Generally speaking, filling up your vehicle’s gas tank is a simple procedure, but if you happen to experience slow fuel pumping, then the entire affair might turn into a hassle. This situation, which is not an isolated one, can be caused by a lot of things, such as equipment failures and issues with your car’s fuel system. Knowing what causes the problem would not only be a time-saving measure for the drivers but also a way to discover the need for maintenance of the vehicle early on. The present paper elaborates on the technical phenomena resulting in slow gas pumping, examines its downside in terms of efficiency and convenience, and proffers practical methods for resolving the issue effectively. If you are an anguished driver struggling with a pump that is too slow or a company trying to get the best out of fuel station performance, then this manual has the right information for you.
What is a Slow Gas Pump?

A slow gas pump is a term for a device that dispenses fuel, and it works at a very slow rate compared to the regular operation; thus, it is said to be slow. This problem can be caused by many reasons, such as a blocked fuel filter, a low-pressure situation in the fuel supply system, or defective parts inside the pump. Pumps that are slow to dispense fuel are a hassle for the drivers because they have to wait longer to get their cars fueled. Also, such a situation could be a sign that something mechanical or operational is not working properly, and the pump will have to be maintained.
Definition of Slow Pumping
When the best fuel dispensing system operates under its best flow rate, for some factors in the system that restrict it, slow pumping occurs. Some of the most frequent causes are blocked fuel filters that are completely or partially blocked and thus slow down fuel passage, and low pressure in the fuel supply line, which is usually caused by malfunctioning or worn-out pumps. Also, problems like vapor lock, which is a situation where fuel vaporization caused by too much heat disrupts the flow, and internal component failures, such as bad valves or nozzles, can make the situation worse. A proper diagnosis usually consists of a systematic inspection of these components, making sure the fuel system is clean, pressurized, and operating within specifications set by the manufacturer. Regular maintenance and monitoring of operational parameters are very important in preventing slow pumping from happening and keeping efficiency high.
Common Characteristics of Slow Gas Pumps
Slow gas pumps are usually described by a decrease in flow rate, which is usually perceived as longer refueling times than the maximum operational speeds. Among the main causes are obstacles in fuel filters or pipes that cut off the fuel flow and defective pump parts, like old or broken diaphragms and seals. On top of that, a lack of suction pressure due to air leaks in the piping system or incorrect storage tank ventilation can take a toll on performance. In addition, environmental conditions such as freezing temperatures may cause the fuel to become less fluid, thus the pump’s power is diminished. Constant checking and fast fixing of the problems are critical for achieving and maintaining the desired performance level.
Impact on Fuel Dispensers
Fuel dispensers are an essential part of the fuel transfer process, and if any of the systems linked to them have problems, it can lead to inefficiency of the whole operation. Problems such as the normal usage of critical components like diaphragms, seals, and nozzles can lead to bad dispenser performance and even fuel leaks. In high-demand situations, especially, air leaks and low suction pressure in the fueling system may cause erratic or cut-off fuel flows, which would then affect the precision of measuring and eventually, customer dissatisfaction. Furthermore, the extreme cold and hot outdoors might change the fuel’s viscosity, hence making the dispensing systems work harder, which may eventually lead to mechanical failures if not regularly maintained. Thus, regular maintenance procedures, such as the examination of pump parts, the piping system, and environmental controls, are of great significance in lessening these risks and in keeping the fuel dispensers functioning reliably.
How to Identify a Slow Pump
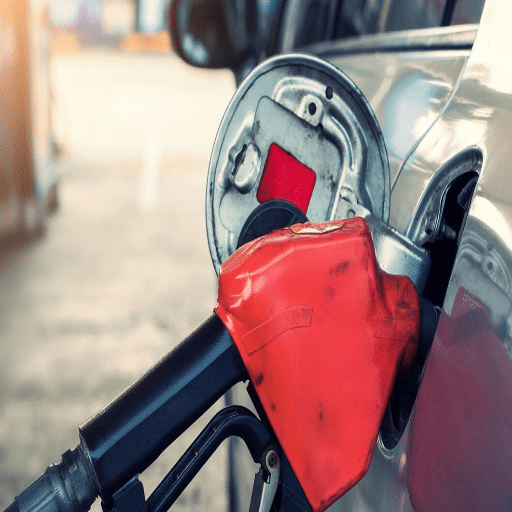
A slow pump can be detected by a noticeable reduction in the rate of fuel flow measured during dispensing. Keep track of the duration needed to dispense a certain amount of fuel and compare it with the normal operation. If customers complain about extremely long waiting times or partial fueling sessions, it could also be a sign of a slow pump. Look for possible reasons, including blocked filters, broken pump parts, or air stuck inside the system. Carrying out performance checks and timing tests on a regular basis is important for the early detection of these issues.
Signs of a Slow Gas Pump
The symptoms of a sluggish gas pump are associated with the entire process of fueling by customers and the efficiency in the service station. The expected pump flow rates that might be displayed could be the result of such maintenance issues as clogged filters or the natural wear of essential parts like the motor or valves. Moreover, the reduction in performance could be traced back to fuel lines having air blocks, which cut off the normal operations. The other sign is the customers’ saying that they had experienced longer-than-usual fueling times or partial fills; these are usually cases of mechanical or system blockages in the pump.
To fix these problems, first, check the fuel filters and the possibility of their clogging, as this is the most likely cause of restricted flow. If issues persist, assess the condition of the pumping mechanism, including seals and hoses, because old or damaged parts can enormously reduce performance. The routine maintenance, consisting of cleaning nozzles and checking for air leaks in the system, will help in preventing slow pump operation. Adhere to the service intervals recommended by the manufacturer to keep the unit in a proper working condition and minimize downtime.
Measuring Pumping Speed Accurately
In order to determine pumping speed with utmost accuracy, it is recommended to employ a methodical way that asserts reliability and accuracy. First of all, the right kind of vacuum gauge should be used, and it should be selected based on the pressure range the pump operates in. The gauge is then to be installed at the suitable measurement location, normally at the inlet of the pump, so that effective pumping speed readings can be taken. Leakages that lead to measurement inconsistencies by disrupting the airtight connections must be avoided; thus, it is important to ensure that the connections are airtight.
After that, the pumping process should be carried out under conditions that do not change, and the pressure readings obtained should be compared with the pump’s theoretically derived speed curve, which the manufacturer should have supplied. The difference between the theoretical pumping speed and the actual one is a good indicator of inefficiency. It is advised, however, to measure the speed at different locations within the system to be sure of the uniformity and point out any irregularities brought about by the system’s constraints or by the presence of impurities.
For more precise results, it would be wise to have in place a controlled environment that is totally and completely isolated from external variables like the changing of temperatures and the shaking of the equipment, since these could end up affecting the results. It is crucial to adhere to the highest industry practices, like those laid down by the ISO or PNEUROP guidelines that one’s experimental procedures are in place and correct. The most accurate measurements of pumping speed that can support performance optimization and system longevity will come from the combination of instrument regular calibrations and best practices.
Comparing Different Gas Stations
Gas stations are assessed based on a few factors to pick out the best. First, the quality of the fuel is a very important factor, as it directly influences the performance and lifespan of the engine. The high-quality gas that the big oil companies use is more often subjected to strict cleanliness and additive standards during refining. Price is another important factor; while it can sometimes differ greatly between locations, a tiny station might have an unbeatable price, but it will not be that trustworthy regarding the quality of the fuel.
Moreover, the service and the atmosphere, e.g., excellent quality convenience stores, clean toilet facilities, and dependable air pumps, might be the characteristics of those gas station chains that are rated very high. Moreover, it is good to compare loyalty programs, as large chains usually offer discounts or rewards to frequent customers. Thus, make a more rational choice by giving fuel quality the highest importance, looking at prices next, and finally checking the service and overall convenience of the given gas station.
Causes of Slow Gas Pumping

- Clogged Fuel Filters: Over time, filters in the pump system can accumulate debris, reducing the flow of gas. Regular maintenance is necessary to prevent blockages.
- Low Fuel Tank Levels: If the station’s underground fuel tanks are nearly empty, the flow rate may slow as the pump works harder to draw fuel.
- Worn-Out Pump Components: Aging or malfunctioning pump equipment, such as worn nozzles or motors, can decrease efficiency and flow speed.
- Regulatory Flow Limiters: Some stations install flow restrictors to comply with local regulations, which can intentionally limit fuel dispensing speed.
- Simultaneous Usage: High demand with many pumps in use simultaneously can limit pressure and slow fuel delivery at individual pumps.
Addressing these causes often involves regular maintenance, timely equipment upgrades, and monitoring tank levels to ensure optimal performance.
Issues with the Gas Pump Mechanism
Gas pump mechanisms can be prone to various issues that may lead to inefficiencies in operation or a complete breakdown. One of the most frequently encountered problems is the nozzle’s automatic shutoff function, which may shut off the dispensing of fuel too soon due to a venturi sensor that is not working properly, blockage, or wear of the fuel nozzle. Moreover, defects in the pump’s vapor recovery system can cause incorrect pressure readings, which will also affect the fuel flow. Flow meters that are not working properly, which are sometimes the result of debris, calibration mistakes, or the aging of parts, can produce measurements of fuel delivery that are either inconsistent or inaccurate. Full pump system failures may also be due to electrical problems, which could be faulty wiring or damage to the circuit board. Maintenance of these issues, however, depends not only on troubleshooting but also on good practices—such as regular maintenance, timely replacement of worn parts, and adherence to manufacturer-recommended diagnostics that ensure consistency in performance.
Problems with Fuel Quality
The quality of the fuel can be of tremendous influence on the operation and life cycle of the fuel systems. A variety of issues arise due to contamination by, for example, water, dirt, and microbial life, leading to a decrease in combustion and possibly even causing the engine’s death. Besides, fuel composition changes, such as incorrect mixing of components or the presence of virtue materials, will always result in high-performance depletion and an increase in the generation of emissions. Moreover, fuel oxidation and degradation, which are primarily due to the long durations of storage or exposure to heat and oxygen, may lead to the production of gums and sediments that eventually clog the fuel lines and filters. To cope with these problems, it is advisable to carry out regular fuel quality tests, practice proper storage, and apply stabilizers and biocides, since all three will keep the fuel quality intact while also providing a smooth running of the system.
Tank and Line Blockages
Tank and line blockages are mainly caused by the build-up of debris, microbiological growth, and the generation of sediments or gums. Particulate impurities, such as rust and dirt, get into the reservoirs through the process of fuel handling or as a result of the corrosion of metal tanks and pipelines. Furthermore, microbial contamination—caused by bacteria and fungi thriving at the fuel-water interface in storage tanks—produces biofilms and sludge that obstruct fuel flow. The accumulation of these factors gradually leads to clogging in fuel lines, filters, and injectors, which negatively affects system performance and reliability.
To combat tank and line blockages efficiently, at the very least, regular maintenance practices should be performed. This consists of tank cleaning, overhauls, and periodic water removal to inhibit the growth of microorganisms. With the installation of hi-tech filtration systems and the regular inspection of tanks and lines, particulate contamination can be kept under control. The usage of industrial-grade biocides has the same effect as extending life for any microbe. Moreover, using chemical analysis to detect any decline in fuel quality and applying the right conditions for storing it—like the temperature and humidity of the environment—will not only minimize the chances of blockages but also contribute to the lifetime of the entire system.
Effects of Slow Pumping on Fuel Accuracy

Fuel accuracy can be impacted adversely by slow pumping due to the introduction of inconsistencies in the measurement systems. The flow meters, which are in charge of determining the volume, might not work at their best precision due to the slow dispensing of fuel, and thus, resulting in under- or over-registration of the product. The slow flow might also lead to the accumulation of the previous fuel in the lines, which might further cause cross-contamination, and so the readings would be inaccurate. It is very important to pump fuel at the manufacturer’s recommended flow rate in order to maintain both accuracy and system integrity.
Measurement Inaccuracies in Fuel Dispensing
Measurement inaccuracies in fuel dispensing systems can be traced back to several main reasons. The first of these is flow rate deviations—whether higher or lower than the operating levels prescribed by the manufacturer—which can result in the incorrect volume being reported when the flow meter is out of calibration. If the flow is high, it might be turbulent, and the reading might be very far from the actual volume, while, in the case of low flow, the meter—especially if it is of the mechanical or turbine type—might not be able to detect even the smallest changes accurately.
The second reason is temperature changes and other environmental factors, which cause the variation of fuel density; thus, the volumetric measurement will also be affected. The majority of dispensing systems are temperature-compensated for the purpose of standardizing readings; however, the improperly calibrated ones may still cause discrepancies if the compensation mechanism fails or the ambient temperature changes drastically.
The wear and tear of the mechanical components—like the meter gears or seals—are also contributing to the long-term inaccuracy. Regular maintenance and adherence to the manufacturer’s recommended service intervals are crucial to keeping the system reliable.
To counteract these problems, the operators need to observe the rules strictly through the continuous monitoring of flow rates, practicing calibrated systems, employing temperature-compensated systems, and performing routine checks. The entire process of measures already mentioned aids in achieving accuracy, minimizing mistakes, and securing against financial and operational losses in the fuel management sector.
Customer Experience and Satisfaction
Customer experience and satisfaction are fundamental elements in the success of fuel management operations. Trust is created, and loyalty is strengthened when services are accurate, reliable, and efficient. The major factors affecting satisfaction are the quality of the fuel, which is provided consistently, accurate transaction records, and very little downtime during the operations. The use of state-of-the-art technologies such as automated monitoring systems and real-time data analytics can lead to the quick resolution of issues and the smoothing of processes. In addition, quick reaction of customer support and good communication about services can be seen as positive relationship reinforcers. To keep their position in the market, companies have to constantly review customer opinions, make changes, and give priority to solutions that are user-centric to the constantly changing expectations of the customers.
Operational Costs for Gas Stations
The gas station operational costs are quite diverse and are made up of various fixed, variable, and compliance costs. The main cost elements are:
Fuel Supply and Transportation
The highest operational cost is represented by the fuel supply. The prices of fuel at the wholesale level are very much influenced by the international oil prices, demand, and political factors. On top of that, the delivery costs, which include the transportation from refineries or depots, also depend on the distance and the efficiency of the logistics.
Staffing and Labor Costs
The employee’s wages, benefits, and training all amount to a high operational cost. In fact, in most cases, the gas stations operating around the clock would need to hire a very large number of workers, thereby increasing the total payroll.
Lease or Property Costs
Monthly lease payments stand out to be the main fixed cost for those stations that are based on leased property. On the other hand, owned properties carry mortgage payments, depreciation, and property taxes.
Maintenance and Utilities
Pump maintenance, cleanliness of the store, and the utilities costs, such as electric, water, and internet, are all part of the daily operation costs. The electricity bill of the station will be higher during the lighting and refrigeration periods.
Regulatory Compliance
The gas stations have to follow the environmental laws, which include underground storage tank (UST) inspections, spill prevention, and emissions control. These may even necessitate upgrades and repairs, thus increasing the costs.
Inventory for Convenience Stores
Most gas stations consist of convenience stores in their business, thus necessitating a large amount of money for the inventory, refrigeration, and stock rotation so as to make the store profitable and also avoid waste.
Insurance and Safety Costs
One of the major costs is the comprehensive insurance coverage that includes liability, property damage, and fire hazards. Additionally, the costs for security measures like surveillance systems and alarms contribute a lot to the operational budgets.
Gas stations that are able to manage these cost categories effectively are also able to take advantage of the economies of scale where applicable; thus, they can keep being profitable in the competitive market with tight margins.
Solutions to Improve Gas Pump Speed

Upgraded Pump Technology
Installing new pumps with a bigger flow rate not only cuts down the fueling time to a great extent but also makes customer service faster.
Payment Systems Optimization
The implementation of contactless payment methods, along with traditional card readers that are quick and reliable, ensures no delays at all during the transaction process.
Regular Maintenance
Pumping equipment that is regularly maintained and inspected is continuously working at its maximum efficiency and thus will not cause any slowdowns due to breakdowns or wear.
Employee Training
If employees are trained to deal with issues such as pump breakdowns or customer help immediately, the company can save time and increase the speed of service.
Pump Layout Improvements
Transforming the gas station’s setup to reduce bottlenecks and promote vehicle movement will result in a faster refueling operation.
A combination of these practical actions will lead to an increase in speed at gas stations, which in turn will lead to higher customer satisfaction and better overall efficiency.
Regular Maintenance of Gas Pumps
Constant upkeep and checking of gas pumps is a very important thing to do, as this would be the only way to keep them going for a long time, to keep them working accurately, and to be totally reliable. The most important components, such as nozzles, hoses, filters, and dispensers, should be checked often to find and fix the deterioration before it is too late and causes major breakdowns. Also, cleaning the pump exterior and keypad would help to maintain a professional appearance from going and at the same time prevent the sensitive areas from becoming places where debris is built up.
Calibration checks would be one more thing that is critical, as it would be the only way to make sure that the local regulations are being adhered to and that the fuel measurements are accurate. Fuel filters must be taken out and replaced at regular intervals so as not to have any clogging up and to have smooth fuel flow. Apart from these, the digital pump systems would need timely software updates, which would be for the purpose of improving functionality and security.
Among the things that are going to be done for routine maintenance would be inspection for possible leaks, seals, and connections checking for being secure, and safety shut-off systems testing will be done too. Following a structured checklist and doing these tasks at recommended intervals will cut down on downtime, repair costs, and, on the contrary, will add to customer satisfaction by providing a seamless refilling experience.
Upgrading Fuel Dispenser Technology
The process of upgrading fuel dispenser technology means the installation of systems that are advanced and that will improve the reliability and efficiency of the whole operation. To make this a reality, I have decided to modernize the hardware components, to have strong software solutions, and to use data analytics for the monitoring that is done in real-time. I am hoping that by utilizing these advancements, there will be an increase in the performance, a decrease in the maintenance problems, and a provision of a refueling process that is both efficient and secure, and thus, more appealing to the customers.
Tips for Consumers When Facing Slow Pumps
In case you find yourself at a gas station where the pump is really slow while you are refueling, try the following steps:
Check Other Pumps: If one pump is slow, switch to another one, as the problem may be confined to that particular pump.
Inspect for Blockages: Check carefully for obstructions that may be visible on the fuel dispensing tip or pipe, as dirt or a rupture might reduce the fuel flow.
Observe Fuel Tank Venting: Make sure your car’s fuel tank venting system is working well, since venting problems can also cause the fuel flow to be slow.
Communicate with Staff: Tell the attendant at the gas station about the problem. He or she can see if there is a fault with the pump or the underground fuel system.
Fuel During Off-Peak Hours: The high demand during the busy hours may lead to the limitation of fuel flow because of low pressure in the system.
Monitor for Maintenance Signs: Look around for any maintenance notices or signs put up at the station warning about possible system downtimes or performance issues.
Taking these steps will help you to manage the situation better and find the right solutions quickly.
Reference Sources
“Enhancing Dynamic Performance in K-Rb-21Ne Co-Magnetometers through Atomic Density Optimization”
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Why is the pump filling my tank so slowly when I squeeze the handle?
When it seems like the pump is taking its sweet time to fill your tank despite you squeezing the handle, the most usual culprits are either the filler tube being restricted, the cap being partially open, or the pump controller malfunctioning at the station. The inflow can be diminished by dirt or debris getting stuck in the thinnest part of the rubber hose, or by a kink occurring at the bottom of the filler tube. Around this time of the year (very cold weather), the flow of gasoline might also be affected, among other things, making it a bit slower. It would be wise to try a different pump or station to find out if it is the dispenser that’s giving you the trouble.
Is it possible that there is a blockage in the filler tube or in the filler, or that there is a leak somewhere?
Definitely. A blockage or a not completely open situation in the filler tube, plus a leak somewhere in the hose assembly, all that combined will lead to less flow, and thus the whole process of pumping will take more time. It’s the station’s responsibility to have the pump maintenance check the tube, the rubber hose, and the bottom connections for any blockages or leaks. In case you smell gasoline near the pump or see wet spots, do not hesitate to inform the staff and also steer clear of that pump.
Is the gas cap or open vent a contributing factor to the issue of gasoline not being pumped fast?
Definitely, the gas cap or open vent could be a contributing factor to the issue, among other things. If the gas cap vent on your vehicle is blocked or not functioning, then air will not be able to escape the tank very fast, which will, in turn, cause filling to be slow. A vent that is not open will prevent the gasoline from flowing into the tank, thus the pump will often pulse or shut off. If you notice that the cap is broken, go ahead and get a replacement, as it won’t cost you as much as the recurring slow fills.
Can I manipulate the pump handle differently, or will squeezing the handle make it faster?
You have the option of trying to squeeze the handle more strongly, but the very fact that the pumps are flow-regulated implies that the hard squeezing won’t result in a greater speed increase. There are some users who do it by slightly pulling the nozzle out and just changing the angle a bit so that the filler tube is just right to avoid the pump’s automatic shutoff sensor that is in the thinnest part of the neck. But you must be careful because sometimes forcing techniques can lead to spills or the top of the filler tube being damaged.
Is the pumping speed of Costco stations very different from that of other smaller stations?
Yes, there are times when the difference is really substantial. Pumping speed at large-volume stations like Costco is usually very fast because they often have high-capacity equipment coupled with well-maintained hoses and controllers. In contrast, an independent or badly-maintained station can have slower flow because of the aged, clogged-up pumps and worn-out rubber hoses. If speed is something you care about, start noting down which stations “pump faster” every time and prefer those.
Was the weather or temperature a possible reason for the gasoline being slow to flow?
The weather is one of the factors involved. When it’s very cold, gasoline becomes slightly more viscous, and as a result, it can flow more slowly through the narrow tubes and the thinnest part of the filler neck. In extremely cold situations, the pump mechanics as well as the controller sensors can also be affected. The other way around, in hot weather, the components expand, and the flow characteristics change. Overall, the impact is usually small but could be noticeable in the marginal cases.
How can I determine whether the problem lies with the controller or the pump hardware?
When the same dispenser shows up multiple times with slow pumping in different vehicles or the pump frequently indicates automatic shutoffs being triggered when it’s actually not, it’s a sign that the controller or internal pump hardware might be failing. Keep an eye out for inconsistent flow, unusual sounds, or frequent shutoffs. Let the station management know about these signs so they will be able to check the controller, filters, and pump internals. Avoid using pumps that leak or have recurring problems.
Is it a requirement that I pay a little extra, or is the price per gallon affected if the pumps are slow?
Pump speed does not affect the price per gallon—it only determines how much time is needed to fill the same number of gallons. But slow pumps could be regarded as an inconvenience and a waste of time. In certain cases, gas stations may turn off a very slow pump due to maintenance issues, which could lead to a decrease in the number of pumps available during busy times, and indirectly cost you more time waiting in line.







