data security issues, as their increased reliance on these technologies has heightened their exposure to breaches. When planned, trained, and implemented in stages effectively, however, these are the very factors that ease transition and enhance the overall benefits of the state-of-the-art systems.
Common Challenges in Automating Fuel Dispensing
The challenges in automating fuel-dispensing systems are numerous, and businesses must ensure that they have been mitigated to streamline operations and offer customers a better experience.
Integration Issues
One major stumbling block in automation is integrating the new dispensing systems into an already existing infrastructure. The incompatibility of legacy systems may necessitate an upgrade at a substantial cost or provide customized solutions to facilitate proper data exchange and operational synchronization.
High Implementation Costs
The initial setup costs for automated fuel systems can be substantial. These include hardware and software installations, as well as staff training. According to industry reports, the average price of installing a state-of-the-art automated fuel dispensing system ranges between $50,000 and $100,000, depending on the scale of the refueling station and the complexity of the installation.
Data Network Reliability
An automated system would always need the right kind of internet and data system. Even intermittent issues with connectivity or downtime would affect operations, thereby creating delays or disappointing customers. Furthermore, rural or remote fuel stations may face additional challenges in maintaining consistent network performance.
Cybersecurity Concerns
With more digitalization in fuel dispensing, systems are more prone to cyberattacks and data breaches. Protecting the privacy of customers and transactional data is paramount, making it crucial to have a solid cybersecurity infrastructure and conduct regular security audits to safeguard operations.
Maintenance and Downtime
With regular maintenance, automatic dispensing systems and their software ensure the smooth operation of the dispensing Process. Any downtime due to faulty equipment or delayed support would result in revenue and customer losses.
Customer Adaptation
While automation improves efficiency, not all customers may find the transition to automated processes seamless. Resistance to change among certain customer demographics, such as elderly users, can create bottlenecks at automated gasoline pump outlets, necessitating easy-to-use interfaces and support services.
When such shortcomings are addressed upfront with proper planning, up-to-date security provisions, and customer education initiatives, the obstacles will be cleared for the industries, enabling them to enjoy the full benefits of these automated fuel dispensing technologies.
Regulatory Compliance and Standards
Regulatory compliance and industry standards play a significant role in the implementation of automated fuel dispensing technologies. Governments and regulatory authorities develop guidelines to ensure the safety of individuals, the environment, and the operation of such systems. Thus, NIST provides regulations in the United States regarding measuring standards of fuel dispensers to ensure transparency in trade for the consumers.
Then, there is compliance with environmental standards, as the aim of almost every country is to minimize carbon footprint and improve air quality. In this ambition, fuel dispensers may need to comply with emission control standards, such as those enacted by the Environmental Protection Agency in the U.S., to reduce fuel vapor emissions during dispensing.
Gone are the days when standard practices and guidelines were sufficient. Now, with the integration of digital payments, standards such as the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI-DSS) are adhered to in order to protect customer data and prevent security breaches.
Strict fuel-related standards, however, prevail worldwide in the European Union under directives such as the ATEX Directive, which regulates the safe operation of equipment in explosive atmospheres. Businesses must be very careful to comply with these requirements. Non-compliance could result in penalties or operational losses, including task delays.
To remain competitive in the market and secure the innovation of automated fuel dispensing technologies, companies must continually update their systems as regulations change, partner with certified manufacturers, and perform regular auditing and maintenance to remain compliant with all international and regional standards.
Maintenance and Technical Support for Automated Systems
Maintenance and technical support are essential for making an automated system reliable, functional, and safe to use, particularly in fuel dispensing operations. Periodic inspection of the system helps identify problems such as component wear and tear, software glitches, or calibration errors. Studies also reveal that the costs attributable to unplanned business downtime caused by system failures are estimated to reach thousands of dollars per hour, thus emphasizing the importance of preventive maintenance.
As far as technical support is concerned, it should offer remote diagnostics, real-time monitoring, and intervention whenever necessary. Another growing trend has emerged in predictive maintenance through data analytics, with sources suggesting that this approach can reduce maintenance costs by as much as 25% compared to reactive maintenance. In addition to these technical support activities, firmware and software updates should be implemented regularly to address cybersecurity vulnerabilities and enhance system performance.
Interaction with certified service providers offers the assurance that automated systems will be maintained as required by evolving industrial standards. By preparing a meticulous maintenance program that covers pumps, controllers, and user interfaces, one can ensure smooth operations without interruptions and enhance the system’s longevity. Businesses should also maintain a record of the maintenance performed, which will be helpful when subjected to regulatory inspections or audits.
With advanced maintenance combined with proactive technical support, less downtime results in increased operational efficiency, as well as improvements throughout the entire lifespan of automated systems.
Future Trends in Automated Fuel Dispensing

The future of automated fuel dispensing is focused on efficiency, convenience, and sustainability. Key trends include the emergence of digital payment modes for faster transaction processes and a smoother customer experience, incorporating contactless payments and mobile app-based payments. On the other hand, artificial intelligence and data analytics support efficient fuel management, enabling businesses to maintain accurate inventory and predict maintenance needs. More environmentally friendly applications of the same technology include the development of systems that work with alternative fuel sources, electric charging stations, and dispensing stations for hydrogen fuel. These technologies thus seek to stem consumer demands while promoting efficient operation and environmental preservation.
Advancements in Technology for Fuel Dispensing
The new systems, in a way, aim to increase speed, accuracy, and efficiency, while promoting sustainability. Dispensers now come with IoT systems that send real-time information about fuel levels, usage, and maintenance needs. This connectivity leads to lower downtime and optimal operations. Automation through machine learning has provided an excellent opportunity to refine the metering of fuel with precision further to avoid wastage, thus improving cost efficiency.
Another innovation towards sustainability and greener technologies is the design of dispensers for alternative fuels, including biofuels, hydrogen (H2), and electricity. Innovative payment systems enhance convenience by supporting contactless card payments and mobile app payments. These advancements collectively aim to overcome operational challenges and meet the growing demand for greener energy alternatives, all while providing enhanced customer service provisions.
Integration with Smart Technologies and IoT
The integration of innovative technologies and IoT has altered sustainability and energy approaches. I regard it as a shift because connected devices provide real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and efficient energy management. These technologies, if used correctly, can efficiently enhance operations, reduce waste, and enable seamless and personalized user experiences, thus supporting our drive toward a better, more sustainable future.
Environmental Considerations and Sustainability
Environmental considerations arise as the international community balances technology with ecological responsibility. Addressing these concerns involves reducing carbon footprints, conserving natural resources, and minimizing waste. IoT devices promote sustainability by enabling energy conservation practices, such as smart grids and connected home solutions, to optimize power consumption. Furthermore, through IoT, predictive analytics help reduce unnecessary energy consumption and prevent possible overuse of resources.
Sustainable development further supports the embrace of renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind energy. IoT integrations enable the seamless management and distribution of renewable energies, ensuring optimization and reducing fossil-fuel usage. Companies and individuals alike must consider the materials used in the production and give higher priority to recycling and reuse to prevent harm to the environment. By leveraging technology effectively, we can create a synergy between innovation and sustainability, offering the world a measure of relief for future generations.
Reference Sources
Automatic Vehicle Fueling System using PLC Controlled Robotic Arm
Fuel Cell Electric Vehicles (FCEV): Policy Advances to Enhance Commercial Success
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is an automated fuel dispensing system?
An automated fuel dispensing system (AFDS) is an innovative solution designed to streamline the vehicle fueling process at gas stations. Utilizing cutting-edge technology, these systems allow users to pump gas or petrol without the need for an attendant, providing a quicker and more efficient service. The system typically involves a fuel nozzle that connects to the vehicle’s gas tank, facilitating seamless fuel transfer.
Can I use an automated fuel dispenser for diesel fuel?
Yes, many automated fuel dispensing systems are designed to accommodate various types of fuel, including diesel. Users should ensure they select the correct fuel type at the pump to avoid any issues with fueling. The nozzle design may differ between petrol and diesel dispensers, ensuring that the proper fuel is pumped into the vehicle’s fuel tank.
What are the benefits of using an automated fuel dispensing system?
Using an automated fuel dispensing system offers several advantages, including reduced wait times at gas stations and the elimination of the need for an attendant. This system also enhances security through automated payment authorization processes. Additionally, the integration of high-quality submersible pumps ensures efficient fuel delivery, making the entire fueling experience more streamlined and user-friendly.
Are automated fuel dispensers safe to use?
Yes, automated fuel dispensers are designed with safety features to protect users and the environment. They often include automatic shut-off mechanisms to prevent overfilling and sophisticated electronics to monitor the fuel transfer process. Proper maintenance of the equipment is essential to ensure safety and operational efficiency at gas stations.
How do I troubleshoot issues with an automated fuel dispenser?
If you encounter issues while using an automated fuel dispenser, such as payment authorization failures or fuel not dispensing, it is advisable to check the instructions displayed on the pump. If the problem persists, it is recommended to contact the gas station attendant or customer service for assistance. They can help resolve any issues and ensure that the dispenser is functioning correctly.
Where can I find automated fuel dispensing systems?
Automated fuel dispensing systems are commonly found at gas stations in various locations, particularly in urban areas. They are becoming increasingly popular due to their efficiency and convenience. You can also find these systems installed at fleet fueling stations and commercial locations where multiple vehicles need to be refueled quickly.







