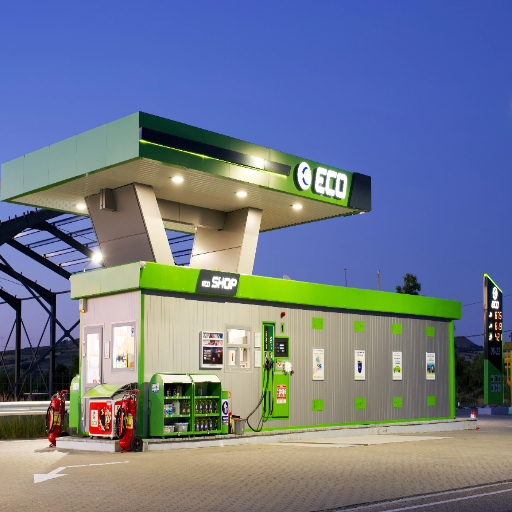
To operate a gas station successfully, one needs to have not only the fuel pumps and an open sign but also a well-planned setup with the necessary equipment that guarantees the efficiency of operations and satisfaction of customers. The well-planned infrastructure for the smooth fuel delivery and the well-thought-out technology for the improved customer experience are among the various components that significantly influence the daily operations of a fuel station. This paper will present a detailed summary of the indispensable apparatus in the case of a contemporary gas station. It will furnish the readers with the necessary information regarding the major tools, technologies, and systems that are important for the realization of profits and the establishment of a long-lasting business. Regardless of whether you are in the process of constructing a new station or modernizing an old one, it is very important to recognize the role of every single piece of equipment in making the fueling environment safe, efficient, and customer-friendly.
Understanding Gas Station Equipment

Gas station gear includes many devices and systems that are important for the proper running and safety of the station. At a minimum, new fuel stations need fuel dispensers to measure and transfer gasoline or diesel accurately and to be coupled with underground storage tanks (USTs) that keep the fuel safe. Point-of-sale (POS) systems are essential for transactions and inventory control, while automated payment terminals make the process more customer-friendly. Safety gear, such as spill control systems and fire suppression devices, is necessary for meeting regulatory requirements and providing a secure atmosphere. Moreover, good lighting, signs, and air compressors add to customer satisfaction and increase efficiency in operations. It is important to maintain a good quality and reliable supply of these components to keep the business profitable.
Overview of Fuel Station Equipment
The operation of fuel stations is effective only when a range of specialized equipment is employed, primarily for safety, compliance, and customer satisfaction. The basic parts of the system are modern fuel dispensers together with the latest metering systems that guarantee the delivery of the right amount of fuel, underground storage tanks (USTs) fitted with leak detection devices, and automated payment kiosks for quick and easy transactions. Vapor recovery units, spill-prevention devices, and fire suppression systems form a protective barrier and, at the same time, ensure adherence to safety regulations and risk reduction. Moreover, air compressors, high-visibility LED lighting, and durable signage are among the auxiliary supplies that not only improve the quality of the service but also increase operational effectiveness. The use of advanced monitoring systems allows the tracking of inventory and tank conditions to be done in real-time, thus making the management easier and less downtime. This combination of elements results in the optimization of functionality while at the same time conforming to the industry standards and regulations.
Importance of Inventory Management
The effective management of inventory is imperative in keeping efficiency and happy customers, as a result of its facilitation of the exact tracking of stock levels, reducing the issues of overstocking and stockouts, thus cutting the cost of excess inventory, losing sales. Sophisticated inventory systems like automated tracking software and real-time monitoring increase the precision and supply the facilities with the data to make decisions, such as optimum replenishment time. Moreover, the right inventory management practices are making it easy for companies to identify and prepare for demand changes, to operate supply chain networks in a more cost-effective manner, and to allocate cash more effectively. Keeping inventory records that are accurate will not only result in increased productivity but also in adherence to industry and legal regulations, which will imply reduced risks and fewer costly mistakes.
Key Components of Modern Fuel Systems
The latest fuel systems have been completely revolutionized by technology when it comes to the way they work. The whole system is designed to improve efficiency, get the most out of performance, and also comply with the strictest emission regulations. Below, you will find the main components alongside their functionalities:
Fuel Tank
At the heart of every liquid fuel system is a fuel tank, which acts as the main storage unit. It is made in such a way that leakage will be prevented, and it is also made using corrosion-resistant materials. The latest tanks come with sensors that are responsible for checking the levels of the fuel and spotting any abnormalities.
Fuel Pump
The fuel pump is mostly placed inside the tank or between the tank and the engine. It guarantees a constant and sufficient supply of fuel to the engine. Modern electric fuel pumps accurately control the flow of the fuel according to the demand of the engine, thus enhancing performance as well as saving energy.
Fuel Injectors
Fuel injectors are very delicate and competent instruments that are in charge of delivering the fuel into the combustion chamber of the engine with the right pressure, amount, and timing. Advanced technologies like electronic fuel injection (EFI) are utilized in these systems for precise control, which further leads to greater fuel efficiency and fewer emissions.
Fuel Lines and Filters
The fuel lines are the means through which the fuel is taken from the tank to the engine, while the fuel filters are responsible for cleaning the fuel by taking out impurities, thus safeguarding the engine parts from being damaged. High-pressure fuel lines, along with multi-stage filters, are the common features of modern systems that provide increased reliability.
Pressure Regulators
These instruments are responsible for keeping the fuel pressure in the system constant, thus resulting in the best possible combustion while at the same time preventing the fuel from being consumed in excess. The new designs can make real-time adjustments based on the conditions of the engine.
Electronic Control Unit (ECU)
The ECU is the mastermind of the system as it manages the stages of fuel delivery, injection timing, and air-to-fuel ratios. It guarantees the engine to be at its most efficient, performing at its best, and being in line with the environmental regulations by processing the input from the sensors and the real-time data.
Sensors
Modern fuel systems are outfitted with all sorts of sensors, such as oxygen sensors, mass airflow sensors, and pressure sensors. These devices give permanent feedback to the ECU, which in turn helps with the precise adjustments and monitoring of the system’s health.
It is the combination of advanced material engineering, electronic controls, and real-time diagnostics that makes contemporary fuel systems one of the greatest innovations in the automotive industry. They not only address energy efficiency and environmental sustainability issues but also do so with pinpoint accuracy.
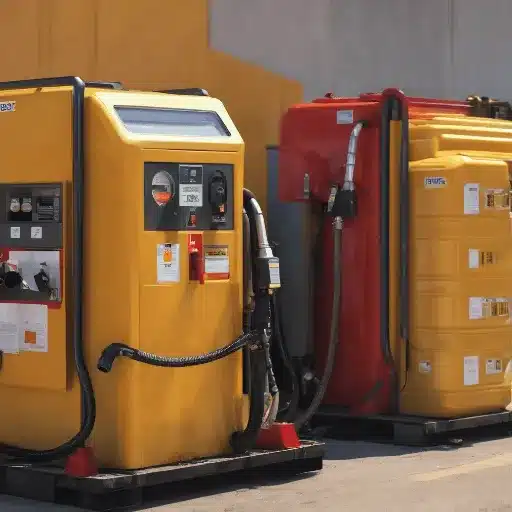
Types of Fuel Pumps and Dispensers
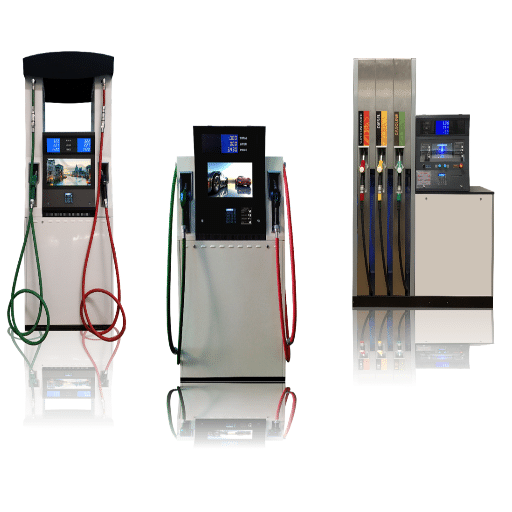

The pumps and dispensers for fuel are mainly divided into two principal types that are distinguished by their functions and areas of application:
| Pump Type | Location | Operation Method | Best Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Submersible Pumps | Placed underneath the surface of fuel storage tanks | Supply fuel from tank to dispenser through underground piping | High-volume dispensing environments such as gas stations |
| Suction Pumps | Above ground, usually within the fuel dispenser itself | Create a vacuum that pulls fuel from storage tank to dispenser | Places with fewer fuel volume requirements |
The selection of pump types depends on site layout, fuel demand, and maintenance considerations. Also, ideal installation along with prompt maintenance is the key to performing the pumps to their maximum potential and being safe.
Different Types of Fuel Pumps
Pumps for fuel are divided into groups according to their configuration, manner of operation, and the specific demands of the application. The most common types of pumps are:
Submersible Pumps
Submersible pumps are positioned within the fuel storage tank, wholly immersed in fuel. These pumps force the fuel to the dispenser rather than sucking it, which boosts the efficiency of the delivery process over longer distances. It is typical for them to be found in very large-scale fueling operations where the demands for flow and pressure are high, and they can still maintain the pressure easily. The noise that these pumps cause is usually low, and the enclosed structure facilitates the prevention of wear and tear due to environmental exposure.
Suction Pumps
Suction pumps, in comparison to submersible types, are placed above the ground, generally inside the fuel dispenser. The principle of suction is used by these pumps to pull the fuel out of the storage tank to the dispenser. The maintenance of these pumps is less difficult and cheaper since they have a simple design; however, they are not the best option for long-distance fuel delivery. They are more frequently used in applications of low demand where high-quality pumping is not crucial.
Rotary Vane Pumps
A rotary vane pump is a type of pump that has a rotor with movable vanes, which creates a sealed chamber that draws the fuel from the storage tank and delivers it to the dispenser. These pumps are very efficient and dependable, hence they are utilized on a large scale for gasoline and diesel fuel as well, because of their ability to work with different viscosities of fuel. Their small size and accuracy make them a sturdy option among many fueling setups.
Important Note: The selection of a fuel pump type is determined by such factors as the flow rate of the fuel, available resources at the site, and the efficiency of the operation. Checking regularly and complying with the set maintenance schedules are vital in ensuring the reliability and safety of the system.
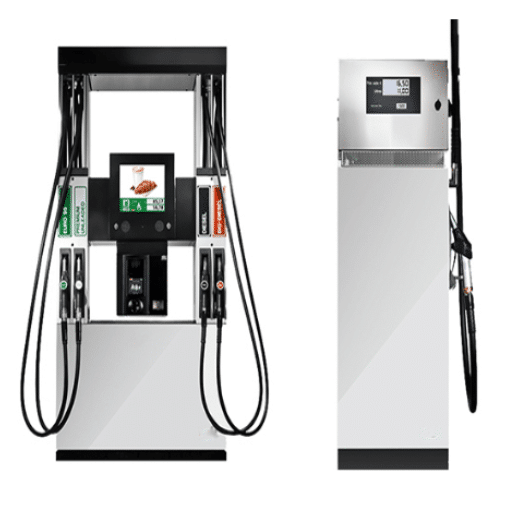
Fuel Dispenser Features and Functionality
Fuel dispensers are precision-engineered systems with the primary function of safely, accurately, and efficiently delivering fuel, all while keeping up with industry regulatory compliance. Among the main attributes are the metering units that accurately measure the fuel, the long-lasting hoses and nozzles, and the filtration systems that prevent dirt and other contaminants from getting into the tanks of the vehicles. The advanced electronic control systems allow the customer to interface with the pump and track the data at the same time, and the different options for integration with the point-of-sale and fleet management systems make the process even more efficient.
The working principle is based on three main components—pumps, meters, and flow controls. Pumps take the fuel either from below or above the ground storage and guarantee a constant and dependable flow. The metering device measures the dispensed volume with high precision, sometimes with the help of a state-of-the-art temperature compensation system to offset the effect of thermal expansion. Safety devices such as auto shutoff nozzles, leak detection systems, and flame arrestors are crucial for preventing risks during the operation of the machine. Furthermore, some dispensers are fitted with vapor recovery units that help to reduce the negative effects on the environment by collecting the fuel vapors.
To maximize workflow and improve user experience, modern fuel dispensers use digital technology, which makes it possible for them to offer contactless payments, remote monitoring, and self-diagnostics as features. The selection of a fuel dispenser must take into account factors such as throughput requirements, local regulations, and the type of fuel being dispensed. It is necessary to properly maintain these systems through regular calibration and inspection, for instance, to keep them running efficiently and to prolong their life.
Choosing the Right Nozzle for Your Needs
Choosing the right fuel nozzle is a major choice, which affects the performance and safety aspects of the system, and it has to be made very carefully. When working with gasoline and diesel, it is also important to take into consideration the compatibility of the dispenser’s flow rate and the fuel tank’s flow rate requirements to avoid overfilling or spillage. The automatic shutoff nozzles are the most commonly chosen type of nozzle because they have the capability of cutting off the flow of fuel once the tank reaches its full capacity, thus minimizing both waste and safety hazards. Furthermore, compatibility with the fuel type is critical—nobody wants to use unfit nozzles that are particularly made for gasoline, diesel, or alternative fuels like biodiesel or ethanol blends. The nozzle material, being it is aluminum or stainless steel, must also be in accordance with the chemical compatibility of the dispensed fuel. Adherence to the industry standards and local regulations, such as UL certification, ensures compliance with safety and operational guidelines. To achieve the best performance, it is always recommended to have the nozzle regularly inspected and cleaned to prevent clogs and to guarantee accurate fuel delivery.
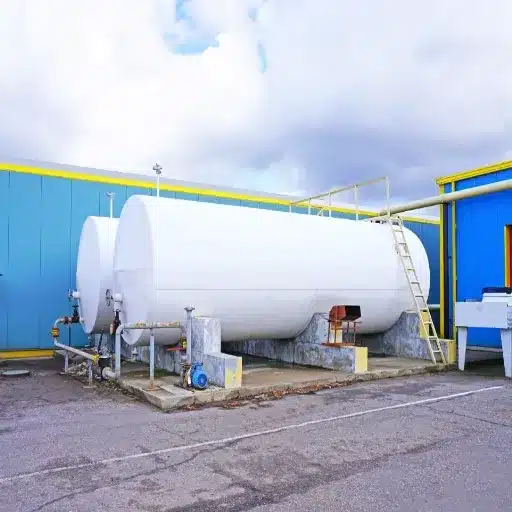
Fuel Storage and Management
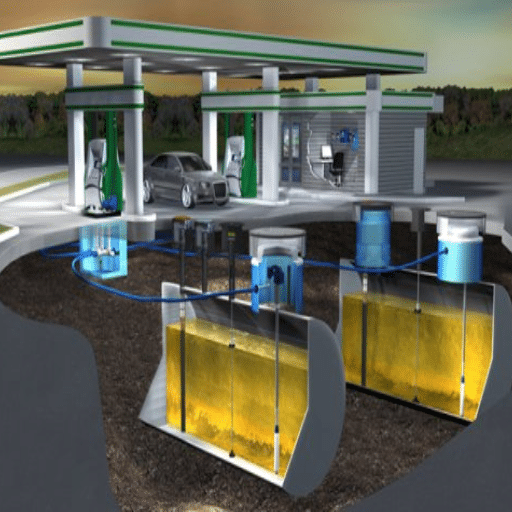

The best practices that together ensure the proper and safe fuel storage and management are going to be no safety, no environmental impacts, and no quality loss. The fuel has to be placed in tanks that are allowed by the authorities and made from steel or high-density polyethylene, which are the best materials to prevent leaks and corrosion, rather than concrete and others. Secondary containment systems play a crucial role in spill prevention; furthermore, the regulations imposed by the EPA and local governments must be strictly followed for both above and below- and below-ground storage tanks.
Spotting water contamination, microbial growth, or sediment build-up occasionally among tanks is vital to preventing the loss of fuel quality and causing equipment damage. Water and fuel leakage is detected through real-time data provided by monitoring systems such as automatic tank gauges (ATGs) and electronic sensors. Proper ventilation, along with temperature regulation in storage areas, is not only the way to go for stable fuel but also a way of reducing vapor accumulation risks. Additionally, the use of inventory management tools is an effective way of keeping track of fuel consumption, spotting inconsistencies, and maximizing storage capacity.
Organizations can merge all three-pronged approaches of proactive maintenance, regulatory compliance, and advanced monitoring systems, and thus they are always capable of safe and efficient fuel storage and management, which means that disruptions of operations can be kept to a minimum.
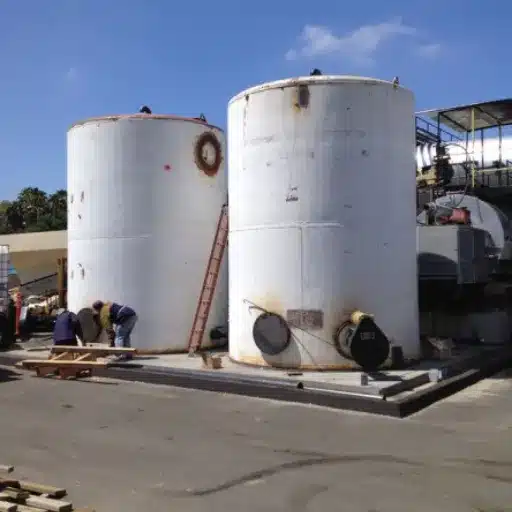
Understanding Fuel Storage Tanks
Categorization of Fuel Storage Tanks
Fuel storage tanks can be divided into two main groups, namely the aboveground storage tanks (ASTs) and underground storage tanks (USTs), and each of these types has been made to cater to certain operational and environmental conditions. Aboveground storage tanks are typically maintenance-friendly, and inspection and replacement are easy; hence, they are suitable for the industry that gives first priority to accessibility. The underground storage tanks, conversely, take up less space and have less impact on the environment visually; however, they need regular monitoring for leak detection as their installation is hidden.
Construction Materials and Designation of Standards
Fuel storage tanks are primarily made of materials like steel, fiberglass, and their combination (steel-fiberglass composites). Each material type has its own specific benefit; steel is durable and cheap, while fiberglass can withstand the effects of moisture and chemicals on the metal underneath. To assure safety and durability, tanks have to follow rigorous design standards like those set by the American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) and the Underwriters Laboratories (UL).
Compliance with Regulations and Environmental Concerns
The storage of fuel requires compliance with environmental and safety regulations that are very strict. The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) in the United States, among others, imposes very strict rules according to the Spill Prevention, Control, and Countermeasure (SPCC) regulation. Regulations are mainly concerned with secondary containment systems, leak detection methods, and tank integrity evaluations to lower the risks of contamination and environmental hazards caused by the storage of fuel.
Periodic and Predictive Maintenance as Inspection Practices
Periodical maintenance as well as predictive inspections are essential for the safety and efficiency of operations in the case of fuel storage tanks. The activities carried out include the monitoring of the structural integrity, corrosion that may be happening, and the checking of the calibration systems. Use of methods such as hydrostatic testing, ultrasonic inspections, and pressure monitoring enables early detection of defects, which in turn reduces the chances of catastrophic events and system failures.
Deployment of New Monitoring and Automation
The interlinking of advanced technologies is a pivotal factor in leading the way towards better management of fuel storage systems. The digital automation incorporated through the remote monitoring system gives the facility the privilege of tracking in real-time the levels, temperature, and pressure of fuel in the tanks. Besides, smart sensors that are coupled with automated alarms instantaneously notify the presence of any irregularities, thus allowing for the immediate response, which can be very crucial in either preventing accidents or losses of fuel.
Key Takeaway: When dealing with tank construction, regulatory compliance, and technological integration all in a comprehensive manner, organizations will certainly have the opportunity to optimize their fuel storage operations for safety, efficiency, and environmental stewardship.
Automatic Tank Gauging Systems
Automatic Tank Gauging (ATG) systems are sophisticated systems that are specifically made to monitor the fuel storage tanks very accurately. These systems measure the fuel levels, temperature, density, and product movement in real time by using a variety of sensors and software. The most important functions of ATGs are leak detection, inventory control, and compliance monitoring, which help companies practice environmental responsibility according to the standards of the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA).
ATGs are the modern-day systems that are more common and incorporate wireless communications and cloud platforms. This allows the operators to remotely access all data that has been gathered for the purpose of better decision-making and increased operational efficiency. In addition, automatic calibration guarantees that the measurements are taken accurately, hence cutting down on manual labor and the possibility of mistakes due to human errors. The implementation of ATG solutions by organizations will come with the benefits of improved safety, reduced losses, and the most importantly, regulatory compliance in all their fuel storage operations.
Leak Detection and Containment Strategies
To be able to effectively lessen the hazards linked to fuel storage systems, it is very important to have leak detection and containment plans that work efficiently. The modern leak detection systems use some very advanced techniques such as pressure decay testing, ultrasonic leak detection, and vapor monitoring. Pressure decay testing checks the tank’s internal pressure for anomalies, whereas ultrasonic sensors detect the sound waves that are caused by leaks. Vapor monitoring is based on assessing the environmental hydrocarbon levels and then doing the opposite if they change.
As for containment, the secondary containment systems are the most common solution to be used, such as installing double-walled tanks and putting up external containment barriers that would catch any leaking product before it gets into the environment. Along with that, monitoring wells and spill basins act as barriers, separating the leaks from the surrounding area by detection and prevention. The combined use of automated monitoring solutions with real-time alerts will be a major contributor to quicker response times, thus having a lesser impact on the environment and less economic losses. A reliable inspection schedule combined with compliance with the standards also fortifies the efforts in leak prevention and containment, thus ensuring safety and efficiency in operational practices.
Integrating Technology in Fuel Management
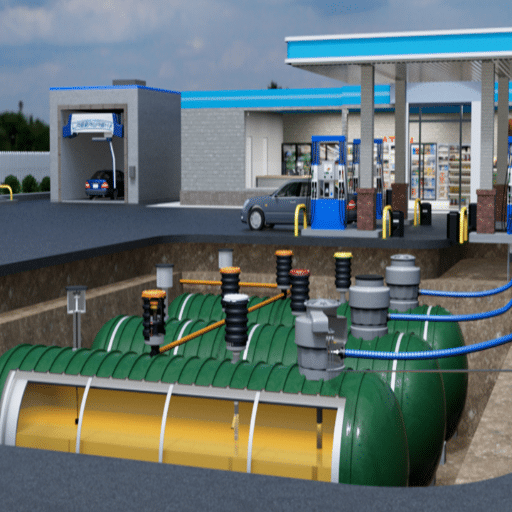

The use of technology in fuel management systems not only innovates the whole process but also increases the accuracy and cuts down the operational costs. The automated fuel monitoring systems give real-time data on fuel usage, storage levels, and even the chance of discrepancies to allow proper tracking and control. The use of advanced analytics tools makes it easy to spot trends in fuel use that can lead to maintenance that is done only when necessary and to the allocation of resources in an efficient manner. On top of that, the use of secure digital platforms helps to lessen the burden of compliance reporting considerably by making sure of accurate record-keeping and seamless compliance with the regulatory requirements. This bundle of features makes it possible for heightened operational efficiency and sustainability in the area of fuel management.
Point-of-Sale (POS) Systems for Gas Stations
Gas station POS (Point-of-Sale) systems are developed to enhance the efficiency of the entire operations and, at the same time, keep them integrated through one central platform, meaning that fuel sales, convenience store transactions, and back-office management are all in one place. They not only give data but also real-time data about inventory levels, sales trends, and transaction history, which are very useful for the operators to manage stock professionally and reduce shortages and delays. The best-in-the-market POS systems generally have the capability of processing payments through various ways, like RFID tags, mobile wallets, and EMV-compliant chip cards, thus guaranteeing security as well as making the transaction smooth and quick for the customers.
Some of the important functions of the latest gas station POS systems are compatibility with fleet cards, loyalty programs that can be customized according to specific needs, and sophisticated reporting tools that can analyze and summarize the data to show the profit and the period of the most frequent customer visits. The prices are done accurately, and the control is done in real-time as the communication between the platforms and the fuel dispensers is direct. Besides, a number of systems are coupled with cloud-based management software to provide the ability to monitor the site remotely and to achieve better scalability, which in turn adds to operational efficiency. These solutions, by taking care of not-so-easy data security issues, in turn, help to keep the customer information safe and at the same time, be in line with the industry regulations.
Fuel Monitoring and Management Systems
On the whole, fuel monitoring and management systems play a vital role in fuel optimization, especially in the areas of operational efficiency and waste reduction. The system’s main features include constant fuel monitoring, automatic reporting, and detecting irregularities. The combination of IoT sensors and GPS technology allows these systems to provide accurate data on fuel levels, traceability of consumption, and reveal empirical use patterns either in fleets or at fixed places.
Moreover, the latest technology predicts the future fuel requirement and thus helps in allocating resources better by reducing downtime. Besides this, the systems employ a high-level control of access, which in turn protects data and mitigates the risk of illegal usage. The telematics and cloud platforms’ integration enables the real-time monitoring and management of fuel data even when the users are away, thus making the existing infrastructure more efficient.
To sum up, the organizations opting for these systems will be the ones that will have cost management under control, meet environmental regulations, and be able to provide better visibility into their operations. The systems, in conjunction with efficient reporting tools, would not only present but also make businesses aware of their potential regarding efficiency and sustainability.
Benefits of Fuel Management Systems
Cost Optimization
Fuel management systems provide impeccably accurate data regarding the fuel usage, which facilitates organizations in spotting their inefficiencies and, consequently, their fuel waste. The companies using this practice may include routing, cutting down idle times for their vehicles, among others, to mention a few, as their cost-saving methods. On top of that, the electronic monitoring of fuel transactions in real-time serves as an effective deterrent against unauthorized usage or theft of fuel.
Enhanced Fleet Efficiency
The fuel management systems not only allow placing orders but also provide very accurate monitoring of the performance of vehicles and their maintenance schedules by automated tracking and reporting tools. In this way, the customer dealing with issues like under-performing engines or excessive fuel consumption can come out with the maximum efficiency of the fleet and the same for the fleet’s lifetime.
Environmental Compliance
The emission of carbon dioxide is being monitored by these systems, thus helping the industry to keep up with the environmental concerns and also recommending eco-friendly habits to be practiced. The interpretation of fuel usage and emissions based on data is of utmost importance for the entire process of getting and keeping compliance with the authorities while also diminishing a company’s environmental footprint.
Operational Transparency
Complete reporting and analytics give access to the whole field of fuel activities. By merging the information into an easy-to-use interface, companies are able to position their accountability better, make decisions faster, and build more trust among their people and with their customers.
Reduced Administrative Burden
The process of tracking transactions, managing fuel inventory, and reporting will be automated, thus reducing human intervention as well as other errors that are usually associated with it. This will lead to higher accuracy, almost no downtime, and the optimum allocation of resources, thus allowing the administrators to move their focus onto the strategic tasks.
Convenience Store Operations in Gas Stations

Operations of convenience stores in gas stations receive great importance in terms of boosting revenue and improving customer satisfaction. Usually, these stores have a pretty varied selection of goods, which includes snacks, drinks, toiletries, and sometimes even basic household items, so they cater to both travelers’ and local customers’ needs. To increase sales, effective inventory control, optimal product placement, and price competition are all very important. Moreover, quick and pleasant service contributes to customer loyalty. Today’s convenience store operations may have integrated payment systems and loyalty programs, which further smooth the transactions and attract customers to come back.
Role of Convenience Stores in Fuel Stations
The presence of convenience stores or mini-marts at fuel stations is an advantage for the business. They offer quick access to the essentials like snacks, drinks, and groceries. Customers can even make additional purchases during their stop, which is especially common among women. These stores greatly contribute to the revenue coming from non-fuel sales, which are usually the leading revenue streams for gas stations or petrol stations. Moreover, many gas station convenience stores have started to use sophisticated technologies such as automated inventory management and self-checkout systems to make the process more efficient.
On the other hand, the convenience stores offer loyalty programs, discounts, or bundled deals to attract and retain customers. They also play a significant role in branding and customer interaction, often going beyond mere retail by including amenities like coffee shops, ready-to-eat food areas, or even providing special services like package collection. Therefore, they not only attract more customers but also meet the needs of today’s consumers, who demand quick service, variety, and easy access.
Inventory Management for Convenience Store Items
The issuing of effective inventory management of convenience store goods relies heavily on the availability of real-time, accurate sales figures and on the proper use of data-based methods. I am planning to apply the use of electronic inventory management devices throughout the Day to keep tabs on the stock level, assuring that high-demand items will never run out and that there will be no extra stock. By conducting a substantial inventory turnover analysis, I am able to spot the poor sellers and change the ordering cycle, thus making a smaller purchase of those items. I, however, hold up the practice of frequent audits and supplier communication as the most important activity to facilitate the restocking processes and alleviate discrepancies. By following these methods, I shall gain control over the inventory in a manner that is very efficient and still meet customers’ needs with good service.
Enhancing Customer Experience at Fuel Stations
To elevate customer experience at fuel stations, it is essential to emphasize the main aspects of convenience, speed, and extra services that go along with the fueling process. Optimizing payment systems via contactless payment terminals or mobile apps not only cuts down the wait times but also boosts customer satisfaction. Besides, a clean and well-kept area, including hygienic restrooms and properly stocked convenience stores, creates an inviting atmosphere. Moreover, high-tech tools like digital signage and loyalty rewards programs are not only to entertain customers but also to make them come back more frequently.
On top of that, bringing on-site services such as car washes, quick service food, and EV charging stations to the customers’ needs area goes beyond mere fuel sales. Regular staff training makes sure that workers provide fast and polite service. By combining these tactics in a smart way, fuel stations can really work on the customer experience, generate return traffic, and also make more profits.
| Enhancement Strategy | Implementation Method | Expected Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Payment Optimization | Contactless terminals and mobile apps | Reduced wait times and increased customer satisfaction |
| Facility Maintenance | Clean restrooms and well-stocked stores | Inviting atmosphere and positive customer perception |
| Technology Integration | Digital signage and loyalty programs | Enhanced engagement and repeat visits |
| Additional Services | Car washes, quick service food, EV charging | Expanded revenue streams and customer retention |
| Staff Training | Regular training programs for employees | Fast, polite service and improved customer relations |
Summary and Conclusion
The successful operation of a modern gas station requires a comprehensive understanding of the various equipment, systems, and technologies that work together to create an efficient, safe, and customer-friendly environment. From fuel dispensers and underground storage tanks to point-of-sale systems and convenience store operations, each component plays a vital role in the overall success of the business.
Key takeaways include the importance of investing in quality equipment that meets regulatory standards, implementing advanced monitoring and management systems for fuel storage and inventory, integrating modern technology for enhanced operational efficiency, and prioritizing customer experience through convenience, speed, and additional services. The adoption of fuel management systems offers numerous benefits including cost optimization, enhanced fleet efficiency, environmental compliance, operational transparency, and reduced administrative burden.
As the industry continues to evolve with technological advancements and changing customer expectations, gas station operators must stay informed about the latest innovations and best practices. Whether constructing a new station or modernizing an existing facility, understanding the role and function of each piece of equipment is essential for creating a profitable, sustainable, and customer-centric operation. By combining proper infrastructure, advanced technology, regulatory compliance, and excellent customer service, gas station operators can position themselves for long-term success in an increasingly competitive market.
Final Thoughts
The gas station industry represents a complex ecosystem where safety, efficiency, and customer satisfaction must be carefully balanced. By understanding and implementing the equipment, systems, and strategies outlined in this guide, operators can build and maintain facilities that not only meet regulatory requirements but also exceed customer expectations while maximizing profitability and sustainability.
Reference Sources
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is a gas station equipment list?
A gas station equipment list comprises the major things, which are fuel pumps, fuel dispensers, tanks for fuel storage, nozzles, vapor recovery systems, leak-detecting gadgets, automatic tank reading devices, and point-of-sale systems. These elements promise to manage the safety and efficiency, besides inventing the tracking of fuel flow, enhancing the service to customers at the station.
In what ways are fuel management systems benefiting station operations?
Fuel management systems separate the operations and, at the same time, are the checkers of fuel stocks, sales, and supply and demand trends. They are the owners of fuel owners and their land will be made smaller, wait times cut down, and petroleum items more manageable, which in turn will increase profit taking area.
What safety features should gas station equipment have?
Gas station equipment should not only be sophisticated but also very safe and secure, and equipped with leak detection systems, vapor recovery systems, containment measures, and staff safety etc. These features play a major role in keeping the environment free from contamination as well as complying with safety and environmental laws.
What is the upgrading of an existing fuel station setup?
Modern filing pumps, creating the point-of-sale system, merging the fuel management system, and tank monitoring, etc., are the steps taken to upgrade an existing fuel station setup. These changes, besides others, can lead to efficiency, customer satisfaction of the customers, and even more income sources.
What is the main role of inventory management in gas stations?
Inventory management is the backbone of gas stations since it is the one that checks fuel levels, records sales, and handles stock. Station managers can always have the right quantity of fuel in stock and also sell the product before the next delivery when they use the advanced inventory management systems.
What are the advantages of having automatic tank gauging in the fueling stations?
Automatic tank gauging is the real-time watchman of the fuel storage levels, so the station owners can find leaks, have a precise fuel inventory, and observe environmental regulations without worry. This system not only secures but also prevents environmental extinction while bringing efficiency and safety.
How does a point-of-sale system help to elevate customer service at gas stations?
A point-of-sale system is an element that can really change the customer experience as it provides different payment methods, faster execution of transactions, and quick access to sales data. This time-saving factor or efficiency is one that reduces the wait time and thereby raises the quality of service, thus ultimately fulfilling the customers’ needs.
What are the main parts of the fuel system of a gas station?
The fuel system of a gas station consists of storage tanks, pumps, dispensers, nozzles, and a monitoring system, which are the most important parts. These elements together assure a safe and efficient refilling process where the management of the entire fuel supply chain can be done effectively.